Content |
|---|
Description “Black-collared Lovebird”:
13 cm. length and weight of 39 to 41 g.
The Black-collared Lovebird (Agapornis swindernianus) has the forecrown, the lores and crown emerald green. Narrow black band at the nape, behind yellow lined. Mantle and scapulars green; rump and coverts bright blue. Upperwing-coverts green. Flight feathers Blackish with vane Green external on the upper face. Underwing-coverts emerald green.
The underparts pale green pretty boring, particularly on chest; flanks brightest. Central feathers of the tail, large black hand with green tips; other red at the base, green tips with broad black subterminal band.
Bill greyish black; irises yellow; legs Dark yellow green.
Both sexes similar.
The immature they are like adult, but without the nuchal collar. The Green head, the Blue rump and red tail, colors are duller than adults. Iris brown. beak pale gray with black spot at the base.
Subspecies description:
- Agapornis swindernianus emini (Neumann, 1908) – Of 13 cm length. The collar is red and black and is narrower, It does not extend to the beginning of chest.
- Agapornis swindernianus swindernianus (Kuhl, 1820) – The species nominal
- Agapornis swindernianus zenkeri (Reichenow, 1895) – Of 13 cm.. length. Under the black band it has reddish coloration extends to the chest diluted.
Habitat “Black-collared Lovebird”:
The Black-collared Lovebird They inhabit lowland tropical evergreen forests, both primary and secondary, generally below the 700 m. although some reports indicate sightings 1.800 metres in Uganda.
Visits occasionally cultivated land. In general, in small flocks (until 20 birds), sometimes in larger groups during the dry season.
It is a bird, generally, arboreal; frequent the treetops, where they can be very difficult to detect when they remain silent.
Forman communal roosts in their favorite places.
Reproduction “Black-collared Lovebird”:
Reproduction of this species is, to a great extent, unknown; They have been observed in arboreal termite nests and it is suspected that breeding in the northern basin of the congo river It is in July.
Food “Black-collared Lovebird”:
Their main food is, apparently, seeds Ficus, extracted from its fruits, in mature forests, light areas near the forest and trees growing areas around the villages; They also take millet, corn and other seeds, as well as insects and their larvae.
birds in the distrito de Ituri, Democratic Republic of the Congo, feeding were observed in the rice crops and Sesame.
Distribution “Agapornis swindernianus”:
The Black-collared Lovebird they are endemic in West Africa center in at least two (possibly three or four) separate populations.
In West Africa The species is found in Liberia, Ivory Coast (Taï National Park) to the South of Ghana, which recently they occurred in the Bia National Park.
In West Central Africa Its distribution extends from southern Cameroon south on Gabon and east to the north Congo river and extreme southwestern Central African Republic.
You can also see from the basin Congo river in West Uganda.
Subspecies distribution:
- Agapornis swindernianus emini (Neumann, 1908) – Spread across the center and east of Democratic Republic of the Congo to the west end of Uganda.
- Agapornis swindernianus swindernianus (Kuhl, 1820) – The species nominal
- Agapornis swindernianus zenkeri (Reichenow, 1895) – Distributed in southern Cameroon and eastern Gabon to the southwest of Central African Republic and West Democratic Republic of the Congo.
Black-collared lovebird conservation:
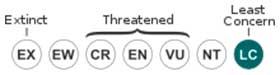
• Current Red List of UICN: Least concern
• Population trend: Stable
The size of the world population Black-collared Lovebird It has not been quantified, but the species, according to sources, It is considered rare in Ghana and probably confined to forest reserves. Described as common in Gabon and Democratic Republic of the Congo and reasonably common in lowlands in Bwamba of Uganda.
The population is suspected to be stable in the absence of evidence of any reduction or substantial threats.
As a curiosity, emphasize that governments Liberia and Uganda stamps have been printed with his image.
The Inseparable Vireo in captivity:
Probably It not kept out of their range; some captured birds died after a few days or weeks; No further information is available.
As with any other pet, it is essential to ensure that the birds one is about to purchase have been captive bred and not wild caught. In addition to conservation and ethical reasons, trapped wild animals are more likely to get sick and die.
Alternative names:
– Black-collared Lovebird, Black collared Lovebird (English).
– Inséparable à collier noir, Inséparable à collier, Inséparable du Libéria (French).
– Grüköpfchen, Grünköpchen, Grünköpfchen (German).
– Inseparável-acollarado (Portuguese).
– Inseparable Acollarado, Inseparable de Cuello Negro (español).
scientific classification:

– Order: Psittaciformes
– Family: Psittaculidae
– Genus: Lovebirds
– Scientific name: Agapornis swindernianus
– Citation: (Kuhl, 1820)
– Protonimo: Psittacus Swindernianus
Images "Black-collared Lovebird"
“Black-collared Lovebird” (Agapornis swindernianus)
Sources:
– Avibase
– Parrots of the World – Forshaw Joseph M
– Parrots A Guide to the Parrots of the World – Tony Juniper & Mike Parr
– Birdlife
– Photos:
(1) – Black-collared lovebird, the great unknown – fischospi
(2) – A painting of a Black-collared Lovebird (originally captioned “Psittacula swinderniana. Swindern’s Parakeet”) by Edward Lear (1812-1888) [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons