Content |
|---|
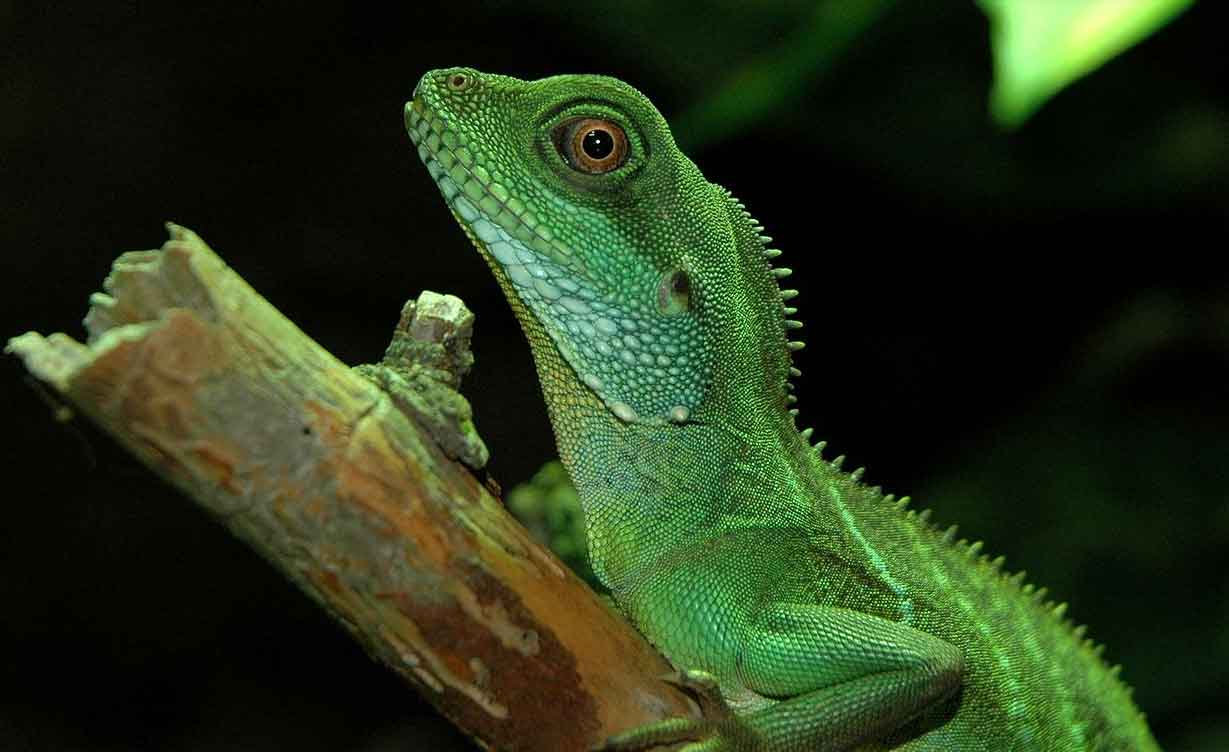
The Chinese water dragon the green (Physignathus cocincinus) lives in the rainforests of Southeast Asia, preferably near bodies of water. On trade, small juveniles from breeding farms in the countries of origin are usually offered. As not only can they grow a lot, they are also very scary, they demand a lot for their maintenance. Unfortunately, this is the reason why many animals can have clearly damaged muzzles; this can only be avoided if they are kept in large aquaterrariums. So, the Chinese water dragon not suitable for beginners.
Behavior
The Chinese water dragon, daytime habits, can raise itself, in pairs or in small harems (a male with 2 to 4 females). If they stay in pairs or harems, care must be taken to provide sufficiently large and well-structured terrariums so that females can retreat if necessary. Males are incompatible with each other and show marked territorial behaviour.. If aggressions occur during socialization, animals must be separated immediately and, as experience has shown, permanently.
