Content |
|---|
Description
31 cm.. length and an approximate weight of 170 gr.
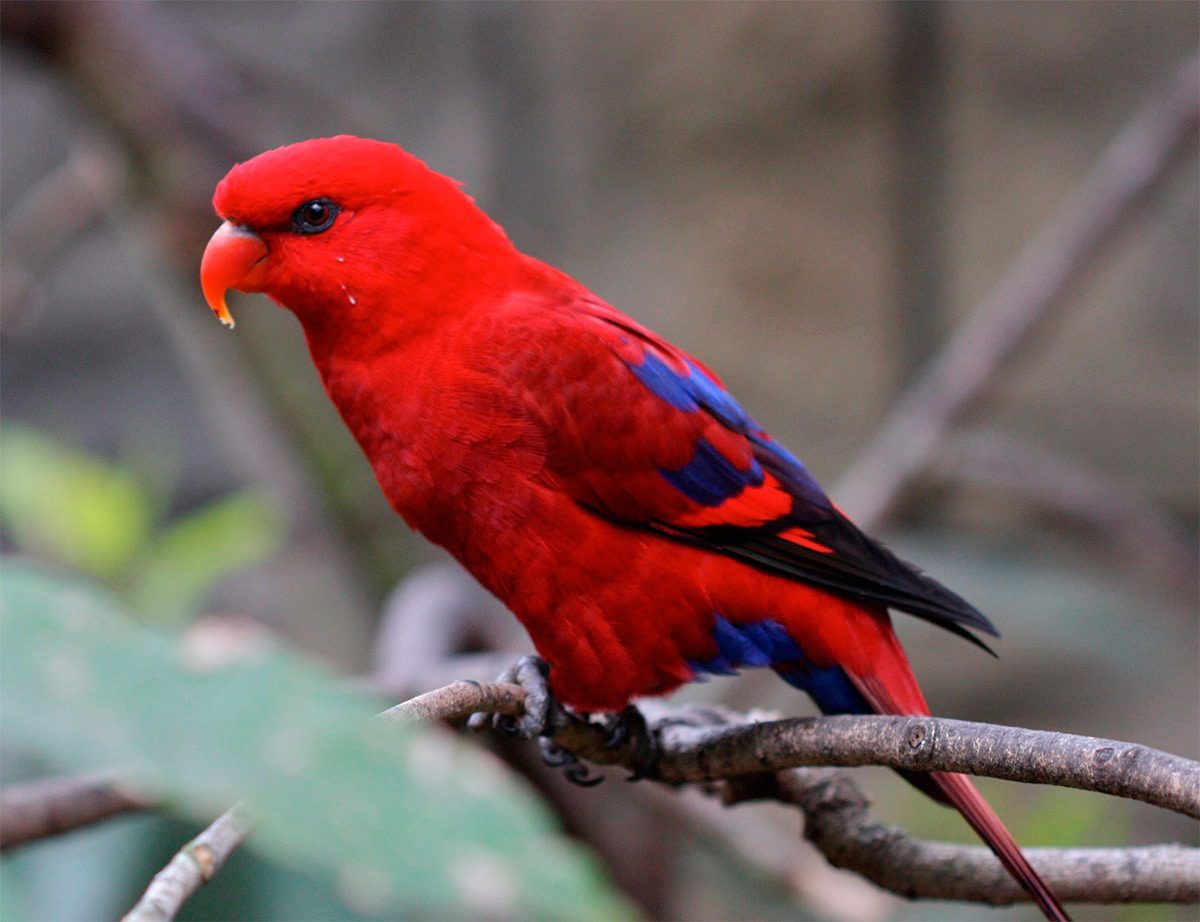
The head and the neck of the Red Lory (Eos bornea) are entirely of a deep red color.
In the adult the primary feathers are black with a large red mirror. The feathers tertiary and the coverts are of color blue. The joint of the feathers of the helmsman they are reddish-brown. The irises they are red, legs grayscale and the bill dark orange.
The immature they tend to be more off than their parents coloring. They show the feathers tertiary grey, lightly stained blue. The ear-coverts Sometimes it tinges of blue. Times, the area of the vent and the thighs it infiltrates with small stains blue. The feathers of the abdomen often carry some edges blue dark. They have the irises brown.
Not exists no sexual dimorphism visible although the males tend to be more corpulent that the females.
- Sound of the Red Lory.
Description 2 subspecies
-
Eos bornea bornea
(Linnaeus, 1758) – Nominal.
-
Eos bornea cyanonotha
(Vieillot, 1818) – The Red of his plumage is much more dark almost brown.
