The Aidi is highly energetic, protective and extremely vigilant. Despite its resemblance to Sheepdogs, The Aidi is not one of them because there are no sheepdogs from the Atlas.
2 – Section 2.2
Group 2 Pinher and Schnauzer â € "Molosoides â €" Mountain type dogs and Swiss boyeros. Section 2.2 Molossoid, mountain type.
▷ The world of Pets: Dogs, cats, birds, reptiles, amphibians
Aidi – Atlas Mountain Dog
▷ The world of Pets: Dogs, cats, birds, reptiles, amphibians
St. Bernard  FCI 61 - Molossoid . Mountain
FCI 61 - Molossoid . Mountain
Content |
|---|
History
The St. Bernard It is a breed of dog whose name in other languages: St. Very, Bernhardiner, Chien du Saint-Bernard, Saint Bernard Dog.
According to breed historians, the St. Bernard, descended from the ancient molossians Asian, whose ancestral form was and is represented by the Tibetan Mastiff.
A team of researchers from the University of Manchester, directed by Chris Klingenberg of the Faculty of biological sciences, reviewed 47 skulls of St. Bernard donated by Swiss breeders to the Natural History Museum in Bern covering a period of 120 years, from modern copies until those old dogs of the time that was initially defined the standard of the breed. It was found that the traits stipulated in the breed standard of the St. Bernard have become more exaggerated over time, as breeders selected dogs that had the desired physical attributes.
Compared to their ancestors, the St. Bernard modern has the widest skull, the angle between the nose and the forehead more pronounced, and also a more significant bump over the eyes. These changes are described exactly as desired in the breed standards. Clearly, not due to other factors such as overall growth, since they do not provide the animal with any physical advantage, so we can be sure of have evolved only by selective breeders considerations.
This research shows how the selection, either natural or in this case artificially influenced by the man, It is the fundamental driving force behind the evolution of life on the planet.
In the year 923 born Bernard of Menthon in Menton, region of Savoy (France), which he became Archdeacon of Aosta, in the Italian Alps, dedicated to spreading the Christian faith among the inhabitants of the Alps. In one of these Alpine passes was founded in the year 1049 the Hospice of the Gran San Bernardo, to help, help and shelter to hikers who were the step. The Holy, Catholic scholar and theologian, He was part of the Cistercian order or better known as Trappist, as fellow (the Trappist monks) in Switzerland they had a dog of this breed as a companion around the 16th century.
In the great Mount St mountain pass. Bernhard, to 2.469 meters above the sea level, monks founded in the 11th century, a hospice for travellers and pilgrims. there they were raised, Since the mid-17TH century, big mountain dogs for guard and surveillance. The existence of those dogs is documented graphically from 1695 written in a chronicle of the Hospice from the year 1707.
These dogs were soon used as guard dogs and, especially, as rescue dogs for travellers lost in the fog and snow.
There are chronicles published in many languages about the numerous lives that were saved by these dogs from the "white death" and stories of soldiers who crossed the mountain pass with Napoleon Bonaparte towards 1800, in the 19th century, they spread the dog's fame for St. Bernard all over Europe.
Already called at that time «Barry Hund«, And the legendary «Barry»It became the symbol of the rescue dog. The direct ancestors of the dog of St. Bernard were the very widespread oversized dogs, peasants of the region. These large dogs became only a few generations, an ideal pattern, in the current race.
As a result of an international cynological congress held on 2 in June of 1887, the dog of St. Bernard was officially recognized as a Swiss breed and the breed standard became mandatory. Since then the San Bernardo dog became the "Swiss national dog".
Heinrich Schumacher Holligen, was the first, in 1867 creating genealogical documents for their dogs. In February of 1884 The «Schweizerische Hundestammbuch” (Swiss races book, SHSB). The first entry was that of St. Bernard «León», followed by other 28 annotations also of dogs of St. Bernard. The 15 in March of 1884 The «Schweizerische St. Bernhardsclub» (Swiss Dog Club St. Bernard) in Basel.
Physical characteristics
The Saint Bernard, is classified in the Group 2: Dog type Pinscher and Schnauzer, Molosoides and mountain dogs and Swiss Cattle Dogs, and other races; section 2; Molossoid, 2.2 Type mountain (without working trial). Of the FCI (Federation Cynologique Internationale).
There are two varieties of the dog St. Bernard:
- The variety of short hair (double hair, Stockhaar).
- The long-haired variety.
Two varieties are of great stature and of a noble general appearance; they have a vigorous body, robust, harmonic and muscular, as well as an imposing head with an expression of attention on the face.
The cross appeal is, minimum of 70 cm for males and 65 cm for females. The FCI standard sets a maximum of 90 cm for males and 80 cm for females (dogs exceeding the maximum height is not devaluarán if its general aspect is harmonic and its proper motion).
In general the size is defined as:
- «Very large«, to be optimal in San Bernardo, When exceeds the 86 cm in males and the 80 cm in females.
- «Grand»When it goes from 82 to 86 cm in males and 75 to 80 cm in females.
- «Media»When it goes from 78 to 82 cm in males and 70 to 75 cm in females.
- «Small»When it goes from 70 to 78 cm in males and 65 to 70 cm in females.
In it "golden period of St. Bernard” (1920-1940) were very rarely seen in exposures lower males to 80 Switzerland cm, of Germany, in the Netherlands and the subjects were not so rare above the 90 cm..
Also currently a good San Bernardo to access the championship would never have to be -with some exceptions- below the 80-82 cm and abundantly exceed such limit to reach above if possible the maximum of the German Mastiff and of the Irish Wolfhound but with greater volume, greater length of the trunk and heavier, course.
Character and skills
The dog's St. Bernard radiates calm and tranquility. He is balanced and self-confident.. Despite its imposing size, it is sensitive and has a gentle nature. His "stubbornness" is typical of this race, not only in appearance. The St. Bernard is trustworthy and kind, even with strangers. There is hardly a dog that has such a tolerant and balanced nature. Quietly he lets himself be caressed and understood by children he does not know. There is hardly a dog as fond of children as the St. Bernard. Nothing seems to bother him.
But, has an alert protective instinct. Defends his family and territory inflexible and extremely effective. One St. Bernard healthy and well socialized never loses control. It is not a barking dog and will stop any intruder quietly and abruptly. How do you like to live outside, still suitable as a guard and protection dog – but it is not in any way a dog to be in a kennel. The basis of this is the close connection with your human family, who should be the center of attention. Because he is affectionate and needs a lot of contact with humans as well as with other dogs.. After all, the close connection with his master is the decisive basis of his education.
Due to its size and strength, a St. Bernard a dog is not for beginners. It also, its maintenance is – as with all big dogs – very complex. If you want to buy a dog from St. Bernard, You must first be clear about some basic things:
The extreme dimensions bring with them quite practical problems. This starts with the car. And what if the adult giant is sick or cannot walk for a while due to age?? The St. Bernard not a dog for an apartment. The floor of the house should not be slippery. The dog should not have to climb the stairs frequently. To the St. Bernard he likes to travel; not an athlete, and take it easy. In the interest of your fitness, one should ensure that he exercises outdoors every day. Ideally, a St. Bernard stay in the field.
St. Bernard Education
To have fun with your dog St. Bernard, consistent education from the puppy's age is a basic requirement. 60 and more kilos of stubbornness, reluctantly following instructions, it's not a fun thing. Also keep in mind that the St. Bernard It, in case of doubt, much stronger than any well-trained man.
A deep and intimate bond with your caregiver is the basis of education, never difficulties or coercion. As puppies it must be carried with a stoic consistency. In his youth, the St. Bernard they are usually very lively and challenge the leadership of their humans. But, the dog of St. Bernard can be well educated. His calm and kind nature even forgives this or that mistake. But a solid education foundation with clear rules for daily life is an absolute prerequisite for your future attitude..
St. Bernard health and care
Coat care is simple. Regular brushing is enough. During the change of coat, twice a year, everything is a little more complex.
