Content |
|---|
Description:
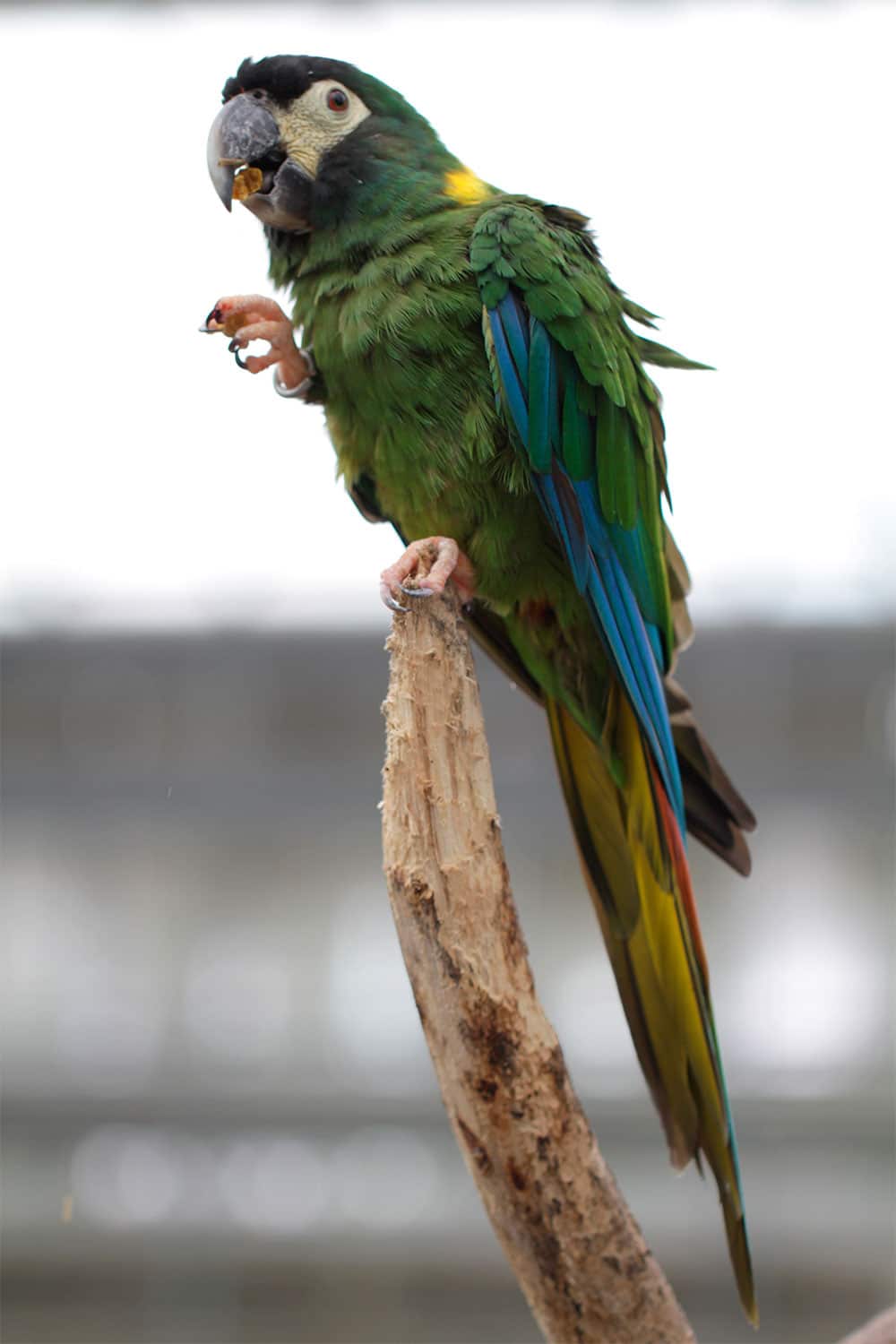
Of 37 to 45 cm. length and a weight between 240 and 250 g..
