Content |
|---|
Description:
21 cm. and a weight of 100-130 g..
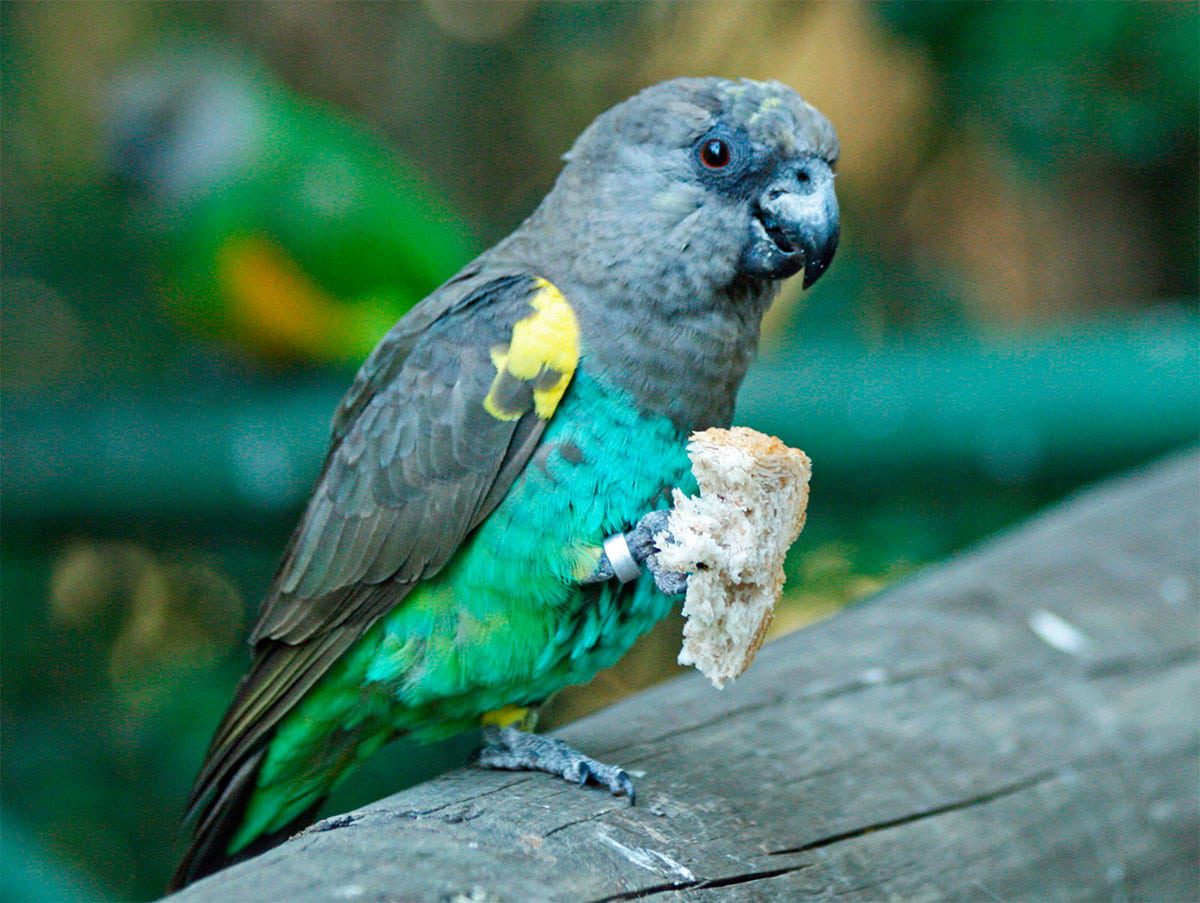
The Meyer's Parrot (Poicephalus meyeri) has the forecrown, lores, cheeks, ear-coverts and ash Brown nape; crown bright yellow. The mantle feathers ash brown edges blue or cyan dye in some birds; scapulars brown ash, some individuals show Tips blue or greenish blue; rump bright turquoise or teal; uppertail-coverts green. Outermost children and wing-coverts above bright yellow, other variables showing green tints, especially towards Tips. The primaries and high schools ash Brown with paler narrow margins to vane outer.
feathers of the wings, undertail, bright yellow in some birds, but grayish-brown in larger in other. The chin, the throat and top of the chest brown ash; remaining chest and belly turquoise or teal; the thighs yellow; undertail- coverts turquoise blue or greenish blue. Tail brown ash.
Bill dark gray or black; cere black; irises orange-red; periophthalmic skin desnuda negruzca; legs blackish.
Both sexes similar.
Youth more generally greenish brown. No yellow in the crown or the the thighs and the yellow area in the wings, at the top, It is lower. Wing coverts, undertail, green and brown with little or no yellow. The underparts más greenish. Iris dark brown.
- Sound of the Meyer's Parrot.
Subspecies description
Habitat:
The Meyer's Parrot It is found in a wide variety of forest habitats from dry savannah to gallery forest and second-growth riparian forest around crops.. Observed in forests dominated by Terminalia laxiflora and Doka Isoberlinia, thickets Combretum acacia grasslands; as well Brachystegia and riparian forests Syzygium-Adina.
Avoid lowland rainforests in the basin Congo and other humid forests including areas of the eastern highlands of the district of Zimbabwe and Cork in Malawi.
Show a preference for the tallest trees in the drier savannah habitats – in particular specimens Adansonia. They may be confined to gallery forests in the drier parts of their range and are generally found in close proximity to water..
Where it is sympatric with the Red-bellied Parrot (Poicephalus rufiventris), the Meyer's Parrot It is limited to riparian forests.
In Kenya, which it is largely in areas with higher annual rainfall 500 mm.