The main health problem of St. Bernard is the extreme breeding, breeding for gigantism. Puppies and young dogs of such breeding already grow too fast. So, it's about body coordination problems. Epilepsy and other diseases accompany the giant that is becoming. Life expectancy decreases dramatically. The enormous growth and associated rapid weight gain is an extreme challenge for the entire body.. The dog's fingerprint is not designed for such giants. the heads, however "typical" they seem, they have also been raised to be unhealthy and powerful, which can cause problems at birth.
One should pay attention to the eyes: Droopy eye or droopy eyelid is a widespread problem, especially with particularly powerful heads, that requires lifelong care and can seriously damage the eyes. Professor Distl of the Hannover University of Veterinary Medicine considers the St. Bernard as one of the breeds in which epilepsy is more common. Various types of cancer such as osteosarcoma also appear to be common in St. Bernard. The breed is strongly affected by dysplasia of the hip joint, as well as other skeletal diseases.
Nutrition / Food
Puppies and young dogs, they grow very fast, require expert guidance for proper nutrition. At the same time, attention should be paid to controlled exercise, neither too much nor too little. In the adult Saint Bernard there is a risk of stomach torsion. Otherwise, as with any big dog, the same applies to food: good and hearty.
The life expectancy of a St. Bernard
The legendary Barry I had 14 years, 10 of which he spent them on active rescue service in the Gran San Bernardo. Today is different, made by the man. Today, the St. Bernard is one of the dogs with the lowest life expectancy. The colossi of today reach only 6 to 8 years. Only very rarely does he reach an age of 10 years or more. On the other hand, a St. Bernard raised healthy with a weight lower than 70 kg is a robust dog and, despite its size, very frugal, without problems can live 10 years.
Buy a St. Bernard dog
Before buying a St. Bernard, you should check very carefully if you really have all the requirements to be able to spend many wonderful years with this giant. Only when all this clears up, a breeder must be found and contacted long before purchase. Special importance must be given to the fact that the breeder avoids exaggeration. Dogs in your kennel should not be large or too heavy. Also the heads should not be too powerful. It also, make sure that no epilepsy occurred in the ancestors. In any case, it should be clear that a puppy is only bought directly from a serious breeder. Better pay a few hundred euros more for a puppy from a serious breeder. These euros have a good opportunity to become the best investment of your life. Coming from a serious upbringing, a puppy of St. Bernard costs between 1.500 and 2.000 EUR.
Characteristics "St. Bernard"
Coexistence is important that you have with your new friend. Before considering the acquisition of a dog of the breed "St. Bernard" you know certain factors. Not all breeds of dogs are apt to live in an apartment, you must take into account his character, their need for exercise, their interaction with other pets, their care and if you have small children, their level of tolerance towards them.
Adaptation ⓘ4,0 of 5 stars (based on 1 review)
|
friendly dog ⓘ5,0 of 5 stars (based on 1 review)
|
hair loss ⓘ3,0 of 5 stars (based on 1 review)
|
|---|---|---|
Affection level ⓘ5,0 of 5 stars (based on 1 review)
|
Need for exercise ⓘ2,0 of 5 stars (based on 1 review)
|
Social need ⓘ4,0 of 5 stars (based on 1 review)
|
Home ⓘ3,0 of 5 stars (based on 1 review)
|
Toilet ⓘ4,0 of 5 stars (based on 1 review)
|
Friendly with strangers ⓘ3,0 of 5 stars (based on 1 review)
|
barking ⓘ3,0 of 5 stars (based on 1 review)
|
Health ⓘ5,0 of 5 stars (based on 1 review)
|
Territorial ⓘ5,0 of 5 stars (based on 1 review)
|
Cat friendly ⓘ5,0 of 5 stars (based on 1 review)
|
Intelligence ⓘ3,0 of 5 stars (based on 1 review)
|
Versatility ⓘ3,0 of 5 stars (based on 1 review)
|
Child friendly ⓘ5,0 of 5 stars (based on 1 review)
|
Surveillance ⓘ2,0 of 5 stars (based on 1 review)
|
joy ⓘ5,0 of 5 stars (based on 1 review)
|
St. Bernard Images
St. Bernard Videos
Type and recognitions:
- FCI CLASSIFICATION:
- Group :
- Section : . .
Federations:
- – FCI – Pinscher and Schnauzer-Molossoid type dogs – Swiss Mountain Dogs and Cattledogs. Section 2.2 Molossoid, mountain type. ⓘ
- – AKC – Workgroup ⓘ
- – ANKC – Group 6 (utility dogs) ⓘ
- – CKC – Workgroup ⓘ
- – KC – Workgroup ⓘ
- – NZKC – Utility dog ⓘ
- – UKC – Watchdog ⓘ
FCI breed standard "St. Bernard"
Origin:
SwitzerlandDate of publication of the valid original standard:
04.04.2016.Use:
Company, Guard and Farm Dog.
General appearance:
There are two varieties of San Bernardo:
- Variety of short hair (double mantle, "Stockhaar")
- Long hair variety.
The two varieties are considerable size and an impressive general appearance. They have a balanced body, powerful, Strong and muscular with an impressive head and a facial expression alert.
IMPORTANT PROPORTIONS
- The desired proportion between the height of the cross and the length of the body (measured from the tip of the shoulder to the tip of the buttock) is of 9 : 10.
- The desired proportion between the height to the cross and the depth of the chest is reflected in the sketch of the beginning.
- The total length of the head is slightly larger than a third of the height of the cross.
- The proportion between the depth of the snout (measured at its root) And its length is approximately 2 : 1.
- The length of the snout is slightly larger than the third part of the length of the head.
Behavior / temperament:
Friendly by nature. Quiet temperament to cheerful; vigilant.
Head:
Powerful, imposing and very expressive.Cranial region:
- Skull: Strong and wide. Seen from the front and profile the top part of the skull is slightly domed. When is the dog at attention, The insertion of the ears forms a straight line with the upper part of the skull which laterally has a soft curvature towards high and strongly developed cheeks. The inclination from forehead to well steep snout. The occipital Protuberance should shortly be accented. The orbitals above arches strongly developed. Clearly marked front Groove starts on the forehead and extends to the top of the head. Skin from the forehead over the eyes forms slight folds that converge toward the central sulcus. When is the dog at attention, they are usually almost imperceptible.
- Depression links (Stop): Strongly pronounced.
facial region:
- Truffle: Wide and square with well marked angles, well open nostrils. The truffles must be black.
- Snout: Uniformly wide. Nasal helm straight with a slight furrow in the Center.
- Belfos: Pigmented edges of black. The Belfos of the upper jaw must be highly developed, shoulder straps, but not too pendants; they form a wide arc towards the nose. The corners must be visible.
- Jaws/Teeth: Upper and lower jaws strong, wide and the same length.
- Bitescissors or well developed clamp, regular and complete. It allows light lower prognathism, provided that the incisors do not lose contact. The absence of the PM1 is tolerated (premolars 1) and the M3.
- Eyes: Medium-sized, they can be dark brown to hazelnut; moderately sunken. friendly expression. The edges of the eyelids are completely Pigmented.
- A full closure is desirable, natural. Is allowed a small fold on the bottom with little visible conjunctival eyelid and a small crease on the upper eyelid.
- Ears: Medium-sized, high and wide insertion. Highly developed Pavilion. Lobes soft triangle with rounded tip. The back edge is slightly separated from the head, While the above should be set to the cheeks.
Neck:
Strong and good long. The double chin neck and throat, moderately developed.Body:
- As a whole: The general impression should be, harmonica, well muscled and imposing.
- Cross: Well developed.
- Back: Wide, powerful and strong. The upper line is straight and level to the lumbar region.
- Rump: Long, slightly descending with a harmonious transition to the insertion of the tail.
- Breast : Moderately deep chest with well sprung ribs, but not abarriladas. You must not get below the elbows.
- Abdomen and lower line: Slight upward backward.
Tail:
Of wide and strong base, It should be long and heavy.
- The last vertebra must reach at least the corvejón joint. At rest you must hang straight or slightly curved up in the last third. In State care may be higher.
Tips
Former members:
- As a whole: Seen from the front, rather wide position. Members must be straight and parallel.
- Shoulder: Inclined scapula, muscular and firmly attached to the body.
