Content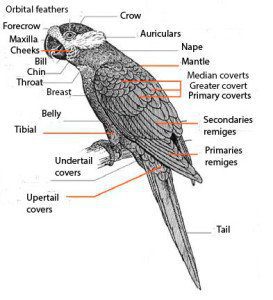
|
|---|
Description
12 cm.. length between 25 and 30 g. of weight.
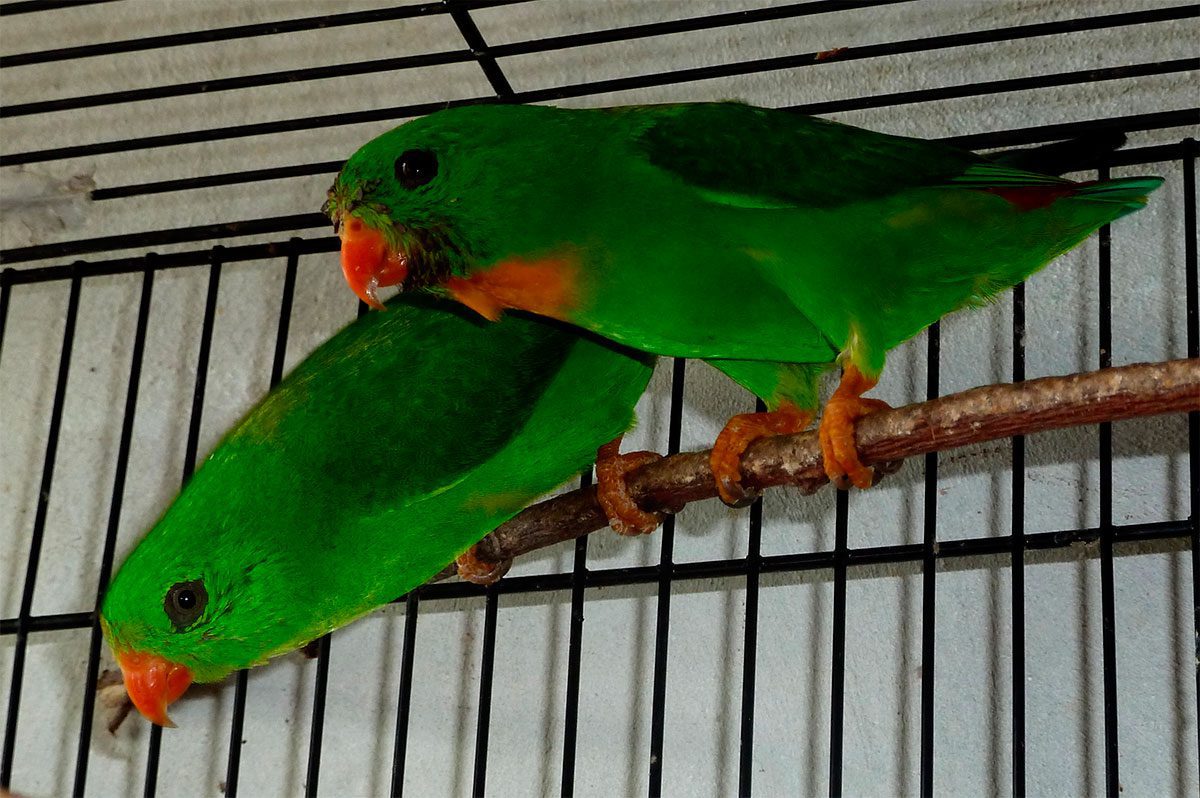
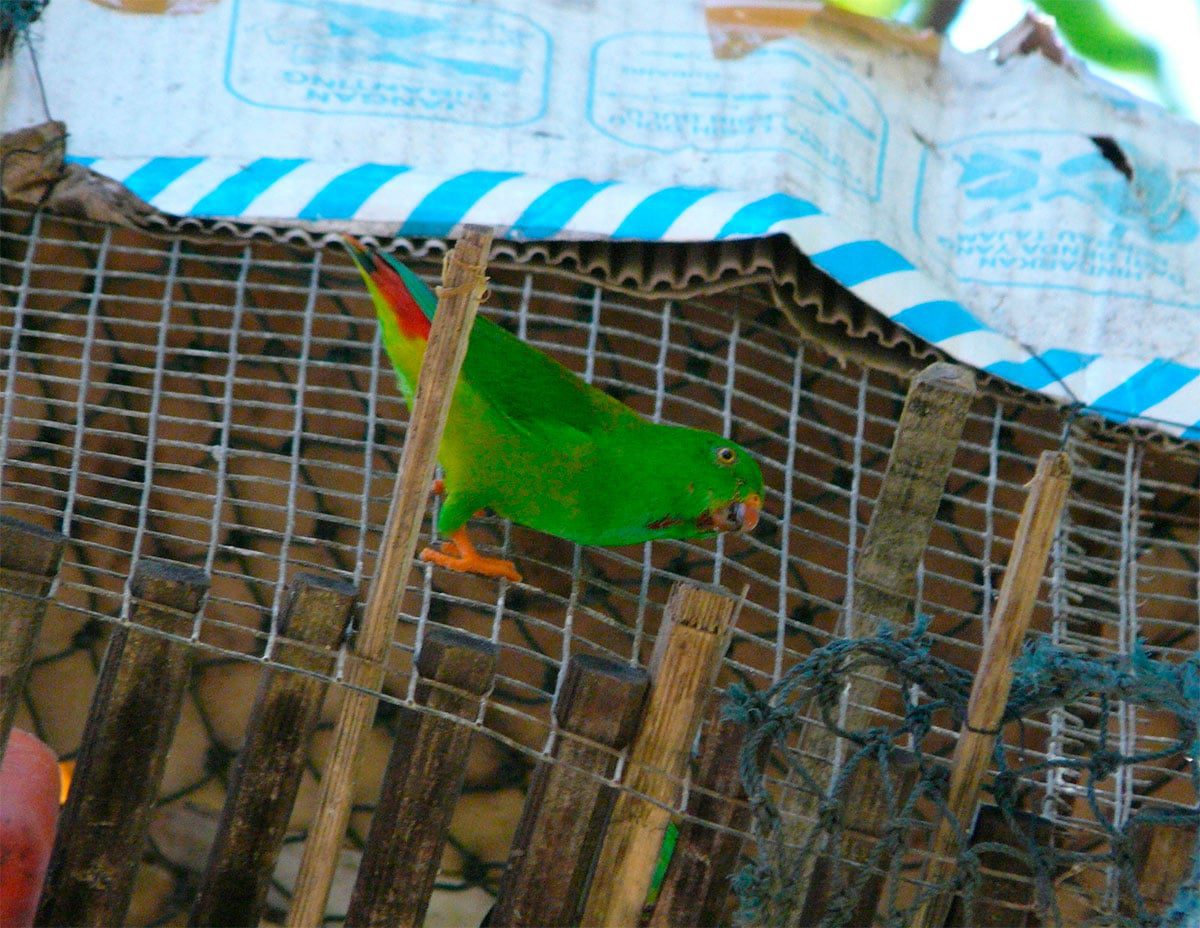
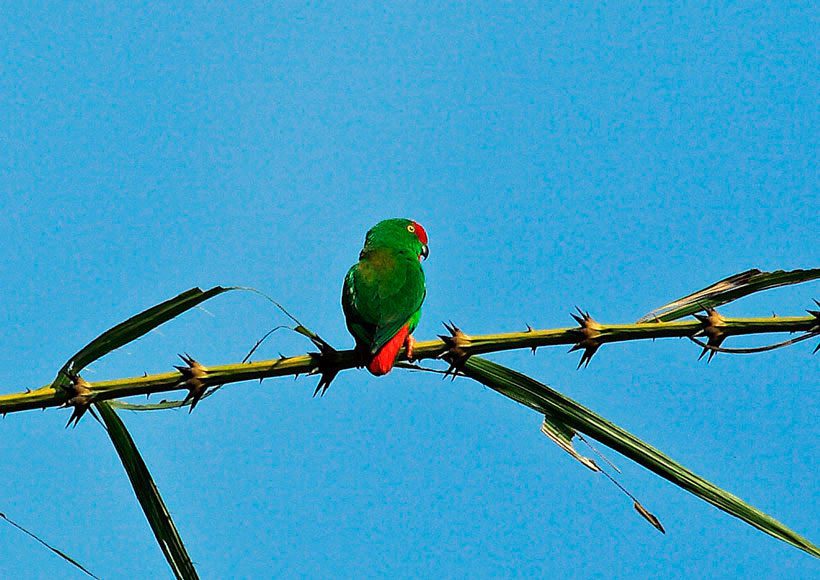