Sometimes observed in suburban areas.
In general, in the lowlands at altitudes of 1,250m in Ethiopia, 2.200m in east Africa and 1.500 meters in the highlands of eastern Zimbabwe.
They are distributed in pairs or small groups 3-5 birds (possibly couples); until 50 birds may congregate in areas where there are food sources in breeding season. Roosts in tree cavities. Usually shy and cautious.
Reproduction:
Solitary nesters in tree cavities at a height between 3 and 10 meters above the ground, during the season, dry (for example Mar-June Zimbabwe, from May to September Zambia and Malawi, July Angola and in December or January Sudan).
The implementation is of 2 to 4 eggs.
Food:
The diet of the Meyer's Parrot fruit is, nuts and seeds, including Ficus, Sound abyssinica, Uapaca nitidula, Monotes glaber, Combretum, Grewia, Sclerocarya, Pseudolachnostylis, fruit of the great growth and riparian trees afzelia quanzensis and Melia volkensii, grown oranges and flowers Schotia brachypetala.
The pulp of the fruit is less important than the hard seeds and the arbolados share, the Meyer's Parrot is one of the few species consume seeds Brachystegia and other leguminous trees.
They also consume grain and is considered as crop pests in some areas.
Eat some insects, including caterpillars.
May vary widely from area to area in search of food during droughts.
Distribution:
Size of the area of distribution (reproduction / resident): 5.840.000 km2
The Meyer's Parrot They are distributed throughout the central and eastern Africa. From the North-East of Cameroon and South of Chad through the North of the Central African Republic, center Sudan and South and West Ethiopia, to the south through Uganda, Kenya Western, east of Democratic Republic of the Congo and Tanzania, coming to Malawi, Zambia, Angola, Northeast of Botswana, Zimbabwe, western end of Mozambique, Namibia and northeast of Sudafrican republic.
A wild population, possibly, is distributed in the eastern province of Cape Town, Sudafrican republic, even if they are probably extinct.
Nomad in some areas during periods of drought, when they distributed outside the normal range; normally resident with local movements.
Distribution Subspecies
Conservation:
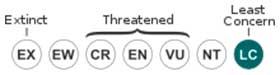
• Current Red List of UICN: Least concern
• Population trend: Stable
The Meyer's Parrot It, in general, common to very common and is the most abundant parrot in some parts of its range (for example, Zimbabue and Angola), although few in other areas and absent from some apparently suitable habitats.
Its population has declined in some parts (for example Transvaal) where is thought to be a result of habitat destruction. I also persecuted in some locations due to crop damage (for example, in the center of Zambezi because of the damage inflicted to the maturation of the berries Boolean).
"Meyer's Parrot" in captivity:
The Meyer's Parrot, is a bird common in captivity, quiet, tender, easy to carry and with a stable temperament.
They are birds social and they tend to bond with everyone in the family, unlike other species that may prefer one person to another. In general, No es voluble – once you liked someone, the person is a friend for life.
They are not as dependent on humans for entertainment as most parrots and therefore no son tan demanding.
They like being handled and petted on the head and neck. A hand-fed hatchling will develop into a fluffy adult if treated properly, and it is not prone to bite, although it may provide a powerful bite if provoked.
You can learn a few words, although They are not known for their ability to speak. They can learn to whistle, making noises, and occasionally they will offer strong squeals. Fortunately, They are not likely to scream or make loud squawks, making good birds for apartment life. Some individuals learn household noises, as the beep of the microwave.
The Meyer's Parrot they are ready to breed at the age of 3 to 4 years and reproduce easily in captivity.
With regard to its longevity, according to sources, Meyer lived a parrot 34,2 years in captivity.
Alternative names:
– Meyer’s Parrot, Brown Parrot (English).
– Perroquet de Meyer, Perroquet brun, Youyou de Meyer (French).
– Goldbugpapagei, Goldbug-Papagei (German).
– Papagaio de Meyer, Papagaio-de-meyer (Portuguese).
– Lorito de Meyer (español).
scientific classification:

– Order: Psittaciformes
– Family: Psittacidae
– Genus: Poicephalus
– Scientific name: Poicephalus meyeri
– Citation: (Cretzschmar, 1827)
– Protonimo: Psittacus Meyeri
Images “Meyer's Parrot”:
Videos "Meyer's Parrot"
————————————————————————————————
“Meyer's Parrot” (Poicephalus meyeri)
Sources:
– Avibase
– Parrots of the World – Forshaw Joseph M
– Parrots A Guide to the Parrots of the World – Tony Juniper & Mike Parr
– Birdlife
– Photos:
(1) – A Meyer’s Parrot at Birds of Eden, Western Cape, South Africa. It is eating what looks like a piece of bread By SandyCole (mailto:sandyc@dicksandy.org) (Own work) [CC BY-SA 3.0 or GFDL], via Wikimedia Commons
(2) – Two Meyer’s Parrots in Zimbabwe By Oce Eeco (DSC_0108Uploaded by snowmanradio) [CC BY 2.0], via Wikimedia Commons
(3) – Brown parrot also known as Meyer’s Parrot (Poicephalus meyeri) by Papooga – Flickr
(4) – A Meyer’s Parrot near Kwara Camp, North-West District, Botswana By Benjamin Hollis from Seattle, WA, USA (Meyer’s parrotUploaded by snowmanradio) [CC BY 2.0], via Wikimedia Commons
(5) – A Meyer’s Parrot in Akagera National Park, Rwanda By Lip Kee Yap [CC BY-SA 2.0], via Wikimedia Commons
– Sounds: Derek Solomon (Xeno-canto)