Suitable accommodation
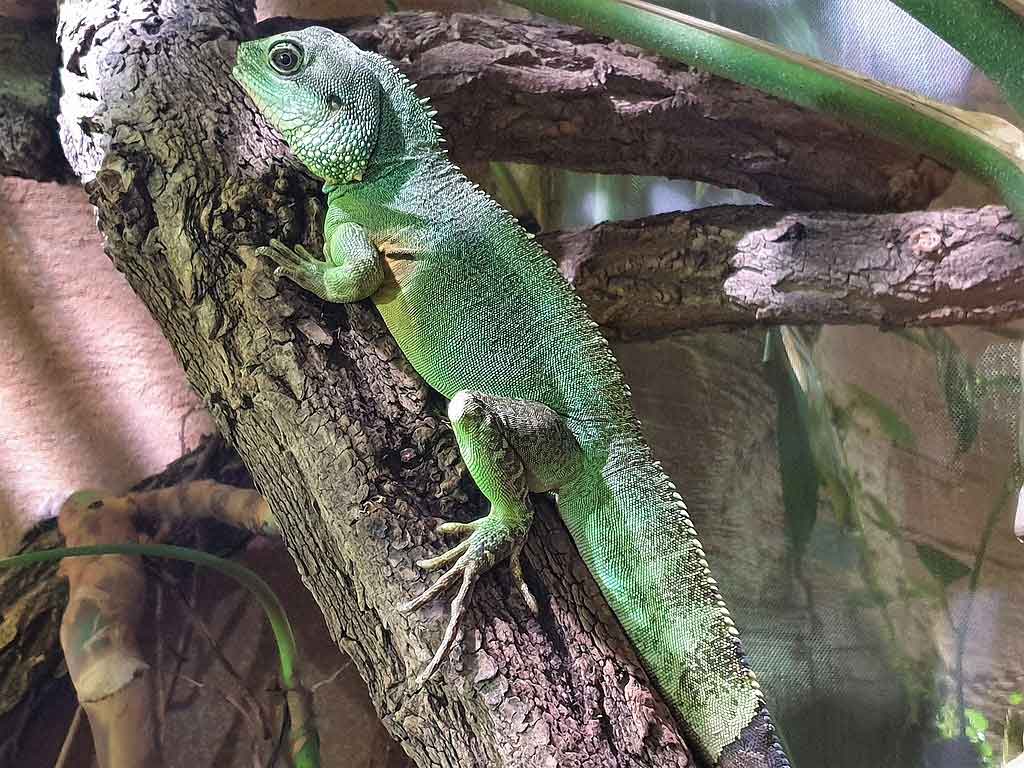

The Chinese water dragon usually reacts to disturbances with a panic flight, so you need as big terrariums as possible. For a maximum of two adult animals, the terrarium must measure at least 200 x 100 x 150 cm. (length x widht x hight). The underside of the crystals should be covered with opaque tape; This reduces stress on the animals considerably and reduces the danger of them running towards the glass..
Like cold-blooded animals, water dragons need a temperature gradient in the terrarium that allows them to reach their optimal body temperature. Ideally, mimic natural conditions with bright sunny areas and cooler shady areas in the terrarium.. As such, a powerful heat radiator with UV components is installed on one side of the terrarium (for example, a metal vapor lamp), that guarantees a localized heating to 35 °C. The rest of the zones can be heated to a temperature of 25 °C. The remaining zones may have a temperature of 25 to 30 °C. At night, the temperature of the terrarium should drop to 20 – 23 °C.
The humidity should be around 70-80% and can exceed the 95% At night. This can be achieved by spraying the terrarium with lukewarm water or using a sprinkler system. Precise thermometers and hygrometers are needed to measure temperature and humidity.
Fluorescent tubes are suitable as basic lighting; the duration of illumination should be 10 to 14 hours. The water dragons need high light intensity and lots of UV light. How light sources emit less and less UV radiation over time (see manufacturer's instructions), must be replaced regularly. Attention: normal glass is impervious to UV-B rays. The lighting, especially heat emitters, should be placed out of the reach of the Chinese water dragon or secure with a wire mesh basket (Burning danger!).
for shy animals, the side and back walls of the terrarium should be covered with cork or something similar. This prevents the muzzle region from being bumped or rubbed. The horizontally and vertically mounted climbing facilities and rest areas made of cork, estate, remained, etc. have proven to be successful. Animals need a large water area, possibly heated, where they like to flop when they escape. The water bucket can occupy half of the floor space of the terrarium and must have at least 80 x 80 x 20 cm.. The temperature of the water part can be about 25 °C. Installing a filter (term) external facilitates the maintenance of the water section.
Bark mulch or other absorbent substrate for terrariums is suitable as a substrate. (no sand), which should always be kept slightly moist (NOT wet) and must have a height of 20 cm.. Natural planting with robust plants creates additional retreat possibilities and ensures uniform moisture.
Diet
The Chinese water dragon eats exclusively animal food when young, but as an adult he also likes to eat sweet fruit (Apple, berries). Live insects (crickets, domestic crickets, grasshopper, cockroaches, etc.), sprinkled with a mineral preparation, are an adequate food to prevent deficiency symptoms. Mealworms, zophobas or wax moths should only be fed in moderation due to their high fat content. Fresh water must be available at all times.