Habitat:
They are mostly primary forests, in the wooded areas during regeneration, Forest Hills, coconut plantations, in abandoned gardens and mangroves.
They are mainly in coastal areas, What does not climb up to 900 m in the island of Ceram and up 1.800 m in the of Buru.
Throughout its area, the Red Lory are fairly common, However, some populations are more dispersed around the villages, since they are very cautious towards humans.
Behavior:
The Red Lory they live in pairs or in small groups, but sometimes you can observe large flocks of 50 individuals.
They are birds noisy and quite easy to observe, as they often fly above the canopy attracted by the red flowers of the tree of coral (Erythrina).
They have a fast and direct flight and when moving, make your buzz due to its quick flapping.
In the Kai Islands, their movements are common: all days, they cross the arm of sea that separates the different islands flying rapidly and at high altitude.
During the rest hours that occur at noon, the Red Lory they spend most of their time smoothing their feathers in the shade of a tree. Probably, This practice is designed to strengthen marital ties. Parties that enjoy priority are the head and neck; as you can not reach these areas with its beak, you will always need your partner collaboration. The “patient” that is subject to this preferential treatment seems to express a deep sense of satisfaction.
Reproduction:
The couples begin to look for the location of the nest between the months of August and September. It is located high in a big tree.
In mid-December some young leaving the nest have observed.
As in all loris, the nesting period is very long and hard 7 to 9 weeks.
In captivity, the Red Lory puts 1 or 2 litters per year. Each spawning has usually 2 white eggs that are incubated for a period ranging from 24 to 26 days.
Food:
In their natural habitats, the Red Lory feed of nectar, pollen, fruits and insects of fashion casual.
Your food › seem to be them flowers of the trees of the species Eugenia and Erythrina.
All the Loris they have a language that is especially suited, with a brush tip made up of elongated papillae. This characteristic allows birds to collect pollen from flowers and compress it in a suitable way for swallowing.. They play an important role in the pollination of flowering plants and trees.
Distribution:
Size of the area of distribution (reproduction / resident): 57.900 km2
The Red Lory they have a very restricted distribution area. They live South of the Moluccan Islands, halfway between Sulawesi and the western end of New Guinea.
Distribution 2 subspecies:
-
Eos bornea bornea
(Linnaeus, 1758) – Nominal.
-
Eos bornea cyanonotha
(Vieillot, 1818) – Is located in the island of Buru.
Conservation:
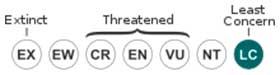
• Current IUCN Red List category: Least concern
• Population trend: Decreasing
This species has a very large range, and therefore not approaching the thresholds for Vulnerable according to the range size criterion.
The population is suspected of being in decline due to unsustainable levels of exploitation.
The species has undergone intense trade from 1981, When it began trading in Appendix II. 99.834 wild-caught specimens have been recorded in international trade, Although none from 2000 (UNEP-WCMC trade database, January 2005 CITES).
"Red Lory" in captivity:
This lori is considered one of the most widespread within poultry. It's an interesting bird, robust and easy of play, ideal for a start in the world of the loris. It also has a very attractive red color; It playful and is easy for tame.
It is a great conversationalist. Some have entire sentences in their vocabulary. Unfortunately, his voice is sometimes very strong, with a high sharp squeal. Most are docile, even at maturity. They can be prolific breeders and are fairly easy to find as hand-raised pets..
Too much protein in the diet can lead to gout., a type of arthritis that crystals are deposited in the joints. May be a bit uncomfortable due to liquid diet.
Alternative names:
–
Red Lory, Buru Red Lory (ingles).
– Lori écarlate, Lori rouge (French).
– Rotlori (German).
– Lóris-vermelho (Portuguese).
– Lori Rojo (español).

scientific classification:
– Order: Psittaciformes
– Family: Psittaculidae
– Genus: Eos
– Scientific name: Eos bornea
– Citation: (Linnaeus, 1758)
– Protonimo: Psittacus borneus
Images “Red Lory”:
Videos "Red Lory"
——————————————————————————————————–
“Red Lory” (Eos bornea)
Sources:
– Avibase
– BirdLife.org
– mundoexotics
– Oiseaux.NET
– Photos:
* A Red Lorry at Taronga Zoo, Sydney, Australia by Navin – wikimdia
* Red Lory (Eos bornea) looking upwards by shahram sharif – Wikimedia
* Red Lory (Eos bornea) at Singapore Zoo by Joost Rooijmans – Wikimedia
* Red Lory – KL Bird Park – Malaysia by diego_cue – Panoramio
* Moluccan Red Lory – Parrots Australia
– Sounds: BAS van Balen (Xeno-canto)