Content |
|---|
Description “Marigold Lorikeet”:
26 cm.. length and a weight between 100-157 g..
The Marigold Lorikeet (Trichoglossus capistratus) has the forecrown, the cheeks and chin, dark blue; and the rest of the head It is green with a broadband yellow-green in nape (part posterior of the neck). The upper breast is yellow with green narrow edges feathers. Underwing-coverts are yellow with scattered orange marks. Males may have some red on their edges. The abdomen is dark green. Their peaks They are hooked.
The males and females and players seem to depend on DNA or endoscopic sexing to determine gender.
Taxonomic status:
This taxon is considered a subspecies of Trichoglossus [haematodus, rosenbergii, moluccana, forsteni, capistratus, weberi] (sensu lato) by some authors.
- Sound of the Marigold Lorikeet (1).
(1) Some species are under extreme pressure because of traps and harassment. So, the open availability of high-quality recordings of these species may further worsen the problems, this being the reason why downloading these recordings is off. In conclusion, recorders themselves are free to share these files on xeno-canto, but they will have to approve access to these recordings.
We do not take this action lightly, and we wish it wasn't necessary, but we are convinced that the negative impacts of offering easy access to these recordings outweigh the benefits. To access these recordings, You can contact directly with the recorder.
Description 3 subspecies:
-
Trichoglossus capistratus capistratus
(Bechstein, 1811) – Nominal.
-
Trichoglossus capistratus flavotectus
(Hellmayr, 1914) – Head green with purple/blue veins on the forecrown up to the cheeks; variability of yellow to deep orange in chest; neck wide and yellow; abdomen dark green to green / black; underwing-coverts yellow with orange markings variables.
-
Trichoglossus capistratus fortis
(Hartert, 1898) – Head black/brown with purple/blue veins on the forecrown up to the cheeks; lores , throat, line from top to back of the eyes and occiput, green; chest bright yellow with orange but not barred / red marks; abdomen dark green, with occasional shades blue / black; underwing-coverts yellow.
Habitat “Marigold Lorikeet”:
The Marigold Lorikeet They are in mixed flocks with other parrots; small and noisy groups. Nomads, since they depend on flowering trees. It perches communally in groups of hundreds of birds.
It is more common in lowlands, but it is up to altitudes of 2400 m. Wide variety of areas including settlements, forests, coconut plantations, Savanna, eucalyptus forests and mangroves, including dry forest Roti.
Reproduction “Marigold Lorikeet”:
Total of 21 nests found in Sumba between late August and early October 1992, all cavities in large trees (principalmente deciduous).
Food “Marigold Lorikeet”:
Few specific dietary data, but presumably similar to Trichoglossus haematodus and it is known to take nectar and pollen from native trees, as well as figs and insects.
Distribution “Marigold Lorikeet”:
Extension of the distribution (breeding/resident): 171.000 km2
The Marigold Lorikeet It is a species of parrot endemic to the islands of Southeast Asia Sumba, Roti, Wetar and Blend (Indonesian) and Timor (Indonesia and East Timor).
Distribution 3 subspecies:
-
Trichoglossus capistratus capistratus
(Bechstein, 1811) – Nominal. Observed in Timor.
-
Trichoglossus capistratus flavotectus
(Hellmayr, 1914) – It is located on the islands Wetar, Romang and Blend, to the northeast of Timor.
-
Trichoglossus capistratus fortis
(Hartert, 1898) – Is located in Sumba, Lesser Sunda Islands.
Conservation “Marigold Lorikeet”:
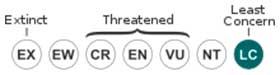
1. Current red list category of the UICN: Least concern.
2. The population trend: Decreasing.
3. Population size : —.
Rationale for the Red List category
Although this species may have a restricted range, It not believed to approach the thresholds Vulnerable under the criterion of size range (Scope of the presence <20.000 km2 combined with a decreasing area size or fluctuating distribution, extension / habitat quality, or population size and a small number of places or severe fragmentation).
While the trend of the population seems to be decreasing, the decline is not believed to be rapid enough to approach the Vulnerable thresholds according to the population trend criterion (decrease of more than 30% in ten years or three generations).
The population size has not been quantified, but it is not believed to approach the thresholds Vulnerable under the criterion of population size (<10.000 mature individuals with an estimated> 10% continuous decline in ten years or three generations, or with a specific population structure). For these reasons, the species is assessed as Least concern.
Justification of the population
Global population size has not been quantified, but the species is described as common in Timor (pit et to the. 1997).
Justification trend
They suspected that the population is declining due to unsustainable levels of exploitation.
Threats
The species has been the subject of a intense trade: from 1981, When it was included in the Appendix II of the CITES, they have been 100.388 individuals captured in international trade (UNEP-WCMC CITES Trade Database, January 2005).
In captivity:
It's one of the lori rainbow less noisy although uncommon in captivity except for Dili (Capital of Timor Oriental), where it is quite common. Its longevity It 20 years en libertad, 15-25 years in captivity.
Alternative names
– Marigold Lorikeet, Rainbow Lorikeet (Marigold) (English).
– Loriquet à tête bleue (harnaché), Loriquet à tête bleue [capistratus], Loriquet d’Edward, Loriquet harnaché (French).
– Blauwangenlori, Timor-Allfarblori (German).
– Periquito-arco-íris-de-timor, Lóris-de-timor (Portuguese).
– Lori de Caléndula, Lori embridado, Lori Arcoiris [capistratus Group] (español).
scientific classification:

– Order: Psittaciformes
– Family: Psittaculidae
– Gender: Trichoglossus
– Scientific name: Trichoglossus capistratus
– Subpoena: (Bechstein, 1811)
– Protonimo: Psittacus capistratus
Images “Marigold Lorikeet”:
Videos "Marigold Lorikeet"
“Marigold Lorikeet” (Trichoglossus capistratus)
-
Sources:
1. Avibase
2. Parrots of the World – Forshaw Joseph M
3. Parrots A Guide to the Parrots of the World – Tony Juniper & Mike Parr
4. Birdlife
Photos:
(1) – Trichoglossus (haematodus) capistratus group by Matthew Hoelscher from Doral, FL, USA [CC BY-SA 2.0], via Wikimedia Commons
(2) – A Marigold Lorikeet at Denver Zoo, Colorado, USA by William Andrus from Greeley, CO, USA [CC BY 2.0], via Wikimedia Commons
(3) – A Marigold Lorikeet at the Aquarium of the Pacific, Long Beach, California, USA by Greg Goebel from Loveland CO, USA [CC BY-SA 2.0], via Wikimedia Commons
(4) – Photo by David J. pole [CC BY-SA 4.0], via Wikimedia Commons
(5) – Edward’s Lorikeet (Trichoglossus haematodus capistratus) by coracii – Flickr
– Sounds: travertine Cooleman, XC179171. accessible www.xeno-canto.org/179171