
Content |
|---|
Origin / Distribution
two species (Brachylophus fasciatus and Brachylophus vitiensis) belong to the genus Brachylophus (Fiji iguanas).
Its geographical distribution is limited to some islands of the archipelago of Fiyi y Tonga. Son, Therefore, the most isolated members of the subfamily Iguaninae (major iguanas), whose other representatives live in America. Until a few years ago, gender was supposed to Brachylophus was monotypic. The nominal species Brachylophus brevicephalus is considered a synonym of Brachylophus fasciatus. Was not up 1981 that a second valid species of Brachylophus, Brachylophus vitiensis.
Characteristics / Appearance
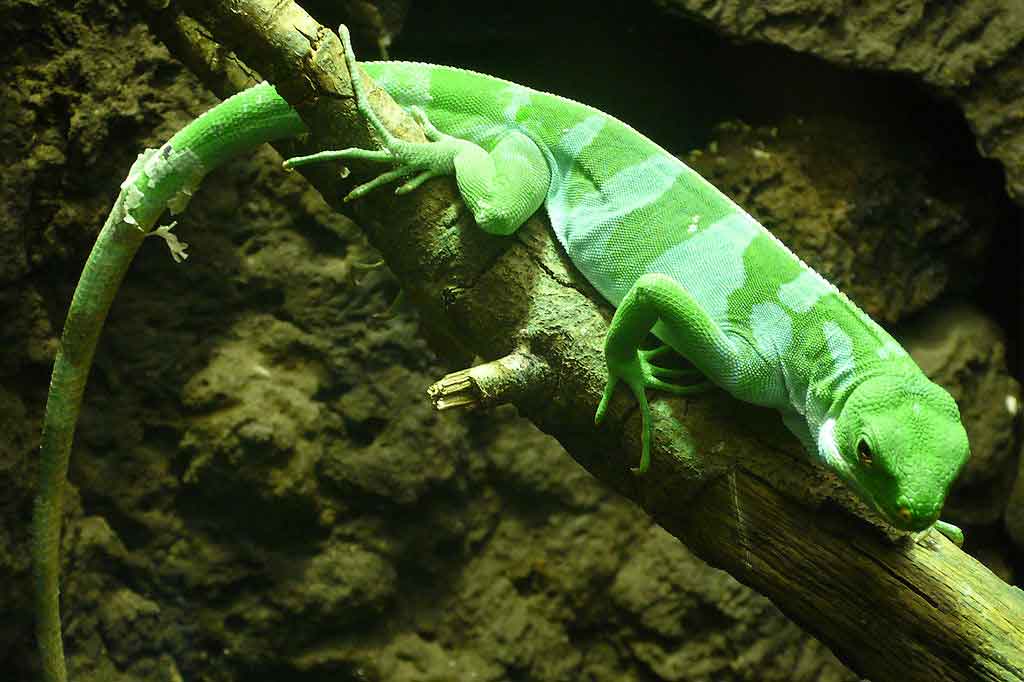
The Lau banded iguana It is a slender build iguana that reaches a total length of more than 70 cm.. The difference in size between both sexes is minimal. The measures, (head – torso), for adults are in the range of 14-19 cm. (male) and 14-18 cm. (female) with a mass of 95-210 g (male) and 105-220 g (female). These weights refer to mating males and egg-laying females..
The Crest Ridge is little pronounced in both sexes. there is between 11 and 17 femoral pores on the bottom of each thigh, which are more pronounced in males. Each animal has an individual pattern, neither looks like the other. The normal coloration of females is mostly uniform green, with a light green or white stripe on the front of the body in some specimens. The nostrils are edged with yellow in both sexes.. Males, on the other hand, have a contrasting cross-hatching (green and light blue to two different shades of green) of the body and tail. The intensity of the coloration depends a lot on the mood. In courtship or aggressive phases, light blue stripes on males turn almost white and green stripes dark blue to black.
When the coloration is very intense, yellow spots also appear on front and back legs.
Habitat
The Lau banded iguana feeds on leaves and other plant material. During the day these animals rest in the tops of tall trees. Life expectancy is about 10-15 years.
Behavior
The species is diurnal, spending their days looking for food, basking in the sun and guarding their territories during the day and retreating to the treetops at night. Male iguanas are highly visual and aggressively defend their territories from rival males.. Iguanas deepen their green coloration to intensify their bands, and shake their heads and intimidate intruders by pouncing on them with their mouths open.
