Content |
|---|
Description:
90 to 100 cm.. of length and a weight of 1,5 to 1,7 kg.
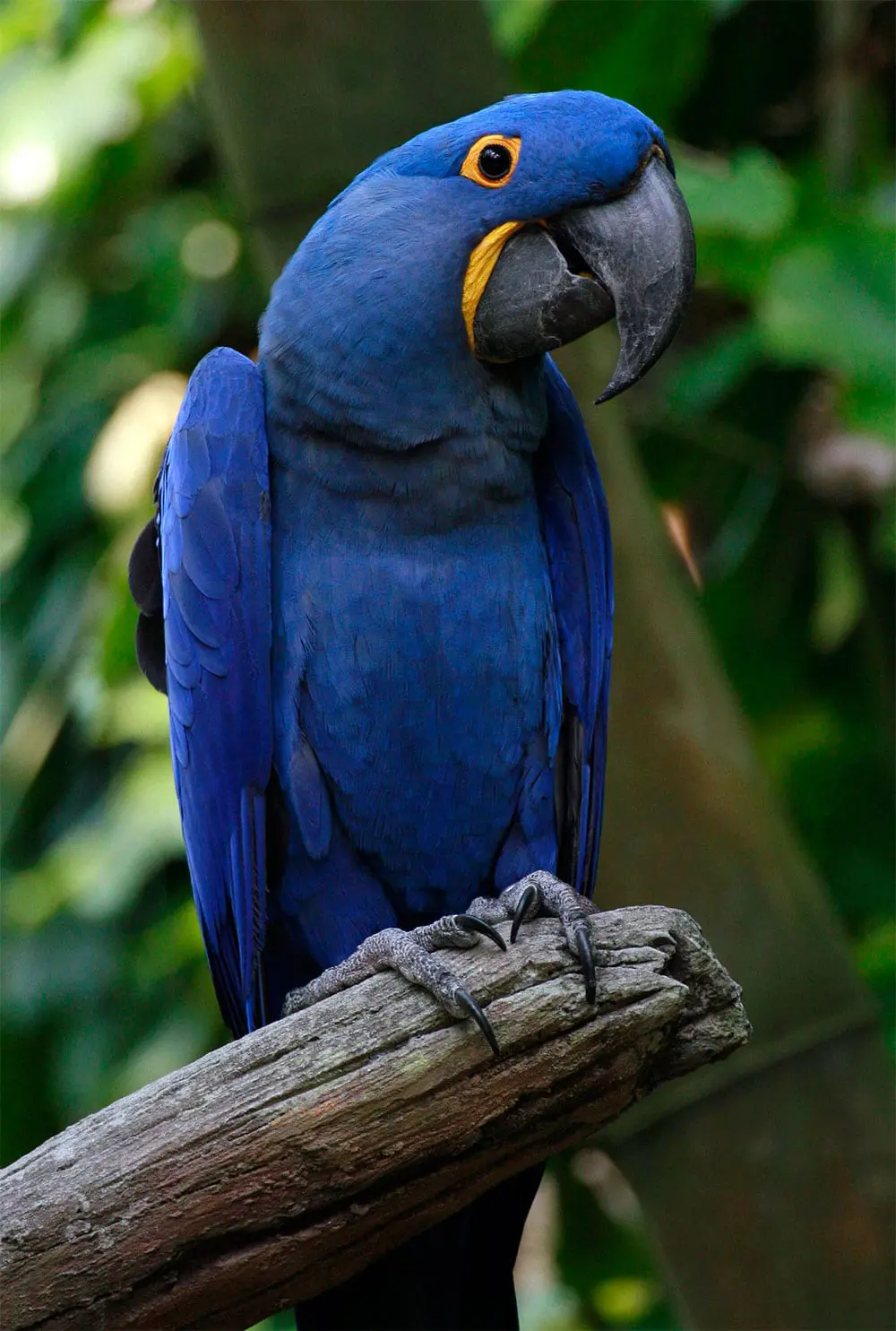
The Hyacinth Macaw (Anodorhynchus hyacinthinus) is the largest parrot; has a distinctive coloration, mostly blue intense, with different colors. Wings and tail below black. The basis of the bill and periocular ring, naked and yellow. The tail is very long, and its powerful bill Black is deeply curved and pointed.
The species Anodorhynchus glaucus, similar but smaller, extinct in the early 20th century, It may have been present in Bolivia.
- Sound of the Hyacinth Macaw.
Habitat:
The Hyacinth Macaw take advantage of a great diversity of habitats rich in various species of Palm trees with large seeds, of which feeds.
In the Brazilian Amazon avoid areas of more moisture, preferring lowland forests and seasonally wet formations with clear zones. In the drier parts of the northeast of Brazil inhabits areas of Plateau cut by Rocky valleys, steep with closed deciduous woodland, gallery forest and swamps with Mauritia flexuosa.