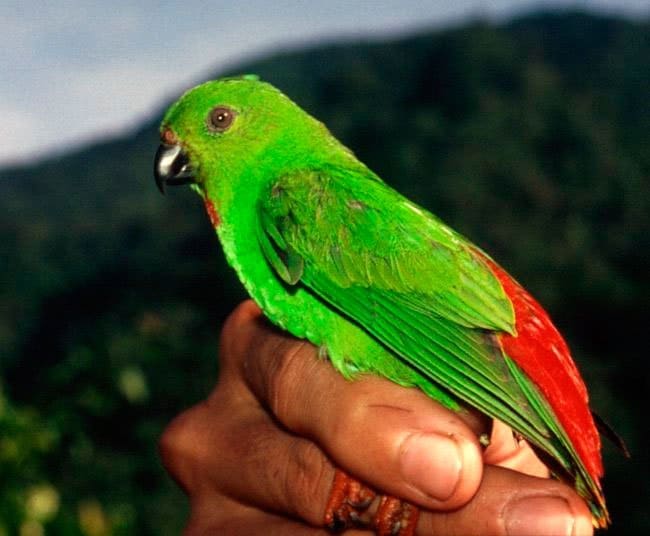
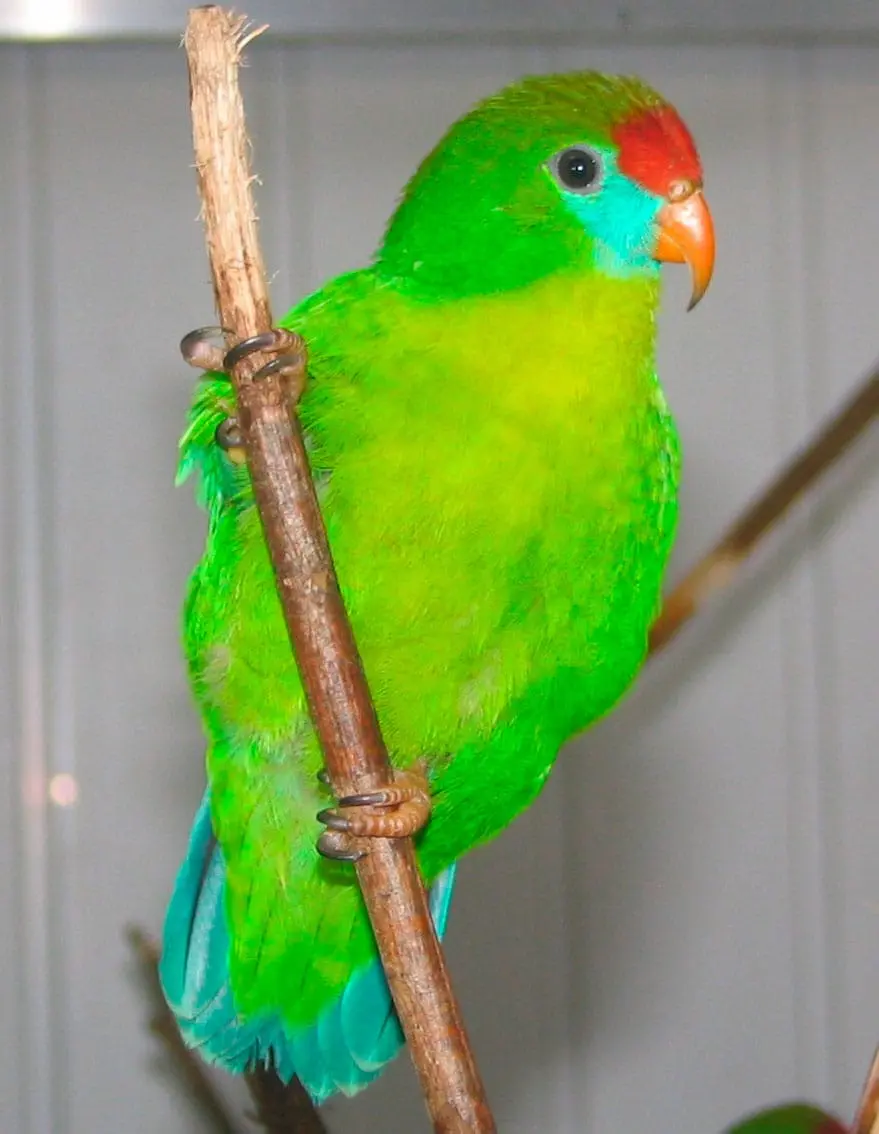
