Content |
|---|
Description:
15 to 18 cms. length and 38 to 48 g. of weight.
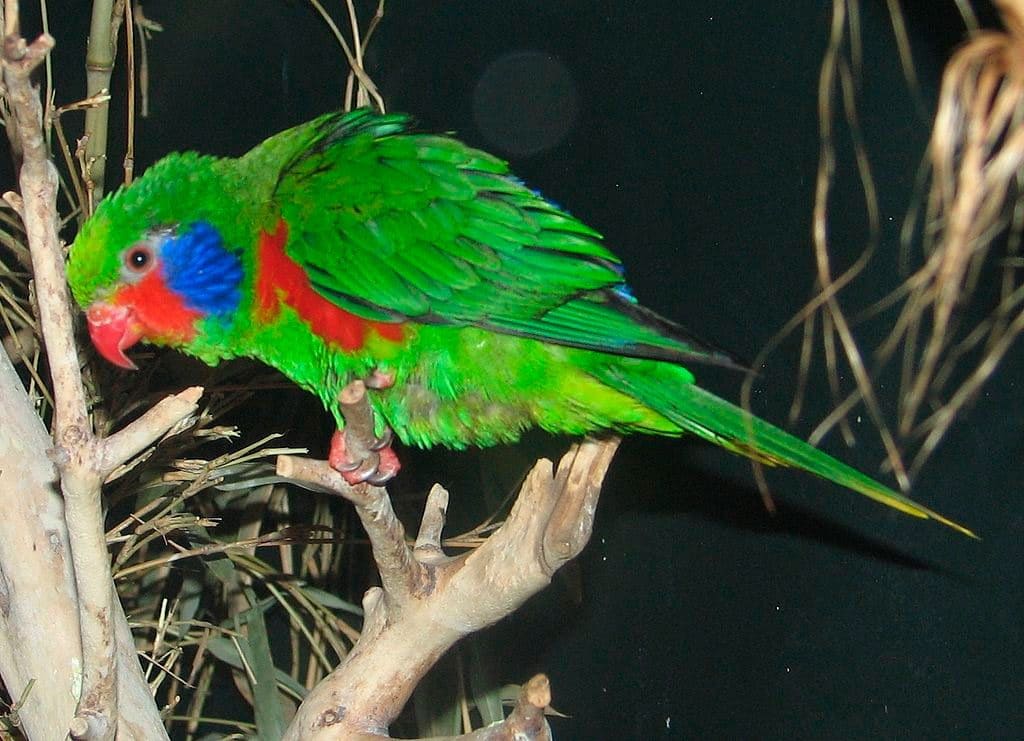
The Red-flanked Lorikeet (Charmosyna placentis) has the forecrown and yellowish-green crown; nape green; chin, throat and lores red; ear-coverts dark blue striped strongly light blue. Top green with rump matte blue: uppertail-coverts green. The part superior of the wings It is green with innerwebs and ends the blackish flight feather. Underwing-coverts red; intense yellow band across the innerwebs of the flight feather blackish. Underparts lighter green than yellow upperparts; Strong red marks on the sides of chest and in the flanks below the sides of belly.
The upper part of the tail It is duller green than upperparts, tipped bright yellow, with lateral feathers red in the center of the innerwebs and slightly in outerweb, with a subterminal black mark; lower tail is basal yellow, with black and red marks.
Bill red; irises yellow to orange; legs opaque red.
The female no yellow-green spots on the top of the forecrown, Red in the face, in the chest, in the flanks and at the bottom of the wings (the underwing-coverts are green-yellow). The blue of the ear-coverts It is replaced by a dark patch badly scratched yellow.
Immature as the female, but duller green, and less extensive yellow streaks in ear-coverts (the young male can present a red stain on the face and greenish yellow in forecrown). Iris pale yellow, legs orange-brown.
- Sound of the Red-flanked Lorikeet.
Habitat:
The Red-flanked Lorikeet It, mainly, a kind of lowlands found in primary moist forest, in the forest edge, in Savannah, the secondary high growth, in the monsoon forest, in the swamps of forget (when they are in bloom), in the gallery forest, in eucalypts, in the coastal forest and, occasionally, in the mangroves and coconut palms. It is also found in flowering trees in cultivated areas.
Can be Quiet and discreet and, even when feeding active and noisy, can be difficult to see through thick foliage. They are mostly in pairs, but occasionally in groups 25 or more, looking for food with others Loris with flowers and trees epiphytes or flying through or above the tree tops in small compact and noisy flocks.