Threats to the species
State of conservation ⓘ |
||
|---|---|---|
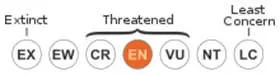 in danger ⓘ
(UICN)ⓘ
in danger ⓘ
(UICN)ⓘ
| ||
The Lau banded iguana (Brachylophus fasciatus) is unfortunately highly endangered in its natural habitat and is listed on the IUCN red list. If you want to have this species of iguana in Europe, you must have the corresponding papers and regularly document the animals with photos. feral pigs, the goats, dogs, cats and introduced species, like the mongoose, has contributed to the fact that there are only less than 10.000 animals of this species in freedom.
But, in the meantime, there are breeding projects to increase the natural population of the animals again. Unfortunately, A few years ago it was not known that both Brachylophus bulabula as the Brachylophus fasciatus were kept in private homes. The two species were thought to be the same. As the animals hardly differ from each other visually, many animals mixed with each other. It is very likely that there are no pure species of the Lau banded iguana in Europe.
The "Lau banded iguana" in captivity
The terrarium
The Lau banded iguana should be housed in terrariums 200 x 80 x 120 cm.. Containers can be made of plastic plates (of 1 cm thick). This material is lighter, more hygienic and easier to work with than for example, timber. It also has a much longer shelf life.
Since Lau banded iguana only kept singly or in pairs, the terrariums will be designed so that they can be separated in the center with a plastic plate. The advantage is that the iguanas can be separated and reunited without removing them from their usual environment.. Plastic strips will be placed on the front (20 cm height at the bottom, 10 cm at the top). ventilation (round plastic grilles) will also be incorporated into these two front panels. This has the advantage that there is sufficient air circulation but no drafts. But, this design is not suitable for small terrariums. The front is completed with sliding glass panels of 4 mm thick.
Illumination
Lighting is provided by a fluorescent tube (18 watts) per side and one HQL mercury vapor lamp (80 W). The weights are outside the terrarium. The fluorescent tubes will be on during 14 hours all year (of 7:00 to 21:00 hours), HQL lamps will light at 10:00 hours and will be on until 15:00. In general, It should be noted that the intensity of light plays a decisive role in the breeding.
Terrarium Decoration
The terrariums they are provided with thick branches and cork tubes. Pressed cork boards or coconut fiber mats are placed on the rear wall, that are increasingly accepted by juvenile iguanas to climb.
The plastic plants are used as decoration, Since the Lau banded iguana consider real plants as food. This makes food control difficult and can lead to deaths if the plants are poisonous or hard-fibered.. The substrate is filled with river sand (height of 5 to 15 cm.). The females also use it to lay their eggs.. A water reservoir 45 x 20 x 5 cm. , not used for drinking, complete the assembly.
Bottom heaters are not used, as they would be atypical for tree dwellers. Hideouts are not necessary, Since the Lau banded iguana does not seek visual protection from human observers in terrarium conditions.
Terrarium temperature
The air temperature is about 30°C during the day in summer and about 27°C in winter. At night, values drop by about 5°C each. On very hot summer days, temperatures rise to 35°C, but this does not cause any negative reaction in animals.
Measurements are always made at the center of the sidewall, outside the radiation zones of light sources. The iguanas cover their water needs by spraying the terrariums. This is done daily, depending on the season, once in winter to four times in summer.
Food
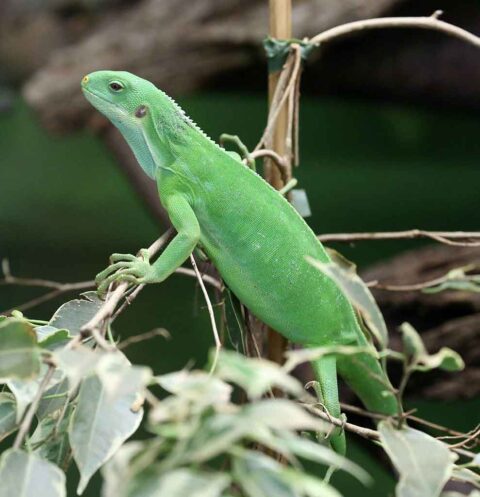

Feeding is done at different intervals. Seasonal conditions and the weight of the animals play a decisive role. As a rule, iguanas feed every five days.
Overweight specimens are only offered vegetable food every two days.