In the the Pantanal region birds frequent gallery forest with palm trees in areas covered with wet grass.
Apparently performs migratory movements.
Usually seen in pairs, family groups or small flocks (usually up to 10); much larger flocks reported before the decline.
Reproduction:
They nest in large tree hollows, in cracks in rocks from cliffs in the northeast of Brazil or in moriche or aguaje (Mauritia).
The favorite for nesting trees in the Mato Grosso, Brazil, include Enterolobium and Sterculia striata. In Northeast Brazil, the nest is located in Palms Mauritia dead or on cliffs.
They usually put one or two eggs, although only one young usually survives if the second egg hatches a few days after the first, since the smaller calf cannot compete with the larger for food.
The incubation period lasts about a month, and the male will assist his partner while she incubates the eggs.
Young people remain with their parents up to three months of age. They reach maturity and begin to play on the seven years.
The breeding season is from August to December, Maybe a little later in areas of pantanal.
Food:
The diet Hyacinth Macaw consists mainly of nuts, locally available of various Palms, including (on Amazonia) Maximiliana regia, Orbignya martiana and Astrocaryum, in the northeast of Brazil, of the Syagrus coronata and Orbignya eicherir, in areas of wetlands of Bone collectors and Acrocomia.
The palm nuts they take them from the own soil or plant (especially after a fire or when available as undigested remains in livestock droppings).
Other fruits that have information are the from the Ficus sp., as well as aquatic molluscs Pomacea.
Birds drink liquid from green palm fruits.
Distribution:
Its distribution includes the Centre of South America, Perhaps in several spacious separate areas.
In the Amazonia in For from the Tapajos River, to the East of the basin of the Tocantins River, extending to the South, possibly to the Northwestern area of Tocantins. At least before present North of the Amazon River (in Amapá, amazon and Roraima, Brazil) and perhaps some specimens can still inhabit, Although there is no known recent records.
Distributed, as well, through the Northeast interior of Brazil, more or less centered on the Microregion of the Chapadas das Mangabeiras in the union between Maranhão, Piauí, Goiás and Bay, Brazil (the region Gerais).
A third important population focuses on habitats wetlands of the upper basin of the Paraguay River in the southwest of Mato Grosso, Mato Grosso do Sul, Brazil, and extending into the adjacent area of the East of Bolivia and North end of Paraguay.
Reported as probable for the Mapori River to the South-East of Colombia (Vaupés).
Movements General residents but perhaps seasonal in the Amazon in relation to the ecology of the plants on which they feed.
The territory between the three current major distributions, can still be busy even though recent trends given, They seem to indicate that this seems unlikely.
Formerly common in some areas (for example, Mato Grosso). Now they are rather unevenly distributed, with the recent and likely declines continuous in its population due mainly to the illegal trade internal and to the smaller, but significant, international market of live birds. Also hunted for its feathers (especially Pari) and as food. Declining in some areas (for example Eastern Amazonia), because of the alteration or loss of habitat.
Total estimated wild population in 3000 (1.992). CITES Appendix I.
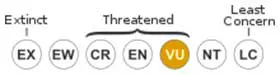
VULNERABLE.
Conservation:
• Current Red List of UICN: Vulnerable
• Population trend: Decreasing
The Hyacinth Macaw It has been subjected to a massive illegal trade. At least 10.000 birds were captured in the wild, in the decade of 1980, with a 50% destined to the Brazilian market (Mittermeier et to the. 1990).
Among 1983-1984, more than 2.500 birds were moved out of Black Bay, Paraguay, with others 600 extra at the end of 1980 (J. Pryor in litt., 1998). Although these numbers are now much smaller, illegal trade continues (for example 10 bird went through a pet market in Santa Cruz, Bolivia, in August 2004 until July 2005, where the birds were changing hands for 1.000 $ US and went to Peru [Herrera and Hennessey 2007]). More recently it has been noted that there appears to be almost no illegal trade in this species in Bolivia (B. Hennessey in litt. 2012).
Through its area of distribution, There is something of the local game for use as food and for its feathers.
In the Amazon, habitat loss has occurred for cattle ranching and hydroelectric power systems in the rivers Tocantins and Xingu.
In the Pantanal, only the 5% trees S. apetala have suitable cavities (Guedes 1993, Johnson 1996). Young trees are used as food for livestock and burned by frequent fires (Newton 1994).
The Gerais is it being quickly transformed by mechanized agriculture, ranching and plantations of exotic trees (Conservation International 1999).
In Paraguay, the preferred habitats of the Hyacinth Macaw are considered seriously threatened (N. Kochalka Lopez in litt. 2013) and the Paso Bravo National Park suffering from illegal logging.
Conservation Actions Underway:
-
– CITES Appendix I and II, protected under Brazilian and Bolivian law and prohibition of exports from all countries of origin.
