Content |
|---|
Description
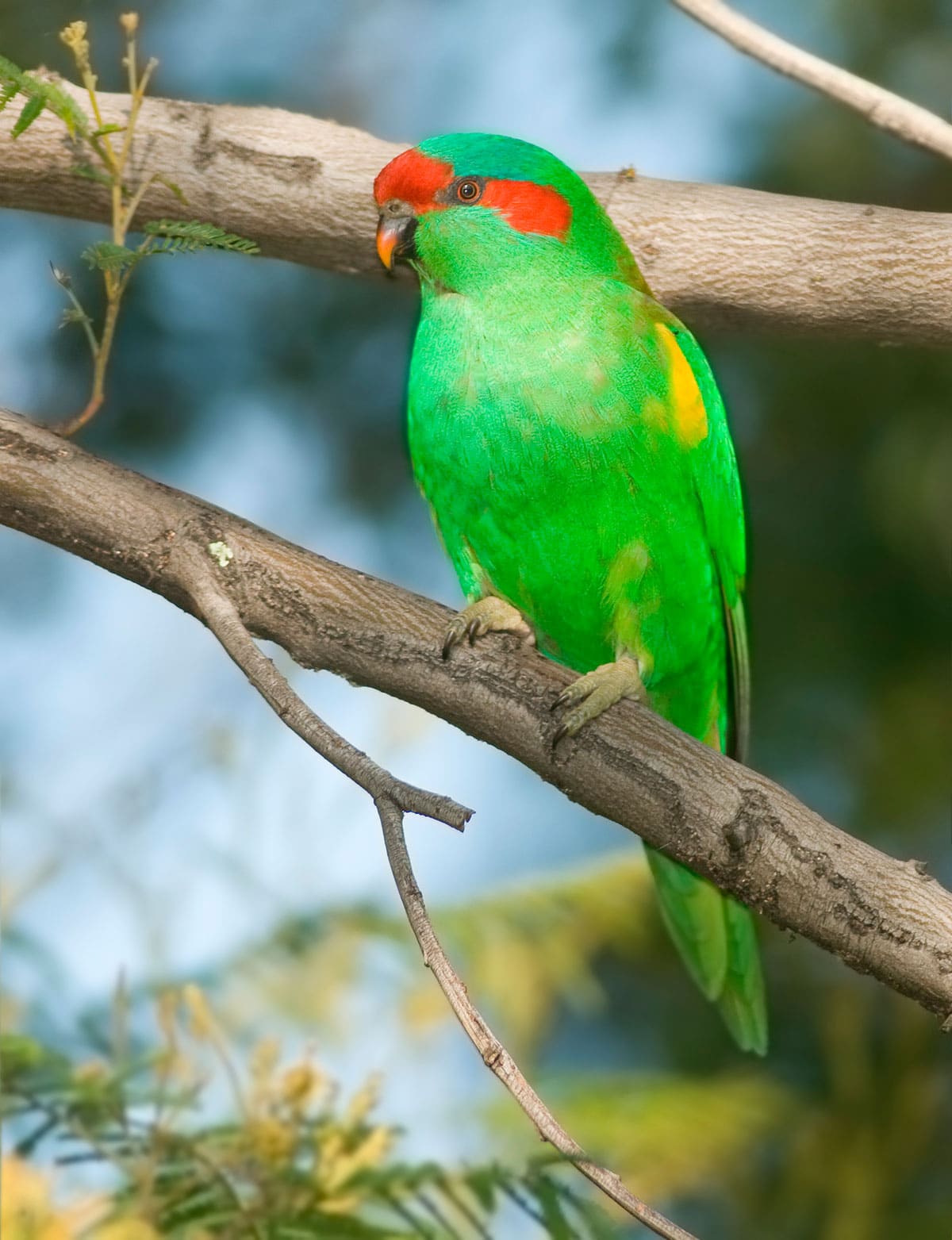
20 to 23 cm.. length and a weight between 52 and 56 g..
The general plumage of the Musk Lorikeet (Glossopsitta concinna) is green.