- Arm: As long as the scapula. The angle between the scapula and the arm must not be too open.
- Elbow: Attached to the body.
- Forearm: Straight, strong bone and muscles dry.
- Metacarpus: Seen from the front must be vertical in its extension to the forearm. Viewed laterally must be slightly oblique.
- Front feet: Widths, with strong fingers, together robust and highly arched.
Later members:
- As a whole: Moderately angled rear limbs and muscled. Seen from the rear must be parallel and not together.
- Thigh: Robust, muscular and wide.
- Knee: Well angled and not turn inward or outward.
- Leg: Fairly long and oblique.
- Hocks: Moderately angled and strong.
- Metatarsals: Seen from the back as straight and parallel.
- Hind feet: Widths, with strong fingers, together robust and highly arched. The Spurs are tolerated if not they interfere with normal movement.
Movement:
Harmonic, long steps. Good push from the hind limbs. The back remains firm and stable.
The previous and subsequent members must advance in a straight line when walking.Mantle
- Short hair (double hair): Dense outer layer, smooth and stuck to the body. Internal NAP thick. Thighs with fringes of not very notable hairs. Tail with thick hair.
- Long hair: Outer layer of hairs of medium length, smooth. Abundant internal NAP. On the hip and rump, the hair can be somewhat wavy. Thighs with fringes of abundant hair and forelimbs with flags. Face and ears with short hair. Tail with abundant bushy hair.
COLOR: The basic color is white with reddish brown spots smaller or larger (spotted dogs), to form a continuous blanket of uninterrupted reddish brown on the back and flanks (dogs with mantle). This mantle interrupted by white veins have the same value. The reddish brown tabby is allowed. The yellowish-brown is tolerated. The dark brown on the head is much appreciated. Will tolerate some light traces of black color on the body.
- Major brands: Sill, feet, the tail, nose cane, headband and nape.
- Desirable markings: White collar.
- dark mask symmetrical.
Size and weight:
Minimum height:
- Males: 70 cm..
- females: 65 cm..
Maximum height:
- Males: 90 cm..
- females: 80 cm..
- Dogs exceeding the maximum height is not devaluarán in its judging if their general appearance is harmonious and correct movement.
Fouls:
Any deviation from the above mentioned criteria is considered as missing and the gravity of this is considered in proportion to the degree of deviation to the standard and its consequences on the health and well-being of the dog.
- Characteristics of sex not sufficiently developed.
- Non-harmonic overall appearance.
- Very short relative to the height of the cross member.
- Excess of folds in head and neck.
- Muzzle too long or too short.
- Belfos of lower jaw hanging and turned out.
- Lack of teeth (except the PM1 and the M3) ; small teeth (especially the incisors).
- Slight lower prognathism.
- light eyes.
- Eyelids too loose.
- Back saddle or in tent.
- Rump too high or too falling.
- Tail coiled on top of the back.
- Absence of white markings deemed important.
- Curved or very returned former members out.
- Later in the form of Coop members, de “X”, or too straight.
- Faulty movement.
- Curly hair.
- Incomplete or lack of it in the truffle pigmentation, belfos, eyelids and around the nose.
- Wrong basic color, small splashes or spots of wetwood color on white.
MISS PLAYOFFS
- Fearful dogs, aggressiveness.
- Upper prognathism, marked lower prognathism.
- Blue eyes.
- Entropion, ectropion.
- Completely white or completely brown reddish coat (absence of the basic color).
- Coat of a different color.
- Dogs that do not reach the minimum height.
- Any dog showing clear signs of physical or behavioral abnormalities must be disqualified..
N.B.:
Males should have two normal-appearing testicles., fully descended into the scrotum.
- This revised standard shall be applicable from April 2004.
TRANSLATION: Brígida Nestler.
Source: F.C.I - International Cynological FederationAlternative names:
1. St. Bernhardog, Bernhardinner, Alpine Mastiff (archaic), Saint, Saint Bernard (English).
2. Grand-Saint-Bernard (French).
3. St. Bernhardshund, Chien du Saint-Bernard, Saint Bernard Dog, Perro San Bernardo (German).
4. Cão de São Bernardo (Portuguese).
5. Gran San Bernardo (español).
▷ The world of Pets: Dogs, cats, birds, reptiles, amphibians
Newfoundland  FCI 50 - Molossoid - Mountain
FCI 50 - Molossoid - Mountain
Content |
|---|
History
The Newfoundland was born on the east coast of Canada. The great island of Newfoundland, which is in front of Canada, gave him his name. The fact that it descends from the dogs of the Vikings of pre-Columbian times or from the dogs of the Indians is a legend that has not been proven until now.. Its relationship with the molossi can be seen but also proved in the genetic map of the Heidi G dog breeds. Parker.
Probably the ancestors of the Newfoundlands came with the first settlers as molossi from Europe. It proved to be an aid to fishermen and sealers and was occasionally useful when hunting bear and big game on land.. It transported loads and served as a draft dog for the sleds with the dead game.. Working with fishermen in the rough North Atlantic was extremely demanding. The Newfoundland had to think, had to do heavy work on the networks. The Newfoundland saved the lives of the castaways over and over again. In this way, he developed the peculiarities of his character and physique that allowed him to face the harsh weather conditions on land and the dangers of the sea as a water and rescue dog..
With the cod ships he came to England over and over again as early as the 18th century. Here he became famous early on due to his impressive achievements. Was not up 1886 that the Club of Newfoundland in England, and soon after, in 1893, The club of Newfoundland for the Continent, now called the "German Club of Newfoundland«. Even today, Newfoundland keep working as a water rescue dog.
Did you know??
One Newfoundland named Rigel sank with the Titanic and swam alongside a lifeboat for three hours in the icy water, apparently looking for its owner, that had gone down with the ship. The people in the lifeboat were nearly run over by the steamer Carpathia because the crew could not hear their faint cries., but Rigel's bark was noticed and the people and the dog were saved.
Physical characteristics
The Newfoundland is a big dog. According to the standard, adult males must weigh an average of 68 kg and females 54 kg. It is a very strong dog, very muscular and with long dense hair. Her coat is water repellent. It has a strong and soft undercoat, which makes it look even bulkier. This shouldn't tempt you to raise him like a teddy bear.. Because the real Newfoundland combines enormous power with agility, sportiness and impressive skills in the water. Its exterior does not deceive its interior. Master challenges with a committed calm. The hair on your head, muzzle and ears is short and thin. The front and rear legs are covered in fur. The tail is completely covered in long thick hair. The black, brown and black and white are allowed as coat colors.
Character and skills
Even the mere appearance of Newfoundland has a relaxing and calming effect, at least for people who are not usually afraid of dogs. The Newfoundland radiates majestic serenity. Its character is as stable as it appears on the outside. It has a friendly and kind nature. But that must not be misleading: He knows very well how to distinguish between friend and enemy, which you can unequivocally underline by your calm but more determined appearance. If required, defends his family with all his might without hesitation. Barking is not necessary to be heard.
He is extremely friendly with his friends. The Newfoundland he is very close to his family and loves children more than anything. He wants education and he absolutely needs it. Because like a powerful big dog it is always stronger than the other end of the leash.. Sometimes he has a hard head, but after a friendly request from his master or caretaker he does everything, as long as it's well connected. The Newfoundland impresses by the unity of two apparently irreconcilable poles: on the one hand it radiates calm and tranquility, on the other hand it can save people from drowning in a short time in the most difficult conditions. Usually, the Newfoundlands are real water rats. They are excellent swimmers, which they are happy to proudly demonstrate.
The Newfoundland not a dog for the city or a flat. He likes long walks, but water is the best for him. Due to its strength and the high technical demands of its maintenance, not suitable for beginners, although it can be trained and managed well. It is a great family dog. But he also likes to sleep outside, even with wind and rain. What you don't need is running or doing activities in the heat.
The Newfoundland It is a natural lifeguard and can be a good helper for parents who have a pool or enjoy taking children to the lake or ocean, although you should never be solely responsible for your safety.