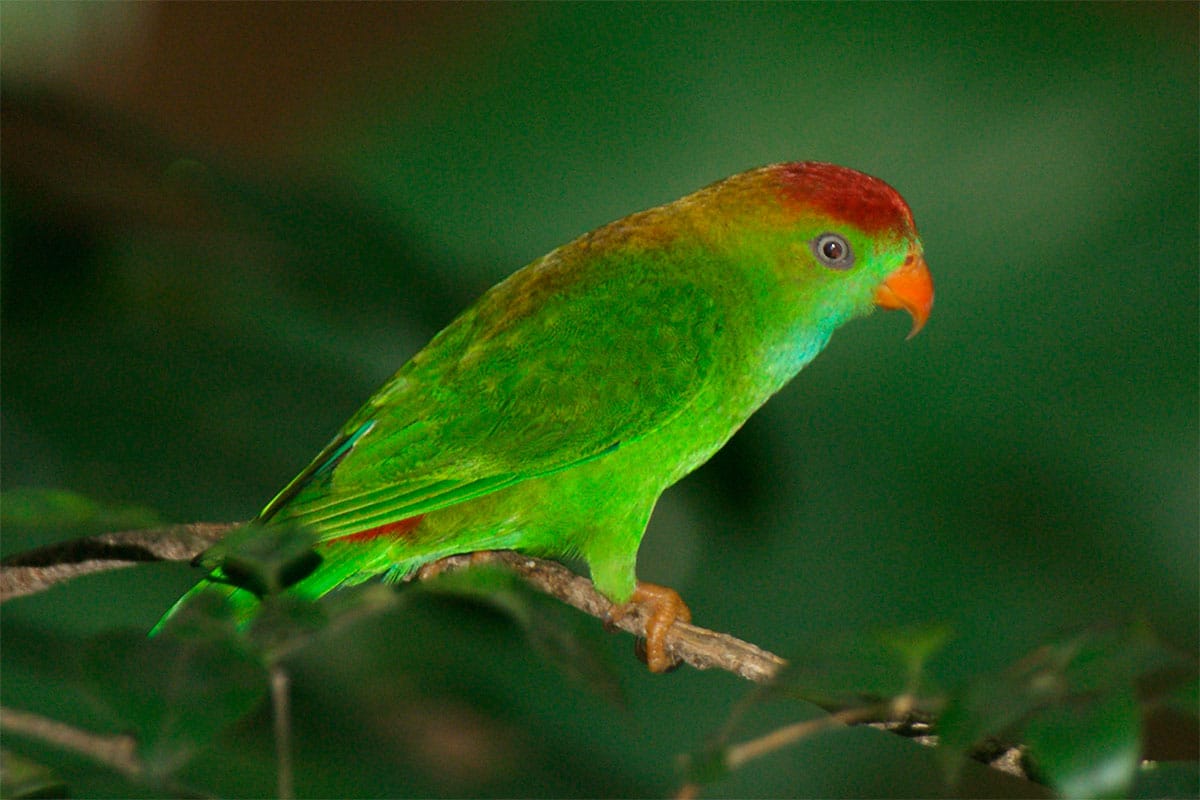
The head of the Yellow-throated hanging parrot (Loriculus pusillus) is bright green.
