Content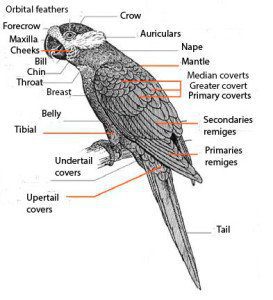
|
|---|
Description
Of 50 cm.. length and an average weight of 480 g..
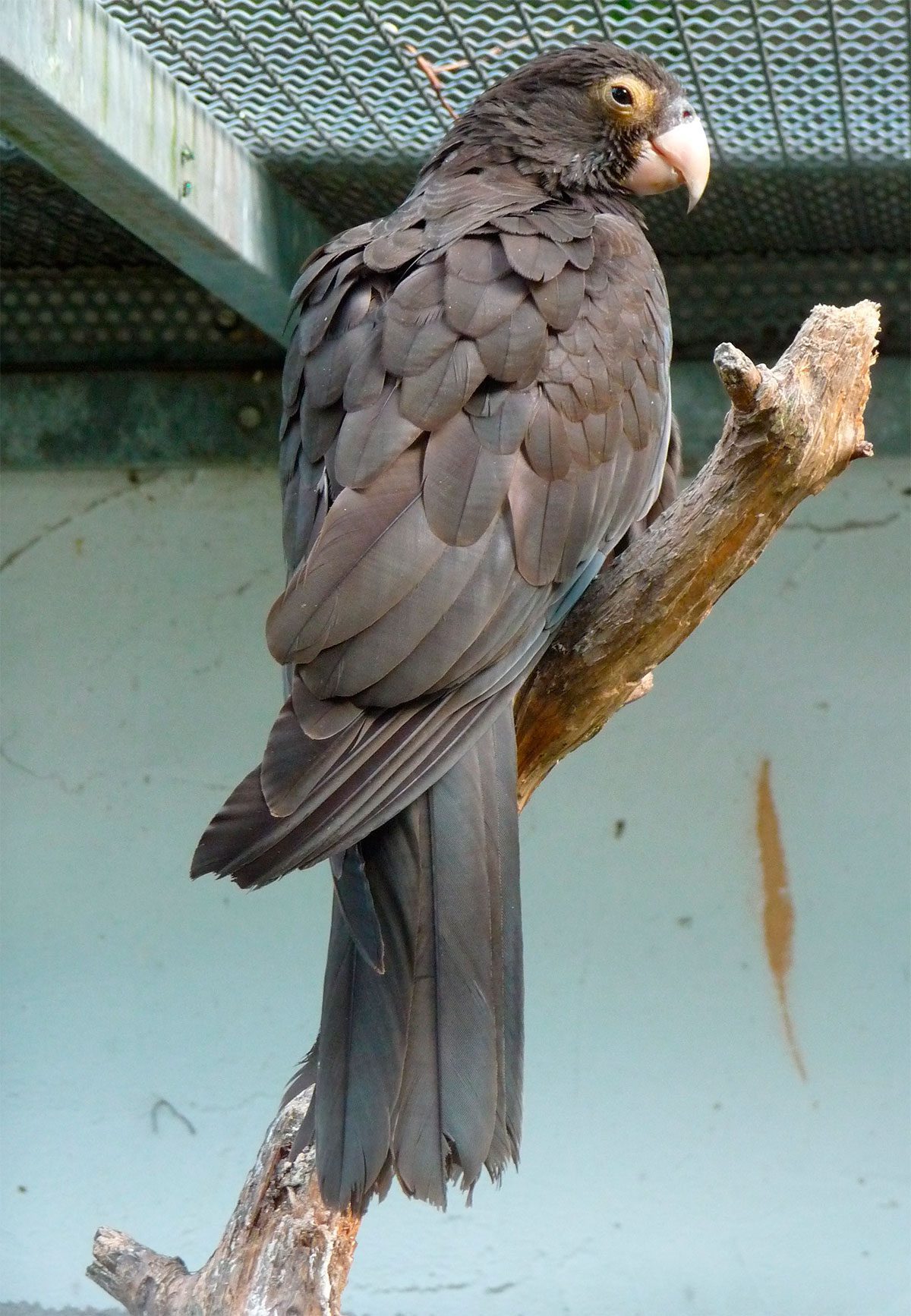
The Vasa Parrot (Coracopsis vasa) It has a few shades between black and Brown, big enough, grim looking, with the rounded tail and a powerful bill pinkish.