Newfoundland Education
The Newfoundland can be educated very well. It is intelligent, interested and quickly understand what you are allowed to do and what you are not. Sometimes it's a little slow, but a little motivated, he is very cooperative and strives to make his master and lady happy. The puppy should already show itself clearly and without exception where the hammer hangs. There should be no doubt about the orientation of your humans, as well as about the intimate relationship and respect for him.
It must always be kept in mind that this dog is the physically strongest and that leadership only works through unquestioning recognition of the human leadership role.. With praise and results, basically you can achieve everything with it. On the basis of a good education you can train him very well Newfoundland. Many terranovas they are successfully used as guide dogs for the blind and especially as water rescue dogs, but also on land. For this you can do work tests with water in the clubs.
Caring for a Newfoundland
Maintain and care for the Newfoundland it is very expensive. The dense, weather-resistant coat must be brushed every day with a special brush.. Should not be sheared or trimmed. Due to its constitution and dense coat, do not tolerate heat well.
Nutrition / Food
Like all large dogs, Newfoundland need a lot of food. Especially in the growth phase you need professional nutritional planning.
Newfoundland life expectancy
Life expectancy is between 8 and 12 years. That depends a lot on the upbringing. Thin and light dogs tend to age more than heavy, plump dogs.
Newfoundland Health
as could be predicted, given its large size, the Newfoundland can suffer a series of joint and structural problems. It is important that young and growing dogs are kept lean and are not allowed to exercise too hard or eat too much, since this will cause injuries and problems that can be paralyzing in the future. In fact, all the Newfoundland they need to stay slim, since obesity increases the chances of them developing structural problems and makes them more painful when they occur.
One such structural problem is genetic hip deformation known as hip dysplasia.. The head of the femur does not fit well into the hip socket; with the time, the cartilage in the joint wears away and the underlying bone is damaged. Serious arthritis occurs that usually affects very young dogs. In some cases, expensive surgery required, including total hip replacement surgery. If not treated, the dog will suffer pain and a poor quality of life. Elbow dysplasia is another inherited joint problem, resulting from abnormal elbow formation.
The possibility that a Newfoundland develop dysplasia of the hip or elbow just because the parents are free of the disease, although it reduces the possibilities. And while a puppy's bones keep growing, it can sometimes be difficult to confirm a diagnosis, depending on the tests performed and the severity of the condition.
To each Newfoundland X-rays of your dog's hips and elbows should be taken by two years of age, regardless of whether or not he shows symptoms of lameness or stiffness. For dogs that show lameness before that age (that is to say, during the puppy stage), diagnostic tests should be performed promptly.
The Newfoundlands are at risk of heart disease, including dilated cardiomyopathy and subaortic stenosis (SAS). There is currently no genetic test for SAS, who has a complex inheritance, making it difficult to develop a test. Breeders must not breed Newfoundland with no signs of SAS and puppies should be examined by a certified veterinary cardiologist.
Cystinuria is a genetic kidney defect that leads to the formation of bladder stones that are very difficult to manage with diet or medication and often requires surgery both to remove the bladder stones and to repair urinary obstructions.. There may be no early signs that the dog is forming cystine stones, which can create a life-threatening emergency if they cause an obstruction. Fortunately, there is a genetic test for cystinuria. Given the availability of the genetic test, no need for a breeder to produce a dog with the disorder
Not all of these conditions are detectable on a growing puppy, and it can be difficult to predict whether an animal will be free of these diseases, so a reputable breeder must be found who is committed to raising the healthiest animals possible. Must be able to produce an independent certification that the parents of the dog (and grandparents, etc.) have been screened for these defects and considered healthy for breeding. That's where health records come in..
Not all visits by Newfoundland to the vet they are due to a genetic problem. It is known that the Newfoundland experience cruciate ligament rupture. They are also among the deep-breasted breeds predisposed to bloating., a condition in which the stomach is distended by gas and may twist in on itself (called gastric torsion), cutting off blood flow. Swelling and torsion appear very suddenly, and a dog that was fine a minute can die a few hours later. Watch for symptoms such as restlessness and pacing, la baba, the paleness of the gums, lip licking, unsuccessful attempt to vomit and signs of pain. Swelling requires immediate veterinary intervention, and surgery is necessary in many cases. Unfortunately, dogs that have swollen can do it again, So most veterinarians offer a procedure known as gastropexy or "stomach turning.", which anchors the stomach to the body wall to help prevent future twisting. This procedure can also be done as a preventive measure.
Buy a Newfoundland
You should only buy a puppy locally from a breeder who is affiliated with the FCI. should come from a baby, where dogs are rather sporty, thin and not too fat and «beary». A puppy in the kennel is usually sold at a price between 1500 and 2000 EUR.
Valuations "Newfoundland"
Coexistence is important that you have with your new friend. Before considering the acquisition of a dog of the breed "Newfoundland" you know certain factors. Not all breeds of dogs are apt to live in an apartment, you must take into account his character, their need for exercise, their interaction with other pets, their care and if you have small children, their level of tolerance towards them.
Adaptation ⓘ5,0 of 5 stars (based on 1 review)
|
friendly dog ⓘ4,0 of 5 stars (based on 1 review)
|
hair loss ⓘ5,0 of 5 stars (based on 1 review)
|
|---|---|---|
Affection level ⓘ4,0 of 5 stars (based on 1 review)
|
Need for exercise ⓘ3,0 of 5 stars (based on 1 review)
|
Social need ⓘ4,0 of 5 stars (based on 1 review)
|
Home ⓘ3,0 of 5 stars (based on 1 review)
|
Toilet ⓘ5,0 of 5 stars (based on 1 review)
|
Friendly with strangers ⓘ4,0 of 5 stars (based on 1 review)
|
barking ⓘ3,0 of 5 stars (based on 1 review)
|
Health ⓘ5,0 of 5 stars (based on 1 review)
|
Territorial ⓘ5,0 of 5 stars (based on 1 review)
|
Cat friendly ⓘ5,0 of 5 stars (based on 1 review)
|
Intelligence ⓘ4,0 of 5 stars (based on 1 review)
|
Versatility ⓘ3,0 of 5 stars (based on 1 review)
|
Child friendly ⓘ5,0 of 5 stars (based on 1 review)
|
Surveillance ⓘ3,0 of 5 stars (based on 1 review)
|
joy ⓘ5,0 of 5 stars (based on 1 review)
|
Images "Newfoundland"
Photos:
1 – Terranova by Maria Amaro Jimenez / CC BY-SA
2 – Terranova by https://pixabay.com/es/photos/terranova-perro-negro-609531/
3 – Terranova by https://pxhere.com/es/photo/112392
4 – Terranova by https://www.publicdomainpictures.net/es/view-image.php?image=197196&picture=newfoundland-cute-puppy-dog
5 – Terranova by https://www.pxfuel.com/es/free-photo-obraa
6 – Terranova by https://www.pxfuel.com/es/free-photo-jttkx
Videos "Newfoundland"
Type and recognitions:
- FCI CLASSIFICATION:
- Group :
- Section : . .
Federations:
- – FCI – Pinscher and Schnauzer-Molossoid type dogs – Swiss Mountain Dogs and Cattledogs. Section 2.2 Molossoid, mountain type. ⓘ
- – AKC – Dogs working ⓘ
- – ANKC – Group 6 (utility dogs) ⓘ
- – CKC – Group 3 ⓘ
- – KC – Working dogs ⓘ
- – NZKC – Utility dog ⓘ
- – UKC – Watchdog ⓘ
FCI breed standard "Newfoundland"
Origin:
CanadaDate of publication of the valid original standard:
29.10.1996.Use:
Sled dog for heavy loads, water dog.
General appearance:
The Newfoundland has a powerful body, solid, muscular. Their movements are well coordinated.
IMPORTANT PROPORTIONS: The length of the body, measured from the scapulo-humeral joint to the tip of the ischium, is greater than the distance from the cross to the ground (height to the cross). The body is compact. The female's body may be slightly longer and less massive than the male's. From the withers to the lower chest the distance is slightly greater than from the lower chest to the ground.
Behavior / temperament:
The expression of the Newfoundland reflects kindness and sweetness. Worthy, happy and creative, is characterized by its genuine gentleness and serenity.
