
Content |
|---|
Origin / Distribution
Two subspecies are recognized as valid, including nominate subspecies.
The Eastern mud turtle (Kinosternon subrubrum) found in the US states of Alabama, Arkansas, Delaware, Florida, Georgia, Illinois, Indiana, Kentucky, Louisiana, Maryland, Mississippi, Measure, New Jersey, New York City, North Carolina, Oklahoma, Pennsylvania, South Carolina, Tennessee, Texas y Virginia.
In Indiana, the Eastern mud turtle is listed as an endangered species.
Characteristics / Appearance
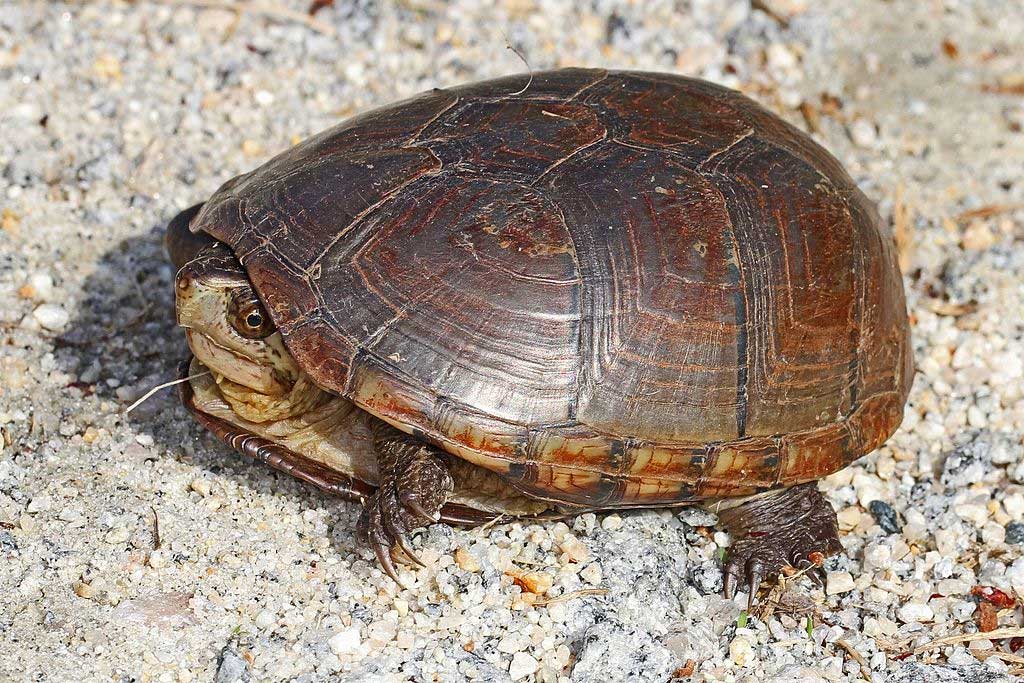
The Eastern mud turtle it is a small species, with a carapace length of 7 to 10 cm for adults. The head is irregularly mottled or streaked with yellow. The shell is convex, yellow to black, and lacks a keel or distinctive pattern. The plastron is yellow to brown in color and may have a variable number of dark markings.. Sometimes they are confused with the Common musk turtle. But, the plastron of the Eastern mud turtle differs from that of Common musk turtle in that it has two hinges and a triangular-shaped pectoral shield. As well, Unlike in the Common musk turtle, he doesn't have two stripes on his face.
The sexes are similar in size. Males have a longer preanal length with the vent posterior to the edge of the carapace.. The youth of the Eastern mud turtle are darker in color, they lack head markings and their plastron is orange to red with a dark center.
Habitat
The Eastern mud turtle it is semi-aquatic and prefers relatively calm and shallow bodies of water. wet meadows, ponds, swamps and drainage ditches are their typical habitats. in coastal areas, eastern mud turtles can tolerate brackish water and are found on the edges of mudflats and offshore islands. Although they do not sunbathe often, They are much more terrestrial than the Common musk turtle and can often be seen on land from spring through fall. They reach maturity between 4 and 8 years of age. Individuals in captivity have lived up to 38 years. The Eastern mud turtle feeds mainly on the bottom of the sea. Their diet consists of a variety of insects, mollusks, Tadpoles, crustaceans, carrion and aquatic vegetation.