The Lau banded iguana can be fed with tomatoes, cucumbers, carrots, courgettes, various lettuces, chinese cabbages, dandelions and their flowers, as well as with the following fruits: apples, grapes, oranges, tangerines, peaches and bananas. It also, can accept insects (black beetle larvae, Argentine giant cockroaches, grasshopper, crickets and house crickets). All insects are given only with tweezers to prevent their unhindered dispersal.
The Lau banded iguana develop a character of their own and also have individual food preferences. But, the favorite food of adult iguanas is black beetle larvae (Zophobas morio), that are only offered recently dead for security reasons. Females are less picky eaters than males.. The vitamin preparation, minerals and amino acids Korvimin-ZVT is added to each feed.
Management "Lau banded iguana"
The management of Lau banded iguana too easy, since they are not aggressive and do not bite. But, watch out for their sharp claws. Females are usually a bit more shy than males.. It should be noted that the Lau banded iguana seem to be very susceptible to stress when moved.
Reproduction
Good conditioning of the animals is important as a prerequisite for successful breeding. Fat animals are largely unsuitable for breeding. The females of more than 230 g could only have false pregnancies. Males with excess fat just sit in the terrarium. Males reach sexual maturity already under the year. Females do not reach sexual maturity until they are two years old.. In some cases even before.
The Lau banded iguana does not have a specific breeding season, but can reproduce throughout the year. However, the best time for successful copulation is spring..
The male will approach the female with a strong movement of his head.. If the female is willing to mate, does not change color and retains its normal green coloration. The males are normally very gentle in their approach.. But, this can change drastically if the female is unwilling to mate. The chase then becomes increasingly vehement and aggressive and ends with the female seeking shelter and hiding places on the ground.. Then takes on a stress coloration (dark olive green to almost black). I eat very late, stop the experiment and separate the animals to avoid serious bite injuries. Females can also injure smaller males if they are not ready to mate.. Dominant females do not discolor, they do not take stress coloring. when you put them together, always take the time to observe if they harmonize. In the early years, the iguanas were kept in pairs between one day and four weeks.
Otherwise, they were staying individually. with this method, mating is usually quick, but sometimes with little success (false pregnancies, unfertilized clutches). Females that do not lay clutches for a long period of time are mixed with other males on a trial basis.. With this breeding method, females do not show any stress behavior. When copulation occurs, the male carefully approaches the female from behind and harasses her. This is followed by the typical bite on the neck of lizards. In most cases, copulation takes place on branches or cork tubes. No mating has been observed on the ground. Mating lasts only a few minutes.
As places of oviposition, some areas of the bottom substrate remain more or less moist. Moist sandy areas are preferred, whose surface is additionally protected with a cork branch or tube. The first signs that oviposition is approaching are shown by the female searching the ground and exploring suitable places in the sand.. The period of burrowing activity is highly variable. In the fertilized clutches, the burrowing activity of the female is much more constant than in the non-fertilized. If wet sand areas are not prepared, it can happen that the female destroys the entire floor of the terrarium. Post-inserted storage containers are not accepted, e.g. with peat substrate. The females need between one and two weeks from the beginning of the excavation until the laying of fertilized eggs.. For unfertilized eggs, deposition may occur spontaneously; often, the eggs are simply distributed on the ground without the need to dig. In the upper part of the branches, unfertilized eggs can also be deposited., then they will fall to the ground. But, the period can also last 2 months, with the animal taking several breaks.
When the female has found a suitable place, dig a hole about 10 cm in diameter with a lot of intensity, observing their surroundings carefully. It is barely possible to observe the female doing this. If a male is in the terrarium at the time, the female is not disturbed by him. It also ignores the egg-laying activities of the female.. No matter how high the bottom substrate is filled, animals always dig to the bottom of the terrarium. So, the ground level in the planned storage places must be at least 10 cm.. When they are satisfied with their work, its color changes from green to dark olive green (work coloring). This transformation can only be observed for a very short time. This is followed by egg laying. According to observations, clutch size ranges from 1 and 7 eggs, these two being the extremes. They usually put on 3 to 5 eggs. Once the setting is finished, the eggs are placed in the correct position and the clutch is sealed.