Head:
Solid. The female's head has the same general configuration as the male's, but it is less massive.Cranial region:
- Skull: It is wide; the apex is slightly arched and the occipital bone is well developed.
- Depression links (Stop): It is well observable, but never abrupt.
facial region:
- Truffle: Wide and well pigmented. Windows are well developed. In black dogs and black and white, It is black; it is brown in dogs of this same color.
- Snout: Definitely square, deep and moderately short. It is covered by short fine hair and has no wrinkles. The corners of the lips are apparent, but not too pronounced.
- Belfos: soft.
- Jaws / Teeth: The bite is uniform or scissor-shaped.
Eyes: Moderately sunken and relatively small. They are well separated and there is no presence of a third eyelid.. They are dark brown in black and black and white dogs. Lighter shades are allowed in brown dogs.
Ears: They are relatively small, triangular and rounded edges. They sit back on both sides of the head and are very heavy.. When the adult dog's ear is extended forward, it reaches the inner corner of the eye on the same side of the head.
Neck:
It is strong, muscular and well-seated on the shoulders. It is long enough to allow a distinguished bearing of the head. The double chin should not be excessive.Body:
The bone structure is everywhere solid. In profile, the body is deep and vigorous.
- top line: It is horizontal and firm from the cross to the rump.
- Back: Wide.
- Pork loin: Strong and well muscled.
- Rump: Wide. Tilts at a 30° angle.
- Breast : Width, deep and spacious; the ribs are well arched.
- bottom line: Almost uniform and never raised.
Tail:
While the Newfoundland is swimming, the tail serves as rudder; therefore, It must be strong and wide at the root. When the dog is at rest, the tail is down, perhaps forming a small curve at the tip; reaches the hock or a little lower. When the dog is moving or animated, the tail is carried straight with a slight upward curve, but it never comes rolled up on the back, nor curved between the hind limbs.Tips
PREVIOUS MEMBERS: They are straight and parallel also when the dog walks or jogs slowly.
- Shoulder: They are well muscled and oblique.
- Elbows: stuck to the chest.
- Metacarpus: They are slightly inclined.
- Previous feet: Large and in proportion to the body. They are rounded and compact, with also compact and firm fingers. The fingers have an interdigital membrane.
LATER MEMBERS: Since the urge to drag heavy loads, swimming and covering a lot of ground efficiently depends largely on the hindquarters, in Newfoundland their structure is very important. The pelvis must be strong, wide and long.
- Thigh: He is broad and muscular.
- Knee: It is well angled, but not enough to give the impression that the dog is crouched.
- Leg: It is strong and quite long.
- Hocks: They are relatively short and are well lowered and separated, parallel to each other. They don't even deviate inwards, nor out.
- Hind feet: Firm and compact. In case of dewclaws, these must have been removed.
Movement:
The Newfoundland's forelimbs have good range and their hindlimbs give a strong boost, which denotes ease and strength. A slight rocking of the back is considered natural. As speed increases, the top line remains uniform.Mantle
- Fur: The Newfoundland has a double layer of waterproof hair. The outer layer is moderately long and straight hair without curls; a slight wave is allowed. The inner layer is soft and dense. It is denser in winter than in summer, but still it is always existing in the rump and chest. The hair of the head, the muzzle and ears are short and thin. Front and rear limbs have bangs. The tail is completely covered with long, dense hair, but it has no flag shape. Any haircut or grooming should not be encouraged.
- Color: Negro, black and white and chestnut.
- Negro: This is the traditional color. It should be as uniform as possible, but a slight tan tone is allowed. White markings on chest are also allowed, fingers and tip of tail, the both.
- black and white: This variety has historical significance for the breed. The preferred marking pattern is: black head, preferably with a white list that extends to the muzzle, black saddle with uniform markings and black upper back and tail. Other parts of the body should be white with minimal mottling.
- Chestnut: This color ranges from chocolate to bronze. White markings on chest allowed, fingers and tip of tail, the both. Black and white and brown dogs must be shown in the same class as blacks.
Size and weight:
Height to the cross: The average height at withers in adult males is 71 cm and of 66 cm in adult females. The average weight is approximately 68 kg in males and 54 kg in females.
A large animal is valued, but this should not be more important than the general state of health, symmetry, strong structure and correct movement.
Fouls:
Any deviation from the aforementioned criteria is considered as a fault and the severity of this is considered to the degree of the deviation to the standard and its consequences on the health and well-being of the dog..
- General appearance: very long limbs, lack of substance.
- General structure of the bones: flojedad, fine bones.
- Character: aggressiveness or shyness.
- Narrow head.
- Long or pointed snout.
- Pronounced noses.
- Round eyes, saltones, yellow, or with a pronounced third eyelid.
- Convex back, float or concave.
- Forelimbs: sunken metacarpus, crushed feet, fingers that turn inward or outward, absence of membrane between fingers.
- Hind limbs: knee joint very straight, cow hocks, crowded limbs, feet twisted inward.
- Short tail, long, doubled or bent.
- Take short, quick steps, dragging the feet, obliquely displaced like a crab; tight and knitting motion, crossing the front limbs, with deviated feet in or out; high movement (hockney action); amble step.
- Sparse hair; absence of inner layer of hair
FALTAS DESCALIFICANTES:
- Aggressiveness or extreme shyness.
- Any dog showing clear signs of physical or behavioral abnormalities must be disqualified..
- Upper or lower prognathism, arch of deviated incisors.
- Short straight hair.
- Marks of a color other than white on black or brown dogs.
- Any color other than black or black and white or brown.
N.B.:
- Males should have two normal-appearing testicles fully descended into the scrotum..
- Only functionally and clinically healthy dogs, with the typical conformation of the breed, should be used for parenting.
TRANSLATION: IRIS Carrillo (Puerto Rico Kennel Federation).
Source: F.C.I - International Cynological FederationAlternative names:
1. Newfs, Newfies (English).
2. Retriever de Terre-Neuve, Chien de Terre-neuve (French).
3. Newfoundland (German).
4. Cão terra-nova (Portuguese).
5. Perro de Terranova (español).
▷ The world of Pets: Dogs, cats, birds, reptiles, amphibians
Castro Laboreiro Dog  FCI 170 - Molossoid . Mountain
FCI 170 - Molossoid . Mountain
Content |
|---|
History
The Castro Laboreiro Dog (Cão de Castro Laboreiro) It is a breed of Portuguese dog of large size. Originating in the parish of Castro Laboreiro, Melgaço, is a dog type Lupoid amastinado is lighter than other breeds of cattle dogs.
The Castro Laboreiro Dog it has its origin in the region that gave it its name, the people of Castro Laboreiro, in the municipality of Melgaço. It is a rugged mountainous region that stretches from the Miño river to the Peneda and Soajo mountains between the Trancoso rivers, Laboreiro and moro, until around 1400 m above sea level.
Like the dog, Castro Laboreiro is one of the oldest regions of the land of Portugal. The prehistoric remains such as dolmens and rock paintings, They demonstrate the presence of man in the region for thousands of years. The strengths are evidence of the strong presence of Celtic culture in the region. Also the Celts and the Romans came here, the roman roads and the construction of bridges with their landmarks. The castrejas communities have always lived of hunting, fishing, grazing and agriculture.
▷ The world of Pets: Dogs, cats, birds, reptiles, amphibians
Estrela Mountain Dog  FCI 173 - Molossoid . Mountain
FCI 173 - Molossoid . Mountain
Content |
|---|
History
The Dog of the Sierra de la Estrela (Cão da Serra da Estrela) It is a breed of dog native of Portugal, in the mountainous region that bears the same name. It has all the qualities required in this wild region, is intelligent, loyal and brave.
There are those who hold the theory that they were introduced to Portugal by the Visigoths and slowly to various parts of Europe.. The Estrela Mountain Dog was used mainly- in mountainous areas to accompany shepherds and flocks on their annual migrations, defending the wolves and thieves.
It is believed that the two varieties of existing hair: short hair and Longhair, they are due to regional variations. Contrary to what might be expected, the warmest region, the region of Manteigas, is where you could find the long-haired dogs, While short hair varieties were most frequent in the North, in Gouveia e Seia. Crosses between these two varieties were frequent.