Behavior

The Eastern mud turtle it is swimming and lonely. They hibernate between November and March., but start and end times vary by location. The hibernaculum of these turtles includes shallow burrows at the edge of wetlands. They are crepuscular. Depending on ambient temperature, they spend their time submerged in shallow water or basking on the surface of the water. These tortoises can sunbathe with conspecifics on the same trunk, but this occurs mostly during the mating season.
These turtles are occasionally aggressive and fight each other with head-to-head confrontations.. Such clashes can lead to possible serious injury, such as limb amputation, but the motive for the attack is unknown. The Eastern mud turtle uses color perception to distinguish the sexes, what plays a role in courtship. when they mate, female musk glands release pheromones to signal males to initiate courtship. The females dig their nests and hide them using their front and hind legs., and then they lay their brood.
Food
The Eastern mud turtle it is omnivorous and its diet is very varied. They feed mostly on the bottom., consuming mainly in the water, but sometimes they rise to the surface if the opportunity arises. Its range of consumption includes seeds, small invertebrates like earthworms (family Lumbricidae) and snails (Lymnaea, Physa, Planorbis), small insects like moths and butterflies (orden Lepidoptera ), june beetles (orden Coleoptera, familia Scarabaeidae, Melolonthinae subfamily), as well as arachnids (order Araneae), green algae, crustaceans and carrion. Strecker (1927) reported that these turtles also consumed a small striped snake (Tropidoclonion lineatum).
Mahmound (1967) investigated the diet Eastern mud turtle
Threats to the species
State of conservation ⓘ |
||
|---|---|---|
 Minor Concern ⓘ
(UICN)ⓘ
Minor Concern ⓘ
(UICN)ⓘ
| ||
The Eastern mud turtle It is classified as a species of “Least concern” according to the IUCN Red List. They are not on the US federal list., CITES or listed by the state of Michigan. The Eastern mud turtle are considered endangered at the state level in Indiana, New York and Pennsylvania, and a species of greatest conservation need in Kentucky (Meshaka et al. 2017).
The main threat to these turtles is habitat loss and road mortality., since few turtles manage to cross them. Habitat loss through roads bisecting aquatic habitats, increased urbanization and climate change that raises sea levels harm these mud turtles. The illegal pet trade of this species has also caused damage to its native ecosystem through loss of biodiversity..
Potential conservation efforts to reduce mortality rates include wetland legislation that protects a terrestrial buffer zone around these semi-aquatic habitats. These terrestrial buffer zones are already intact in national parks. Future conservation efforts need a better understanding of population changes over time, as well as their perceived response to general climate change and microhabitat change.
The "Eastern mud turtle" in captivity
Aquaterrarium
The Eastern mud turtle They can reach a maximum carapace length of 12 cm.. So, they need an aquarium with a rim length of at least 80 cm.. For the benefit of Kinosternon subrubrum, the aquarium should have several hiding places and retreats. So, they need an aquarium with a rim length of at least 80 cm.. For the benefit of the Kinosternon subrubrum, the aquarium should have several hiding places and retreats. The roots, dense plantings of tanks and stone or rock structures are suitable for it. There should also be an integrated area for sunbathing
These turtles are solitary animals. Ideally, keep them individually in a species tank. Especially the males tend to be aggressive. In any case, must be stored separately.
The Eastern mud turtle feels very comfortable in water temperatures between 17 and 28 degrees Celsius. But, they need a fixed change between summer and winter. During the winter months you can reduce the lighting time and lower the water temperature to 10 – 17 Celsius degrees.
Food
The Eastern mud turtle they are carnivorous. They prefer live food, frozen food or dried animals. The insects, the molluscs, amphibians or even plants are at the top of the menu.
Reproduction
The Eastern mud turtle (Kinosternon subrubrum) have already been successfully bred in the aquarium.
Buy one "Eastern mud turtle"
The prices of one "Eastern mud turtle" in the exotic animal market ranges from 50 – 100 EUR.
Videos "Eastern mud turtle"
|
HTTPS://www.YouTube.com/watch?v=U95SSLoQ4dk
|
HTTPS://youtu.be/xnHl0EZqG9g
|
|---|
Alternative names:
1. Eastern mud turtle, Common mud turtle (English).
2. Cinosterne rougeâtre (French).
3. Pennsylvania-Klappschildkröte, Kinosternon subrubrum, Mississippi-Schlammschildkröte, Östliche Klappschildkröte (German).
4. Tartaruga de barro comum, Tartaruga de barro orienta (Portuguese).
5. "Tortuga de pantano común", Tortuga de pantano del este (español).