The Yellow-collared Macaw (Primolius auricollis) already it was described by American ornithologist John Cassin in 1853.
Similar to the Blue-headed Macaw, differs by a characteristic Yellow collar dorado, most notable in the area of the nape. This thin yellow line of feathers surrounding the back of the neck, It is that gives this species its name.
Previously considered you inside of the genre “ARA” for having a bare face of feathers and was also scientifically known as “propyrrhura Macaw”
It is a small Macaw; has the forecrown, the feathered portion of the cheeks and the front of the crown dull blackish-brown color, becoming a blue-green shade at the rear of the crown and both sides of the neck. The neck is covered with a large golden yellow necklace. All upperparts are green with blue markings in some feathers.
The small and medium-sized coverts are green. The alula and primary coverts they are completely blue. The primaries are blue, the secondaries are green with a strong blue tint in the vane outer. The underwing-coverts are, in its entirety, olive yellow, with the exception of the lower part of the flight feather It is yellowish.
The underparts are green. Upper, the central tail feathers are reddish brown at the base, in the middle of green and blue at the tip. The outer tail feathers they are mostly blue. The bottom of the tail is opaque yellow.
The bill is blackish with a tone slate finish. The bare skin about lores and cheeks It is white with a straw tone clear. The irises are orange, legs pink meat.
Both sexes similar.
The youth they resemble their parents. But, they have a bill grey with a white Peak; irises grayscale and the legs pale grey. The immature you have the collar area of the nape reddish.
- Sound of the Yellow-collared Macaw.
Habitat:
The Yellow-collared Macaw they attend a wide variety of habitats from forests. They are found in the humid tropical forests that cover the foothills of the Andes, but also in dry areas of deciduous and grasslands with scattered trees. They are also present in the tree edges and savannas.
Unlike most parrot species, the Yellow-collared Macaw support very well the profound changes occurring in their habitat.
They are relatively common in the waste groves situated in the middle of farmland and around major urban centres.
Mainly noted below 600 m, to 1.700 metres above sea level in the Northwest of Argentina.
Usually they live in pairs or in small groups, even outside the breeding season. Larger meetings may have place when food is abundant or when gather in the dormitories at night. Within these large herds, the matched pairs are less visible than other species of macaws.
They feed on trees and shrubs, Although they occasionally do on land
Reproduction:
The season of nesting is in December in Argentina. The nest It tends to be located in the cavity of a tree, sometimes up to 20 meters above the ground. The spawning usually included in 2 to 4 eggs.
In captivity, the incubation lasts a few 23 days. The reproductive cycle is particularly long, since the young leave the nest at 7 weeks, after the hatching.
Food:
The Yellow-collared Macaw they have a vegetarian regimen that includes fruits Byrsonima, flowers Erythrina, Ficus, corn and seeds Tomentosa Guazuma, Spondias lutea, Adelia mesembinifolia, Astronium Badi and A. urundeuva.
Distribution:
Size of its range (breeding/resident ): 1.950.000 km2
Endemic to the center of South America. The distribution of the Yellow-collared Macaw includes the Northwest of Argentina, in the East of Jujuy and North of Salta (reports of Missions and Formosa they are not correct) going northward through the East and North of Bolivia, in the departments of Santa Cruz, Beni and Tarija, is also distributed by the North of Paraguay, mainly to the West of the Paraguay River, but largely absent in the drier areas of the Chaco.
Extend across the southwest of Mato Grosso and Mato Grosso from the South, in Brazil, where its northern and eastern limits are unclear; They are also distributed (possibly different) in West Goiás, Northeast of Mato Grosso and Southeast end of For, where there are reports of birds in and around the The Bananal island.
Mostly residents, Although apparently, seasonal movements in some areas.
In general is a common macaw and he persists in areas where significant habitat modification has taken place. Scarcer at the edge of its range in Paraguay.
They have been the subject of international trade, but its population does not seem to be affected by the capture.