– Many landowners in the Pantanal (more and more in the Gerais) they do not allow hunters on their property.
– There are several studies long-term and conservation initiatives (for example. Anon 2004).
– In the Refuge Caiman ecological in the Pantanal, the Hyacinth Macaw Project has used artificial nests and hatchling management techniques and raised awareness among farmers (Anonymous 2004).
Conservation Actions Proposed:
-
– Study of the range, the current status of the population and the scope of the negotiation of the different parts of its area of distribution (Snyder et to the., 2000).
– Assess the effectiveness of artificial nesting boxes (Snyder et to the., 2000).
– To enforce the legal measures that hinder trade.
– Experiment with ecotourism in one or two sites to encourage donors (Snyder et to the., 2000).
"Hyacinth Macaw" in captivity:
Rare up to 1970; then, starting at 1980, increased considerably in number of captive birds due to increased breeding.
Despite the prohibitions, many of these Macaws they are still trading at high prices (10.000 euros or more), due to its beauty and ease to mimic human language.
Rearing this species can be difficult and, Unfortunately, many chicks die each year in inexperienced hands.
From this page we strongly preserve these beautiful birds in their natural environment, sincerely not us seems reasonable to his tenure as a pet.
Alternative names:
– Hyacinth Macaw, Blue Macaw, Black Macaw (English).
– Ara hyacinthe (French).
– Hyazinthara, Hyathinzara (German).
– Arara-azul-grande, arara-azul, arara-hiacinta, arara-preta, arara-roxa, arara-una, canindé (Portuguese).
– arara-azul, Arara-azul-grande, arara-hiacinta, arara-preta, arara-roxa, Ararauna, arara-una, canindé (Portuguese (Brazil)).
– Guacamayo Azul, Guacamayo Jacinto, Papagayo azul (español).
– Jacinta azul, Paraba azul (Bolivia).
– Vihina (Desana).
– Kaheta (Carijona).
– Guaía-hovy (Guarani).
– Arara-úna (Tupi Guaraní).

scientific classification:
– Order: Psittaciformes
– Family: Psittacidae
– Genus: Anodorhynchus
– Scientific name: Anodorhynchus hyacinthinus
– Citation: (Latham, 1790)
– Protonimo: Psittacus hyacinthinus
Images Hyacinth Macaw:
Videos "Hyacinth Macaw"
“Hyacinth Macaw” (Anodorhynchus hyacinthinus)
Sources:
– Avibase
– Parrots of the World – Forshaw Joseph M
– Parrots A Guide to the Parrots of the World – Tony Juniper & Mike Parr
– Birdlife
– Parrots, Parrots and macaws (Neotropical)
– Photos:
(1) – Hyacinth Macaw also known as Hyacinthine Macaw at Disney’s Animal Kingdom Park by Hank Gillette [CC BY-SA 3.0 or GFDL], via Wikimedia Commons
(2) – A Hyacinth Macaw at Brevard Zoo, Florida, USA By Rusty Clark from merritt usland FLA (Brevard Zoo Hyacinth Macaw) [CC BY 2.0], via Wikimedia Commons
(3) – Hyacinthine Macaw at Melbourne Zoo, Australia By derivative work: Snowmanradio (talk)Anodorhynchus_hyacinthinus_-Australia_Zoo_-8.jpg: Erik (HASH) Hersman [CC BY 2.0], via Wikimedia Commons
(4) – Hyacinth Macaws at Stone Zoo, Stoneham, Massachusetts, USA By Eric Kilby (originally posted to Flickr as Squawking Heads) [CC BY-SA 2.0], via Wikimedia Commons
(5) – Hyacinthine Macaw (Anodorhynchus hyacinthinus) By Ana_Cotta (originally posted to Flickr as ARARA) [CC BY 2.0], via Wikimedia Commons
(6) – Hyacinth Macaws, Anodorhynchus hyacinthinus at the Aquarium of the Americas in New Orleans, Louisiana By Derek Jensen [CC BY 2.0], via Wikimedia Commons
(7) – A pair of Hyacinth Macaws and thier nest in Mato Grosso do Sul, Brazil By Geoff Gallice from Gainesville, FL, USA (Hyacinth macaws) [CC BY 2.0], via Wikimedia Commons
(8) – A Hyacinth Macaw preening at the Aquarium of the Americas, New Orleans, USA By Quinn Dombrowski (originally posted to Flickr as Dainty) [CC BY-SA 2.0], via Wikimedia Commons
(9) – Anodorhynchus hyacinthinus by Hans – Pixabay
(10) – Illustration Guacamayo Jacinto By Lear, Edward [CC BY 2.0 or Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons
– Sounds: Niels Poul Dreyer (Xeno-canto)










Visitor Rating: 5 Stars