They can be difficult to spot when they combine their dark plumage with shadows under the forest canopy..
To a large extent, sympatric with the very similar Black Parrot (Coracopsis nigra), but the Vasa Parrot It is larger and somewhat paler, greyish Brown rather than dark brown
They can fly at high altitude when they travel to or from the sites of communal rest. It can be very Meek and accessible When feeds below the forest canopy.
In general, the plumage of the Vasa Parrot is brown-black color with a slight greyish tinge clear at the top, in special wings and top of the tail. Primaries with narrow gray margin in vane outer. bottom of the flight feather pale grey. Subcaudales coverts Gray with variable black stripes on the shafts of feathers. Tail with faint dark subterminal band; undertail, the tail pale grey. Bill usually pink but grey color after molting; irises brown; naked periophthalmic patch (that extends to the peak) pale grey; legs greyish Brown clear
Without sexual dimorphism in plumage. Reproductive females can become bald on the head, around the eyes and throat , with the exposed skin of mustard yellow or orange.
Immature with plumage more greyish Brown lighter and paler skin around the eyes. Skin patch naked eye more smaller than in adults or absent.
- Sound of the Vasa Parrot.
Description 3 subspecies
-
(Peters,W, 1854) – Smaller, of 45 cm., and paler than the nominal species, Unlike the subspecies drouhardi by having underparts dyed color chocolate instead of gray, and undertail-coverts Brown instead of gray or whitish.
Coracopsis vasa comorensis
-
(Lavauden, 1929) – It´s smaller, of 45 cm., and paler than the nominal species. The underparts they are more gray with undertail-coverts more whitish, upperparts They show a bluish grey tinge clear. Dark subterminal band on the tail.
Coracopsis vasa drouhardi
-
(Shaw, 1812) – Nominal species
Coracopsis vasa vasa
Habitat:
The Vasa Parrot they are distributed among a wide variety of habitats, from the dense and humid forests, Brambles open forests, until Medemia Palms in the savannas.
It attends the habitats modified by human activity; sometimes visits farmland.
Move, mainly, by lowlands, from sea level to the 1.000 meters above sea level.
In Comoros, the Vasa Parrot, generally, are associated with humid forests, always green, above the 300 m, but visit more open fields to feed.
Within its forest habitat, they are usually seen in the treetops, Although they descend to the ground to feed.
Usually found in small noisy groups, although they congregate in larger flocks when feeding or roosting.
The Vasa Parrot They perch on the top of large trees with at least one individual awake to warn of the danger; It is said that they are most active in the full moon nights.
Reproduction:
The breeding season, probably, of the months from October to December.
The nest It is built in a tree cavity or a trunk. In the western area of Madagascar, the baobabs trees (Adansonia) they are often used, sometimes with several nests in the same tree. These birds (especially the males) they can show cloacal protuberances while breeding.
Food:
Seeds, nuts, berries and fruits are part of their diet. Visit rice fields, millet and corn, causing, sometimes, extensive damage to crops. Apparently less frugivorous than the Black Parrot.
Distribution:
Size of its range (reproduction / resident): 928.000 km2
Endemic to Madagascar and Comoros Islands (Grand Comore, Mohéli, Anjouan).
The species is partly common, in some places abundant, but its distribution in Madagascar possibly contracted due to large-scale deforestation in the center of the island.
Officially treated as harmful species, the Vasa Parrot they are persecuted because of predation on crops (especially rice) and captured for the trade in live birds at national and international level. They are also hunted as food.