In 1934 the standard of the breed was drafted, which was established according to its two varieties of layer. From this point, the cross between two varieties became undesirable. The publication of the rule in 1966 and the recognition of the breed by the FCI, have not brought more popularity to the breed. Over the years 60 and 70, the Portuguese emigrated looking for escape from the regime of poverty. The population of dogs Serra da Estrela declined drastically in that period, but the dedication of some breeders allowed the continuity of the breed.
Today, the Estrela Mountain Dog is highly requested, especially the variety of long hair. While the variety of short hair was more numerous at the beginning of the last century, is the variety of long hair that stands out, especially for being more eye-catching, stylish, with a larger. This made the breeders will focus primarily on the variety of long hair. Today the short-haired variety is particularly vulnerable and rare..
Physical characteristics
The Estrela Mountain Dog is a big dog, rough lines and powerful appearance. The head is huge, rounded and with a stunning skull. It has oval eyes, very expressive, Smart and serene.
The ears they are small and pendants, covered with a soft skin.
mastiff-type molosoid, the Estrela Mountain Dog has a broad chest and a slightly drooping rump. The members are strong and muscular. The tail is long, thick and slightly droopy.
There are two varieties of Estrela Mountain Dog: long hair and short hair. The hair is strong, thick, but not too rough. In some regions it is longer than others, especially in the queue, around the neck and back.
Only allowed the tawny colors, Lupine and yellow, monochrome or marbled.
Observations
Estrela Mountain Dog is a healthy dog, due to the strong natural selection which was exposed. But, There are some diseases of large animals with a higher incidence in this breed. The Dysplasia is one of them, especially that of hip. Due to this trend, owners must use quality diets, not exercise too your dog when he is young, avoid the steep stairs, breaks and slippery floors.
The variety of long hair they require more maintenance: brushed daily to untangle hair.
The variety of short hair only needs weekly brushings. Bathing should only be administered, only, When cannot be avoided,Since the protective greasiness of the skin can be damaged by cleaning products.
Character and skills
The Estrela Mountain Dog has always been kept with the sheep, While pastor was away from his flock the dog developed an independent organization and this led to his character of excellent guard dog.
It is also used for self defense and as a dog shot.
The Estrela Mountain Dog, due to its isolation and difficult access, It has become the home of this breed of dog. His hard hair helps you survive the harsh winters of the region. Each race has its specific character developed throughout its existence, of their own history.
This more or less independent nature makes this breed adapts well to modern times, where instead of caring won, waits for their owners to return from work at the end of the day. They have a lot of patience.
The beauty of this dog, his intelligence and strength, are the characteristics that allow him to be in addition to an excellent guard, a good family dog and very tolerant with children.
Habitat Estrela Mountain Dog
The Estrela Mountain Dog it's a big dog with a big boost. So, an apartment in the city is not ideal for him. Fluctuations of time and temperature do not bother him much, so you prefer to spend the day outdoors. So, the ideal is a house with a large patio or garden where you can move freely. It also, does not want to do without his long walks. For many other canine sports, requiring reliable obedience, is however hardly suitable due to its obstinacy.
Nutrition Estrela Mountain Dog
The Estrela Mountain Dog requires a correspondingly large serving of food, which should also be considered when buying it. Proper dog feeding helps keep it healthy for a long time. Whether one wants to use dry or wet food is a matter of personal preference.. In particular, nutrition during growth, especially in large dogs, sets the course for later life.
While puppies and adult dogs need enough energy, young dogs need an adapted diet, protein rich, to ensure that your muscles and skeleton grow evenly. If the young dog grows too fast on food that is too high in energy, there is a risk of permanent joint problems and malpositions. It also, It should be noted that all large breeds of dogs are at risk of stomach upset if the daily ration is administered at one time.. So, it is better and healthier to divide the food into at least two servings in the morning and at night and then give the animal a break for digestion.
Education and care
Due to the close connection of the Estrela Mountain Dog with humans and their good understanding, good conditions are created for purposeful education. But, the race's own head should not be underestimated. The Hound of the Sierra de la Estrela dog stubbornly reacts to too much hardness in training and the orders he considers meaningless. Therefore, the right key to a successful workout is patience, empathy and a consistent hand. During training special attention should be paid to the tendency to dominate, especially in males.
Although this is rarely directed against humans, but mainly against other big dogs, can disturb harmonious interaction and, above all, The walking. Ideally, great importance should be given to socialization already in the breeder. You should also practice meeting other dogs as soon as possible after your dog has moved in.. You can learn that other dogs are an enrichment and not a danger and that dominant behavior is not tolerated. In a good dog school you will receive many tips when in doubt, which will facilitate the management of your Dog from the Sierra de la Estrela.
A lot brushed in the change of coat
The Estrela Mountain Dog has a dense coat with a lot of undercoat, that adapts to weather conditions. The change of coat is therefore strong in this breed. To facilitate this process for the animal and reduce the amount of dog hair at home, should be brushed sufficiently and correctly, especially during the period. Ideal for this purpose are the special brushes, they can comb the bottom layer. Outside the change of coat phase, brush once a week.. The rest of the preparation is limited to a minimum. Especially if the dog is outside and a lot in the meadows and forests, should be checked regularly for parasites. If required, claws must be shortened with claw pliers.
Typical health and illnesses
The Estrela Mountain Dog it is a very robust animal that does not have to fight with the typical diseases of the breed. But, being a very large breed, you may suffer from dysplasia of the hip joint. Breeders recognized by the FCI only use parents that are not affected by this disease for breeding purposes., which also greatly reduces the risk to offspring.
Estrela Mountain Dog life expectancy
As a healthy race, the Estrela Mountain Dog reaches an age of 10 to 12 years without difficulty and generally without many visits to the vet. Proper nutrition and parenting are the prerequisites for a long and healthy life.
Photos Estrela Mountain Dog
Videos Estrela Mountain Dog
Type and recognitions:
- FCI CLASSIFICATION:
- Group :
- Section : . .
Federations:
FCI ⓘ, AKC ⓘ, ANKC ⓘ, KC ⓘ, NZKC ⓘ, UKC ⓘ – The AKC does not have its own standard and instead is linked to the FCI
FCI breed standard "Estrela Mountain Dog"
Origin:
PortugalDate of publication of the valid original standard:
04.11.2008Use:
Herd guard dog, surveillance and companion dog also used in shooting work.
General appearance:
The Sierra de la Estrela Dog is a mastiff type. There are two varieties of hair: long and short. Rustic, of much substance with a strong movement and stunning attitudes.
The breed has a cheerful look, calm and expressive. Well proportioned, morphologically perfect, compact and rustic; The harmony of the whole is remarkable and demonstrates an ethnic purity of ancient races of the past.
IMPORTANT PROPORTIONS :
Medium long (long sub) tending to the middle line. Depth of chest is less than half of its height at the withers. The muzzle and the skull should be approximately the same length, If that is not the case, the skull should be slightly longer.
Behavior / temperament:
Inseparable companion of the pastor and faithful guardian of the herd protect against predators and thieves. Excellent dog guard farms and households, distrustful of strangers and typically docile towards its master.
Head:
Strong, voluminous. It is elongated and slightly convex profile view. Well positioned and provided to the body, the same as the relationship that keep the skull and facial, accentuate the harmony of the whole. Smooth skin over the skull and cheeks.Cranial region:
- Skull: Well developed, rounded skull facial longitudinal top spindles slightly divergent. Convex profile, superciliary arches slightly developed with a slightly apparent frontal fold. No prominent occipital protrusion.
- Depression links (Stop) : Slightly pronounced, located at a more or less equal distance between the end of the nose and the occipital Protuberance.
facial region:
- Truffle: Straight and aligned with the nasal bridge, well open Windows, big and black.
- Snout: Elongate, slimming progressively towards the tip of the nose, but do not be sharpened. Almost straight nose cane, Although slightly hooked at the end.
- Lips: Well developed but not thick, well bonded without tilting. The mucous membranes of the mouth and palate, as well as the very pigmented black edge of the lips.