Incubation
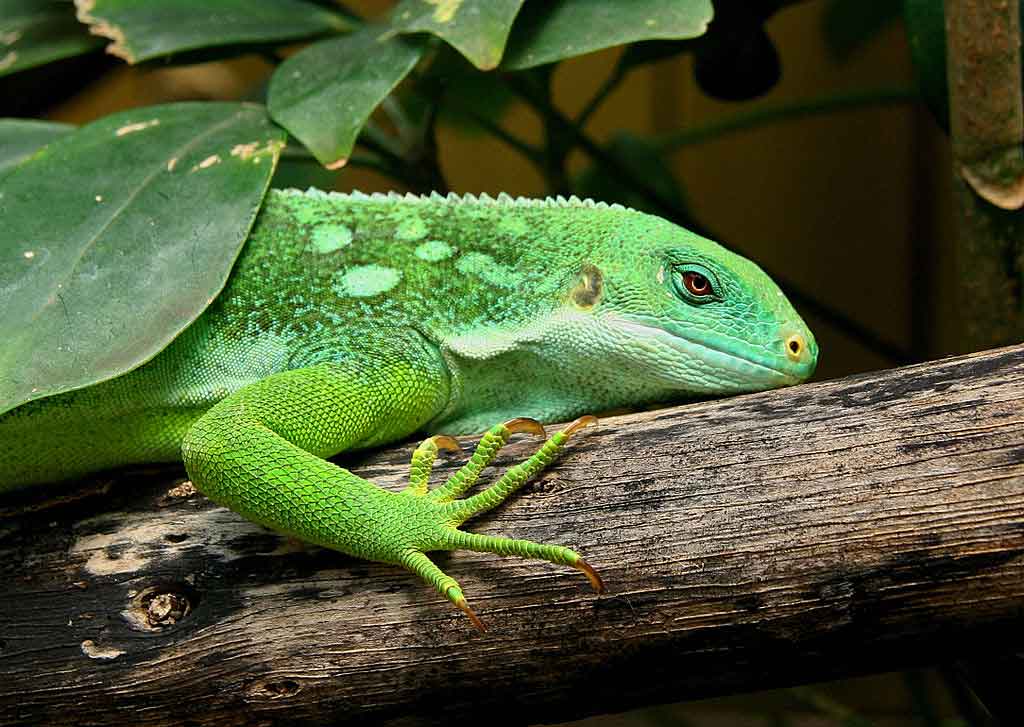

Incubation time varies a lot, although the reasons are not clear. The incubation temperature plays, of course, an important role in this regard, but it does not fully explain this phenomenon. the season of the year, the substrate and predevelopment in the female body probably also play a role. At 28°C the young will hatch after 113 to 126 days, at 29.5°C after 103 to 146 days.
When hatchlings see the light of day, They usually need between 6 and 12 hours from when they open the egg shell until they completely leave it. The sex of the pups can now be clearly recognized by their markings. Usually, the yolk sac has not yet been fully depleted, but falls off on its own after a day or two. The newborn pups have a total length of 17 to 24 cm and a mass of approximately 8 g.
the brood, especially in the first four weeks, requires a lot of time and patience. The food spectrum is the same as that of adult iguanas. So far, young animals have mostly rejected all food in the first period. About five days after hatching, they are offered freshly killed wax worms with tweezers. You have to be careful not to stress the iguanas too much, so the animals should not be surprised. If required, repeat feeding attempts several times a day. after a few days, young iguanas usually start eating waxworms on their own (placed on a branch in front of its snout). Only still mineral water is given as a drink up to nine months of age. The same goes for spraying two or three times a day.. This is done as a precaution (chlorine content in tap water). Young animals are moved to terrariums just as large as adults, since this seems to favor its growth. A small disadvantage is that the insects (except grasshoppers) should always be given with tweezers. Solitary breeding is not necessary in the first months; even several males can be kept together without problems. Only in very difficult cases is solitary breeding preferred.. The character of the young animals is already pronounced individually. Some are more confident, others more reserved.
Buy one "Lau banded iguana"
if you want to buy one Lau banded iguana, you should expect to pay a lot of money for it. They are not easy to find online and you are not likely to find one at your local pet store.. As a result, you could end up paying 1.000 euros for one of these iguanas.
Videos "Lau banded iguana"
|
|
|
|---|
Alternative names:
1. Lau banded iguana (English).
2. Iguane des Fidji (French).
3. Kurzkammleguan (German).
4. Iguana-listrada-de-fiji (Portuguese).
5. "Iguana bandeada de Fiyi" (español).