It is distributed in several protected areas and although his pursuit and capture is intense in some areas, apparently, the species still is not at risk.
Distribution 3 subspecies
-
(Peters,W, 1854) – Distributed between Grand Comore, Mohéli and Anjouan in the Comoros Islands
Coracopsis vasa comorensis
-
(Lavauden, 1929) – Are distributed in the western part of Madagascar
Coracopsis vasa drouhardi
-
(Shaw, 1812) – Nominal species
Coracopsis vasa vasa
Conservation:
• Current Red List of UICN: Least concern
• Population trend: Decreasing
As they are seen as crop pests, is legal to hunt at the Vasa Parrot in Madagascar, and high levels of hunting contributes to a rapid decline in its population.
Like many species of Madagascar, the loss of their forest habitat is also a threat.
The size of the world's population has not been quantified, but the species, according to sources, It quite common in many areas
"Vasa Parrot" in captivity:
Very rare in captivity, difficult to find in aviaries, perhaps because of its initial lack of spectacularity compared to the more striking colors of any other species of parrot.
Although Vasa Parrot they are not very common as pets, comments from owners praise its virtues as a companion animal.
It is an extremely Intelligent and cunning.
Its beak is not strong enough to destroy the hard wood.
During the breeding season, they are very assets and quite noisy.
The female is the dominant, It is recommended as well that the eclectus that for an optimal result in reproduction, two males and one female are used in small aviaries or a greater number of males than females in breeding by means of colonies.
By the time they enter zeal both the male and the female, drop you the feathers of the head practically bald and both players.
The skin of the female head becomes yellow and white male. They tend to put in 2 to 3 eggs that incubate for space of 17 days.
The pups they are born completely devoid of markers, their legs are too long to be parrots and another feature that makes them unique is that they have both sides of their beaks at the corners, some bumps with characteristics similar to some exotic
Tienen facilidad para imitar la voz humana.
In terms of their longevity, according to sources, a specimen lived 53,9 years in captivity.
Alternative names:
– Vasa Parrot, Greater Vasa Parrot, Greater Vasa-Parrot (English).
– Grand Vaza, Grand Perroquet vasa, Grand Vasa, Perroquet vaza (French).
– Vasapapagei, Großer Vasa, Vasa (German).
– Papagaio-vasa (Portuguese).
– Loro Vasa (español).
scientific classification:

– Order: Psittaciformes
– Family: Psittaculidae
– Genus: Coracopsis
– Scientific name: Coracopsis vasa
– Citation: (Shaw, 1812)
– Protonimo: Psittacus Vasa
Images “Vasa Parrot”:
Videos "Vasa Parrot"
————————————————————————————————
“Vasa Parrot” (Coracopsis vasa)
Sources:
– Avibase
– Parrots of the World – Forshaw Joseph M
– Parrots A Guide to the Parrots of the World – Tony Juniper & Mike Parr
– Birdlife
– ornitoloxia
– Photos:
(1) – Coracopsis vasa By 4028mdk09 (Own work) [CC BY-SA 3.0], via Wikimedia Commons
(2) – Greater Vasa Parrot in Madagascar By AEM (Picasa Web Albums) [CC BY-SA 3.0], via Wikimedia Commons
(3) – Coracopsis vasa By 4028mdk09 (Own work) [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons
(4) – Greater Vasa Parrot (caracopsis vasa) in a Antwerp zoo By frank wouters from antwerpen, belgium , Belgium , Belgique (grote vasapapegaai) [CC BY 2.0], via Wikimedia Commons
(5) – Lesser vasa parrot (coracopsis nigra) in Anjajavy Forest, Madagascar By Charlesjsharp (Own work) [CC BY-SA 3.0], via Wikimedia Commons
(6) – Parrots of the World, by Joseph Forshaw (illustrated by William T. Cooper)
– Sounds: Hans Matheve (Xeno-canto)