The part forward of the crown, lores and coverts headphones are of color Scarlet. Top of the head and cheeks, of color green impregnated of Turquoise under eye. The underparts of color green with a washed Brown olive around the sides of the chest. Green bright it rump. Wing coverts green, flight feather of color gray to black and a band of color yellow in the area of the shoulders. The feathers of the tail with brands reddish orange.
Part back from the neck yellowish green. Beside the edges of the wings colour yellow. Bill black-tipped Red. The irises Orange and the legs greenish Brown.
The blue area in the crown of the female It is smaller and paler which in the male.
The name of the species derives from a musky odor that is said to emit these birds.
- Sound of the Musk Lorikeet.
Subspecies description:
-
Glossopsitta concinna concinna
(Shaw, 1791) – Nominal.
-
Glossopsitta concinna didimus
(Mathews, 1915) – Less blue in the crown, nearly absent in the female.
Habitat:
Seasonally nomadic Depending on the flowering of the eucalyptus, at least at the ends of their range.
Found in many habitats of open forest, agricultural and suburban areas, including forests of eucalyptus, dry forests, dense rainforest (particularly in Tasmania) and riparian forests.
It avoids the high open woods and high altitude. Often found in large flocks of more than one hundred of individuals, where couples who form strong bonds, they often live together. It is extremely trusting when feeds.
Flocks have been seen, frequently, flying at high altitude.
Reproduction:
Season of mating from August to January. The nests they are built in holes of eucalyptus. The two eggs are incubated for about 25 days and the young leave the nest between 6 and 7 weeks after hatching.
Food:
like most others Lori, the diet consists in nectar and pollen, as well as small fruits and some insects. They can RAID orchards, vineyards and crops, forming herds with the Swift Parrot (Lathamus discolor) and other gender lori Glossopsitta.
Distribution:
Size of the area of distribution (reproduction / resident): 664.000 km2
The Musk Lorikeet are located in the East of New South Wales, Victoria, South of Australia and Tasmania.
Subspecies distribution:
-
Glossopsitta concinna concinna
(Shaw, 1791) – Nominal.
-
Glossopsitta concinna didimus
(Mathews, 1915) – Tasmania, sometimes King Island. Small population wild in Perth.
Conservation:
• Current IUCN Red List category: Least concern
• Population trend: Stable
The world population It has not been quantified, but the species is reported be very common (pit et to the. 1997).
The population suspected to be stable in the absence of evidence of any reduction or substantial threats.
"Musk Lorikeet" in captivity:
Rare out of Australia, small number in the aviaries of United States and United Kingdom.
A delight, playful, more quiet that the Iris Lorikeet; they can imitate sounds; a bit messy due to a diet of nectar.
Alternative names:
– Musk Lorikeet (ingles).
– Lori à bandeau rouge, Loriquet musqué (French).
– Moschuslori (German).
– Loris Musk (Portuguese).
– Lori Almizclero (español).

scientific classification:
– Order: Psittaciformes
– Family: Psittaculidae
– Genus: Glossopsitta
– Scientific name: Glossopsitta concinna
– Citation: (Shaw, 1791)
– Protonimo: Annual parrot
Images “Musk Lorikeet”:
Videos "Musk Lorikeet"
“Musk Lorikeet” (Glossopsitta concinna)
Sources:
Avibase
Parrots of the World – Forshaw Joseph M
Parrots A Guide to the Parrots of the World – Tony Juniper & Mike Parr
BirdLife.org
Photos:
1 – By JJ Harrison (jjharrison89@facebook.com) (Own work) [GFDL 1.2 or CC-BY-SA-3.0], via Wikimedia Commons
2 – By Steve (originally posted to Flickr as Musk Lorikeet.) [CC-BY-SA-2.0], via Wikimedia Commons
3 – free-pet-wallpapers.com
4 – “Musk Lorikeet 2” di JJ Harrison (jjharrison89@facebook.com) – It operates propria. With license CC BY-SA 3.0 Transact Wikimedia Commons.
5 – Image: Steven Kuiter – biodiversitysnapshots.NET.au
Sounds: Marc Anderson (Xeno-canto)