Conservation:
State of conservation ⓘ |
||
|---|---|---|
 Minor Concern ⓘ
(UICN)ⓘ
Minor Concern ⓘ
(UICN)ⓘ
| ||
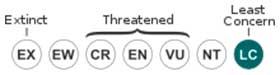
• Red List category of the UICN current: Least concern
• Population trend: Growing
The species is not threatened at the global level. Global population size has not been quantified, but this species is described as “quite common”
At the beginning of the Decade of 1980, in Bolivia, the capture of birds for aviaries reached the alarming figure of over of 3.200 birds per year. Fortunately, the traffic is prohibited from 1984.
It is considered rather low, the population of this species in Paraguay and North of Argentina, But in recent years the trend has reversed., and the species has colonized new areas.
"Yellow-collared Macaw" in captivity:
Quite common, above all in the EE.UU, less frequent in other parts.
Charming, clever, and comedian, These small macaws offer all the personality of a great green Macaw in a smaller size, being more affordable and easier to take care of. It is an extremely Intelligent and easy to train.
Many Yellow-collared Macaw are gifted talkers, and they are able to say several words and phrases. Some owners have pointed out that this little Macaw is able to speak more clearly than other larger species. Even so, our Macaw should not be purchased only by his ability to speak; that ability is never a guarantee.
Reproduce well in captivity. The breeding season It is usually in the spring and early summer, Although some couples are played almost throughout the year. The implementation size It is usually of two to four eggs, but sometimes more. The incubation period is of 23 to 27 days. Some additional high fat seeds, as the Sunflower seed, should be added to the diet during the breeding season to stimulate reproduction.
Marriage bonds are strong, but not necessarily for life.
Alternative names:
– Yellow-collared Macaw, Cassin’s Macaw, Golden-collared Macaw, Golden-naped Macaw, Yellow collared Macaw, Yellow-naped Macaw (English).
– Ara à collier jaune, Ara à nuque d’or (French).
– Halsbandara (German).
– ararinha, Maracanã-de-colar (Portuguese).
– G. Acollarado, Guacamayo Acollarado, Maracaná cuello dorado, Maracaná de Cuello Dorado (español).
– Parabachi de cuello amarillo, Maracaná de cuello dorado (Bolivia).
– Marakana (Guarani).
– Maracaná cuello dorado (Paraguay).
scientific classification:

– Order: Psittaciformes
– Family: Psittacidae
– Genus: Primolius
– Scientific name: Primolius auricollis
– Citation: (Cassin, 1853)
– Protonimo: Ara auricollis
Images Yellow-collared Macaw:
Videos "Yellow-collared Macaw"
Yellow-collared Macaw (Primolius auricollis)
Sources:
– Avibase
– Parrots of the World – Forshaw Joseph M
– Parrots A Guide to the Parrots of the World – Tony Juniper & Mike Parr
– Birdlife
– Photos:
(1) – A Golden-collared Macaw at Kakegawa Kacho-en, Kakegawa, Shizuoka, Japan By Takashi Hososhima from Tokyo, Japan (A bird of dexterityUploaded by snowmanradio) [CC BY-SA 2.0], via Wikimedia Commons
(2) – Two Golden-collared Macaws (also known as Yellow-collared Macaws) at the Pana’ewa Rainforest Zoo, Hawaii, USA By Pat McGrath from Lihue, U.S.A. [CC BY-SA 2.0], via Wikimedia Commons
(3) – Golden-collared Macaw (also known as the Yellow-collared Macaw). A pet parrot By rebeccakoconnor [CC BY 2.0], via Wikimedia Commons
(4) – Golden-collared Macaw (also called Yellow-collared Macaw) parents with a juvenile By Benutzer:Robert01 on German wiki (Bild:Goldnackenaras on German wiki.) [CC BY-SA 3.0 of], via Wikimedia Commons
(5) – Golden-collared Macaw (also known as the Yellow-collared Macaw); two captive By TJ Lin [CC BY-SA 2.0], via Wikimedia Commons
(6) – Ara primoli = Primolius auricollis (copy of Gray's Heritage Library (France) by Francis de Laporte de Castelnau [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons
– Sounds: (Xeno-canto)