Reproduction:
In New Guinea, Several observations of couples investigating arboreal termite mounds They indicate that it is likely that they are preferred for nest. The bases of ferns and moss cultures have also been identified as potential sites nesting. Activity on these sites has been observed between February and October, and it was found that specimens found in eastern Papua New Guinea by Diamond in July and August 1965 They were able to play. In the Vit Islandu, Coates He watched a couple with chicks in mid-August and is likely to play occurring during much of the year.
Food:
Feeds of pollen, nectar, flowers and seeds, mainly in the upper canopy.
Distribution and status:
Extension of the distribution (breeding/resident): 2.800.000 km2
originating Indonesia Oriental, New Guinea and the northern Solomon Islands.
They can be observed from the Moluccan Islands and West Papua New, through lowland West Papua New and Papua New Guinea to Bismarck Archipelago and Bougainville.
Although mostly they found in lowlands, there have been up to 1.600 metres above sea level in Komo, in the highlands of southern Papua New Guinea; They are also common in high altitudes (about 1.150 meters to 1.450 m) in the zone of Karimui, the east, and they do not seem to be anywhere else in the region. reaches 300 metres in New Britain, above which is replaced by the Red-chinned Lory (Charmosyna rubrigularis). In the North of New Guinea It is replaced by the higher altitude Red-fronted Lorikeet (Charmosyna rubronotata).
Widespread and common to locally abundant. It is believed that the world population is at a level of caresses 500.000 individuals and it is stable. small numbers in captivity.
Translation made with the translator www.DeepL.com/Translator
Conservation:
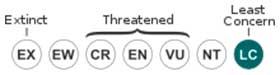
• Current category of the Red List of the UICN: Least concern
• Population trend: Stable.
• Population size : Unknown
Rationale for the Red List category
This species has a very extens distribution areato, and therefore does not approach the thresholds for Vulnerable under the criteria of size range (Scope of the presence <20.000 km2 combined with a decreasing area size or fluctuating distribution, extension / habitat quality, o Population size and a small number of locations o Severe fragmentation).
The population trend appears to be stable, and therefore the species does not approach the thresholds for Vulnerable under the criteria of population trend (decrease> 30% in ten years or three generations). The population size has not been quantified, but it is not believed to approach the thresholds for Vulnerable under the criterion of population size (<10.000 mature individuals with an estimated> 10% continuous decline in ten years or three generations, or with a specific population structure). For these reasons, the species is assessed as Least concern.
Justification of the population
Global population size has not been quantified, but it has been reported that the species is generally common and sometimes abundant (pit et to the. 1997). Some sources estimate the current population of this Lori in about half a million individuals.
Justification trend
They suspected that the population is stable the absence of evidence of decline or substantial threats.
"Red-flanked Lorikeet" in captivity:
Rare in captivity.
Alternative names:
– Blue-eared Lorikeet, Lowland Lorikeet, Red flanked Lorikeet, Red-flanked Lorikeet, Yellow-fronted Blue-eared Lorikeet, Yellow-fronted Blue-eared Lory (English).
– Lori coquet, Loriquet à croupion bleu, Loriquet joli (French).
– Schönlori (German).
– Loris Charmosyna Placentis (Portuguese).
– Lori de Dorso Rojo, Lori Flanquirrojo (español).

– Order: Psittaciformes
– Family: Psittaculidae
– Gender: Charmosyna
– Scientific name: Charmosyna placentis
– Subpoena: (Temminck, 1835)
– Protonimo: Psittacus placentis
Red-flanked Lorikeet images:
Videos "Red-flanked Lorikeet"
Sources:
• Avibase
• Parrots of the World – Forshaw Joseph M
• Parrots A Guide to the Parrots of the World – Tony Juniper & Mike Parr
• Birdlife
Photos:
(1) – A male Red-flanked Lorikeet at Cincinnati Zoo, USA by Ltshears [CC BY 3.0]
(2) – Female Red-flanked Lorikeet at the Louisville Zoo, USA by Ltshears [CC BY-SA 3.0 or GFDL], from Wikimedia Commons
(3) – A pair of Red-flanked Lorikeets at Jurong Bird Park, Singapore by Peter Tan [CC BY-SA 2.0], via Wikimedia Commons
(4) – The image is free from copyright under Creative Commons CC0
(5) – Red-flanked Lorikeet, Male (Charmosyna placentis) at the Louisville Zoo by Ltshears [CC BY-SA 3.0 or GFDL], from Wikimedia Commons
Sounds: Ross Gallardy, XC410521. accessible www.xeno-canto.org/410521.