- Jaws / Teeth: Well-defined mouth with well-developed jaws, full dentition with strong teeth, White and well implemented and good occlusion. Preferably bite in scissors, accepting bite on clamp.
Eyes: Horizontal, oval-shaped, at the level of the head; are medium-sized, aimed at small, symmetrical and wide open, with a calm and alert expression; Dark amber in colour preference. The eyelids are well bonded and pigmented black edges. A little marked eyebrows.
Ears: Small relative to the rest of the skull, form triangular, thin, rounded at their lower edge, pendants; inserted at a medium height, is tilted back slightly and hang to the sides of the head near the cheeks, revealing a part of your inner side in the base (called Pink ear).
Neck:
Straight, short and thick, correctly inserted on the shoulders and with a slight dewlap but not exaggerated.Body:
- top line: Straight. Level.
- Back: Short preferably, well muscled.
- Pork loin: Lumbar region wide, short, muscular and properly inserted to the rump.
- Rump: Slightly inclined, short, broad and muscled. The height at the Croup should be equal to or slightly greater than the height at the withers.
- Breast : Rounded, without being cylindrical, broad, long and well descended.
- bottom line: The bottom line should gradually and gently rise from the sternum to the groin, not too wide belly, in proportion to the substance of the animal and harmoniously connected with the body.
Tail:
Robust, long, whose tip reaches the tibio-tarsal joint when the dog is standing or at rest. It is thick in the shape of a « scimitar », inserted at a medium height, well covered with stripes on the variety of long hair and hair ; is a hook at the end.
The tail is carried below the horizontal line and falls naturally between the thighs when the dog is at rest. ; When stimulated or in action, it is carried higher than the horizontal line, forming an upward curvature., Go ahead, to the sides or down.Tips
PREVIOUS MEMBERS: Plumb, with bones and joints strong, fairly open with unrestricted movement angles.
- Forearm: Straight, parallel, long, with strong bone and always cylindrical in shape.
- Previous foot: Provided, never too round or too long, I in between a Jack's foot and a foot of Hare (not open), thick, fingers tightened with abundant hair between fingers, dark nails, preferably black, well developed, pads thick and hard.
LATER MEMBERS : Plumb, with bones and joints strong, fairly open with unrestricted movement angles.
- Hock: Somewhat low, average opening, never leaning in or out.
- Metatarsus: Vertical, always cylindrical in shape. Possible presence of single or double spur.
- Rear foot: Identical to the previous foot.
Movement:
Normal and light.Mantle
HAIR: Fur: Strong, very abundant, slightly thick, without excessive hardness with texture similar to the goat hair. The subhair is composed of a thin hair, short, abundant and matted. Usually lighter than outer hair color.
- Long hair variety: Exterior smooth or slightly wavy hair, I uneven and some areas. In the Member, Below the elbows and legs it is shorter and thicker, as well as above the head., ears is gradually shorter from base to tip, being more thin and more soft. It is longest on the queue, where is well thick, thick and long hair. Around the neck and throat and on the thighs abundant long hair as well as on the sides of the forearm.
- Variety short hair: Short hair, evenly distributed over the body, somewhat shorter on the head and members without having hair longer.
COLOR
The following colors are accepted and considered typical:
- Solid: yellow, Fawn and grey in all ranges of intensity of color;
- Wolf Gray: leonado, yellow and grey tones, usually with shaders more light and dark.
- Striped: leonado, yellow or gray as a base with a black Brindle color.
In the craniofacial area a dark mask is typical.
White spots are allowed only on the limbs or feet before and after and a very small extension on the lower region of the neck and chest.
Size and weight:
- Males : 65 to 73 cm..
- females : 62 to 69 cm..
Tolerance + 2 cm..
WEIGHT :
- Males: 45 – 60 Kg.
- females: 35 – 45 Kg.
Fouls:
Any deviation from the aforementioned criteria is considered as a fault and the severity of this is considered to the degree of the deviation to the standard and its consequences on the health and well-being of the dog..
- Appearance: Poor overall appearance, thinness or obesity.
- Height: Outside the limits of the standard but with a tolerance of 2 cm.. of the upper limit.
- Very narrow head, long and pointed.
- Eyes: color clear.
- Ears: incorrectly inserted, very long fleshy or round. Hanging completely flat.
- Tail: Port on the back. Absence of hook.
- Color: Absence of dark mask.
SEVERE FAULTS
- Behavior: Animals that show signs of shyness or nervousness.
- Tail: Amputated or rudimentary.
- Truffle: Pale nostrils, Truffle partially nonpigmented.
- Ears: Amputee.
- Fur: Other than described above.
- Height:
- Males : Below the 65 cm.. or above 75 cm..
- females: Below the 62 cm.. or above 71 cm..
MISS PLAYOFFS
- Behavior: Aggressive or too shy.
- Typicity: Atypical.
- Head: Too narrow, very long and very sharp, total absence of molosser type.
- Jaws: Prognathism or enognatismo.
- Eyes: Eyes of different colour or different size.
- Tail: Anurismo.
- Fur: Completely different hair than typical.
- Color: Any other color not mentioned in the standard. albinism.
Any dog showing clear signs of physical or behavioral abnormalities must be disqualified.
N.B.:
• Males must have two normal-appearing testicles fully descended into the scrotum..
• Only functionally and clinically healthy dogs, with the typical conformation of the breed, should be used for parenting.
Alternative names:
1. Portuguese Shepherd (English).
2. Chien de montagne portugais (French).
3. Serra da Estrela Berghund (German).
4. Perro de la sierra de la Estrela (Portuguese).
5. Perro de la Sierra de la Estrela (español).
▷ The world of Pets: Dogs, cats, birds, reptiles, amphibians
Bosnian and Herzegovinian - Croatian Shepherd Dog 
 FCI 355 . Molossoid . Mountain
FCI 355 . Molossoid . Mountain
Content |
|---|
History
The Bosnian and Herzegovinian - Croatian Shepherd Dog, also called Tornjak, it is an ancient breed of dog, and its exact origin is lost in the meanders of history. Most specialists agree that it is one of the descendants of the Tibetan Mastiff (Do-Khy), that arrived in Europe several thousand years ago.
Some accounts suggest that it already existed in the Dinaric Alps (in present-day Bosnia) at the time of the Roman Empire, almost ago 2000 years. But, the first descriptions of a dog corresponding to the Bosnian and Herzegovinian - Croatian Shepherd Dog can be found in documents of the Bosnian Catholic Church dating from 1067.
Three centuries later, in 1374, Petar Horvat, then bishop of Dakovo, Croatia, He also described a dog that resembled the Bosnian and Herzegovinian - Croatian Shepherd Dog in all aspects, size, color and function. At that time it was called Canis Montanis ("mountain dog") and I was already working with the shepherds, leading flocks of sheep in the mountain pastures and, above all, protecting them from the attacks of wolves.
The name Tornjak first appeared in 1752 in the writings of Father Petar Lukic, member of the Dakovo Catholic Church. It is said to derive from the Croatian word «Tor», which could be translated as "flock of sheep".
This dog was found mainly in present-day Bosnian territory, and to a lesser extent in Croatia. The first scientific references to it date back to the beginning of the 20th century., and more precisely to 1905, when Austrian dog fan Franz Laska accurately identified a mountain dog seen in Bosnia, call Tornjak by the locals. But, the Tornjak remained confined to the mountains for a long time. It even declined sharply in the following decades as lifestyles changed and grazing decreased.. Its population grew from several thousand in the nineteenth century to just under a hundred in the decades of 1960 and 1970, when a few Croatian and Bosnian enthusiasts conducted a census to preserve the breed.
If most of the identified specimens then came from Bosnia, it was in Croatia that a breeding program was established in the late 80. In 1979, in Zagreb (Croatia), the Yugoslavia Canine Association officially recognized the breed, and in 1982 the first litter with a complete pedigree was born as a result of this breeding program. Despite this almost rebirth, the Tornjak he was not at the end of his problems, since the explosion of Yugoslavia in 1991 and the civil war that followed caused him many difficulties.