Upperparts green with yellow orange washing pale in the mantle; rump and uppertail-coverts, bright red. Wings green above, undertail, Turquoise with coverts green. Throat bright yellow, rest of the underparts bright green. Feathers of the tail green above, with side coverts yellowed and pale blue below. The bill orange; irises yellowish white; legs oranges.
Female and immature with yellow throat very small.
- Sound of the Yellow-throated hanging parrot.
Habitat:
Reported along the edges of the forest, and in the marshy forests of the lowlands to 1.850 meters above sea level.
Possibly Nomad in response to local plant phenology.
The species shows great activity, climbing acrobaticamente on the canopy at time of collection, and resting and sleeping mouth below as well as other members of the genus.
The birds are alone, in pairs or in groups of up to eight individuals.
Larger groups sometimes gather in trees to feed.. Although discrete, the Yellow-throated hanging parrot They attract attention, since when flying between the trees they beat their wings emitting a characteristic buzz, accompanied by shrill calls.
Reproduction:
The laying tends to be of two eggs, deposited in the hollow of a tree, Palm or arbol-helecho, from time to time in an old nest of a barbet or Woodpecker. The nesting in West Java It was recorded between March and May.
Food:
They feed on nectar, fruit (including the Ficus figs), leaves and flower buds, as Cassia and Erythrina.
Distribution:
Size of its range (breeding/resident): 167.000 km 2
Endemic to Java and Bali, where it is usually uncommon. The world's population is thought to be superior to 10.000, but it may have decreased due to the logging of forests
Conservation:
• Current IUCN Red List category: Near threatened
• Population trend: Decreasing
The world population It has not been quantified, It is thought to be above 10.000 specimens. The species is generally described as rare throughout its area of distribution (pit et to the., 1997).
There are no data on population trends; However, the species is suspected decreasing at a moderately fast pace, due to the loss and degradation of its habitat.
"Yellow-throated hanging parrot" in captivity:
Rare in captivity.
Alternative names:
– Yellow-throated Hanging-Parrot, Javan Hanging-Parrot, Little Hanging-Parrot, Yellow throated Hanging Parrot, Yellow-throated Hanging Parrot (ingles).
– Coryllis à gorge jaune (French).
– Elfenpapageichen (German).
– Lorículo do Java (Portuguese).
– Lorículo de Java, Lorículo Javanés (español).
scientific classification:
– Order: Psittaciformes
– Family: Psittaculidae
– Scientific name: Loriculus pusillus
– Citation: Gray,GR, 1859
– Protonimo: Loriculus pusillus
Videos "Yellow-throated hanging parrot"
————————————————————————————————
“Yellow-throated hanging parrot” (Loriculus pusillus)
Sources:
– Avibase
– Parrots of the World – Forshaw Joseph M
– Parrots A Guide to the Parrots of the World – Tony Juniper & Mike Parr
– Birdlife
– Photos:
(1) – The Bali Children’s Project
(2) – By Jiří Hruška – biolib
– Sounds: Frank Lambert (Xeno-canto)