Young animals grow very fast and, Therefore, need large amounts of food, as well as a good supply of calcium and UVB light.
Care
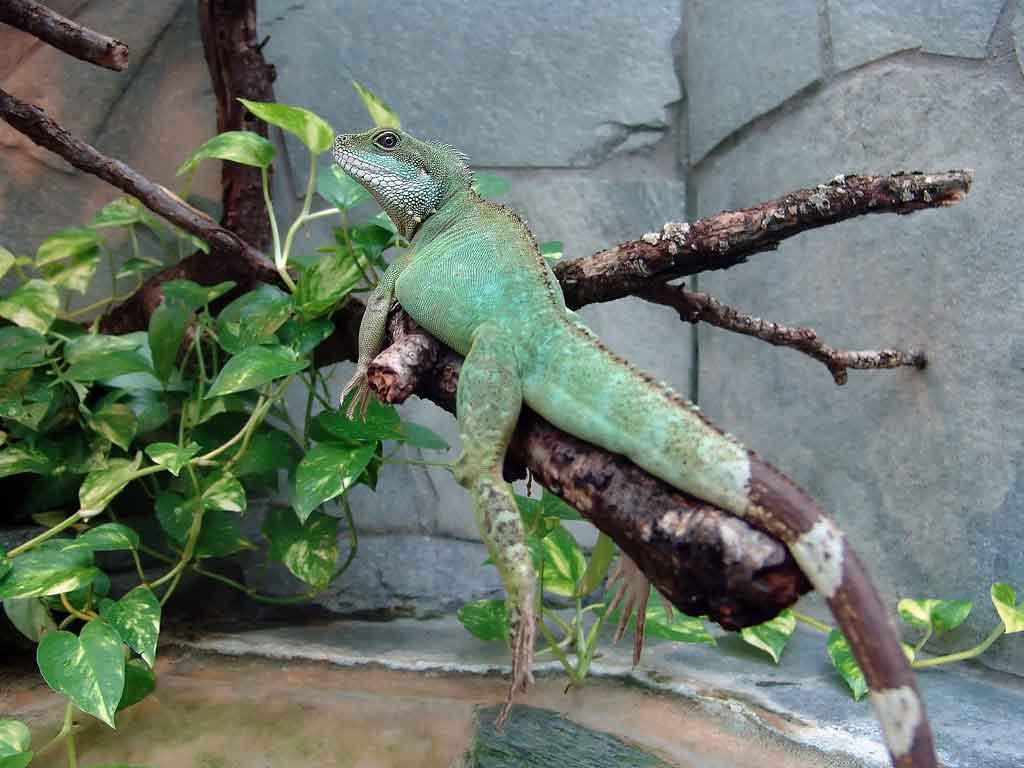

Food scraps, molts and droppings should be removed daily. The water part can be cleaned by an aquarium filter; in case of heavy contamination, a water change must be performed. External filters should be cleaned regularly.
Animal health must be monitored daily. The most common health problems in the Chinese water dragon are the lesions in the mouth area, the emaciation, fecal changes such as diarrhea and softening of the bones. In case of anomalies, a reptile vet should be consulted. Annual fecal examinations are recommended to detect endoparasites.
The intestinal flora of the Chinese water dragon also includes salmonella, that are harmless to animals but can cause disease in humans. Hygiene measures (wash your hands well, etc.) can prevent infection.
Acclimatization and handling
Reptiles are animals of pure observation and should NOT be petted. The Chinese water dragon, in particular, can become very nervous when approached or moved (suddenly). So, the first days in your new home, animals need adequate rest to get used to their new environment.
Animals should only be captured when necessary. To avoid injury, the easiest way to catch young animals is with a net. Larger animals can be held with the bare hand behind the head. In doing so, body and tail must be well secured. By principle, lizards should never be held or fixed by the tail.
Breeding
The female is courted by the male. This can also lead to persecution. If the female is ready to mate, He pauses and the male applies the so -called "bite in the neck". This involves biting the female on the nape.. This is followed by mating. Some time later, the female builds a nest pit of about 10 to 20 inches deep and lays up 16 eggs, from which the young are born after 67 to 101 days, depending on outside temperature conditions.
Special features
If animals get used to picking up food from the forceps, they will lose some of their shyness towards humans. The Chinese water dragon knows how to swim very well and they also hunt fish in the wild.
The Australian water dragon (Physignathus lesueurii) it can grow even larger and its breeding differs in some respects from that of the Chinese water dragon.
Its price ranges from 60 and 100 EUR.