The new Croatian Canine Association decided to identify a breed Tornjak croata, while his counterpart in Bosnia-Herzegovina spoke of the Tornjak bosnio. Although these dogs were in all respects the same, the fact that they were considered two separate breeds prevented them from breeding with each other, for example.
Was not up 2003 that the two organizations unified their standards under the name of Tornjak. In 2007, the Fédération Cynologique Internationale (FCI) provisionally recognized the Tornjak, that took the name of Bosnian and Herzegovinian - Croatian Shepherd Dog. At that moment, there was 1800 specimens recorded in Croatia, and 2700 in Bosnia.
After this recognition, the breed timidly began to make a name for itself outside the countries of the former Yugoslavia. El American United Kennel Club (UKC) accepted it in 2011, while the American Kennel Club (AKC), the other reference organization in the country, included it in 2012 in his Foundation Stock Service (FSS), a preliminary step before full recognition, what has not yet been produced to date. The first specimens arrived in Great Britain in 2013, and steps were taken to gain recognition from the prestigious and influential Kennel Club (KC), the reference body of the country. They haven't been successful yet. in Canada, the Canadian Kennel Club (KC) does not recognize the Bosnian and Herzegovinian - Croatian Shepherd Dog. But, year 2017 marked its final acceptance by the CFI.
Very popular in his home region, the Bosnian and Herzegovinian - Croatian Shepherd Dog struggles to win over audiences beyond his native region. It is extremely rare in North America, and it is not very common in Western Europe either. In France, He came in 2010. At the end of this decade, there were an average of fifty registrations per year in the Livre des Origines Français (LOF).
Physical characteristics
Great and powerful, the Tornjaks retain above-average agility and flexibility for a mountain dog.
They have an almost square shape, with strong bones that are not heavy, giving them a harmonious overall appearance. The tail is long, very mobile and bushy. When falling to rest, rises well above the level of the back when in action, which is uncommon in mountain dogs. Legs are powerful, parallel and raised.
The head is elongated, with a slight stop. The muzzle is rectangular and ends in a dark nose with wide nostrils.. The eyes are also dark and almond-shaped. The ears, triangular and hairy, stand tall and fall along the cheeks.
The undercoat is dense and thick, with a woolly texture in winter. The stiff top coat is long all over the body, except on the face and front of the legs. It is particularly abundant on the neck, forming a mane that protects it from predator bites.
The Bosnian and Herzegovinian - Croatian Shepherd Dog and the Croatian Sheepdog are the ones that most often have a particular color, although there are white subjects, with only a few small spots of color. White is the most common background color, with markings of various colors: black, brown, cervato… More rarely, some individuals have a black coat stained with white.
Last, sexual dimorphism is well marked in this breed: the female is not only smaller on average by about 5 cm., but also less massive.
Character and skills
The Tornjak he is surprisingly outgoing and caring for a shepherd who has worked for centuries in the mountains. He likes to spend time with his family, and is willing to play with older and smaller animals. In fact, he is a dog that adores children, and can spend hours entertaining them – The opposite also is true. But, due to its size and power, could easily inadvertently push a small child, so it is better if you are already a certain age, especially since then he is more likely to learn to behave with an animal and to respect it. In any case, a young child should never be left alone with a dog, regardless of race.
His attachment to the family he grew up with also means he can hardly get used to life in a new home if life's perils mean he has to change owners.. You are likely to have the greatest difficulty recovering from abandonment.
In addition to their great closeness to their caregivers, the Bosnian and Herzegovinian - Croatian Shepherd Dog he's also surprisingly personable with strangers. It barks when they approach and perfectly fulfills its guardian mission, but do not hesitate to go greet them and accept some caresses once their carer has validated their arrival.
But, it would be a mistake to forget that their main function is to protect their flock. Under his cheerful and friendly airs, hides boundless courage and amazing strength. However, is not aggressive and is content to bark when a threat approaches. But if the threat becomes clearer and your family is in danger, does not hesitate to force its non-aggressive nature and take action; few things can stop it. It also, a malicious person would have no chance to persuade and corrupt him with sweets and caresses, because he is infallibly loyal.
His sociability is also expressed against his peers, to the point that you can generally share your home perfectly with one or more dogs. It also, has no predatory instinct, so it does not see cats or rodents as prey, and therefore is not inclined to chase them. However, the difference in size means that cohabitation can sometimes be dangerous. In practice, if there are small animals in the house, it's better for him Bosnian and Herzegovinian - Croatian Shepherd Dog live outside.
This would not be to displease you. In fact, used to large spaces, not really made for indoor living. You do not need to do a lot of intensive exercises every day, but must be able to move at any time, so it is not at all suited to apartment living, even if his master takes him out for more than an hour a day. Needs a large enclosed garden, where I can patrol, run, to play…
If it can be easily installed outdoors it is because, like any mountain dog, is independent and tolerates loneliness well. It can easily stay at home while its owners are out for the day, and does not suffer from separation anxiety if this absence lasts for a weekend. But, under no circumstances should it be constantly left alone in the garden throughout the day. You need to spend time with your family, and two or three daily walks of at least half an hour each are ideal.
Games and sports activities are also great ways to bond with him., while being physically and mentally stimulated. With an excellent memory that allows you to easily assimilate tricks and commands, has the potential to shine in dog sports like flyball, obedience or agility.
But, you cannot start too early with physically demanding activities. In effect, given its size, when is a puppy, you experience growth spurts during which you need to slow down your burning, or at least avoid any overly intense strain on your joints and skeleton. Otherwise, there is a real risk of injury (sometimes with lifelong sequelae) or malformations.
If you live in a residential area, it is better that the fence that surrounds the garden is solid, to avoid accidents. Similarly, walks in parks and relatively crowded places should always be done on a leash, so you can hold back if you sense a threat. On the other hand, in an environment where encounters are rare (for example, in the mountains), can be free, If and when, of course, has assimilated the withdrawal orders.
Finally, the Bosnian and Herzegovinian - Croatian Shepherd Dog has a serious and powerful bark that can be heard from a distance. Can be heard from a distance, and is also heard when approaching a stranger or when you perceive a suspicious noise. This is reassuring and enjoyable when living in an isolated area., but can quickly cause neighborhood problems in a residential neighborhood.
Education
Like all dogs, the Tornjak should be socialized as soon as you get to your new home. Give you the opportunity to meet all kinds of people, animals and situations during your first months helps you become familiar with the unknown, and to avoid being surprised or even reacting badly as an adult. So, you should not hesitate to take any opportunity to meet the neighbors, friends, dealers, the vet… but also other animals, be it dogs, cats, rodents, horses, cows… You also have to deal with situations that you are not yet used to., especially the ones you will have to deal with regularly afterwards: travel by car, walk around the city, go out in a hectic environment…
It also, given its size, it is advisable to accustom it from an early age to being handled obediently. Brush, bathing or even clipping the claws can turn into moments of complicity with your caregiver, instead of being dreaded tests each time by both protagonists. In any case, trying to groom or bathe a dog 50 kg not accommodated can quickly become an adventure…
Although they have the independent character of herding dogs, to the Bosnian and Herzegovinian - Croatian Shepherd Dog they like to please their owners. It also, as his intelligence and memory are admirable, a caregiver who combines patience and know-how can go a long way in your education, even teaching them many tricks. But, although easier to handle than most mountain breeds, this does not make him a recommended dog for a novice sitter. But, It can be an interesting option for a person with a little experience who wants to face the challenge of a large independent dog..
In any case, traditional training methods should not be used with the Tornjak, as they only reinforce their independent side instead of developing their potential. On the other hand, positive reinforcement, with the help of caresses, treats and stimuli, motivates you to want to learn more and more and allows you beautiful moments of complicity.
The assimilation of memory is of particular importance: given its size, it is better for such a dog to obey the finger and the eye when his handler asks him to stop pulling on the leash or to come back to him. This is the essential condition so that you can enjoy nature with total freedom, without being put on a leash.
On the other hand, protection of the pack is instinctive in the Tornjak: you don't really need any training to play this role perfectly.
Health
The Tornjak it is an extremely robust breed of dog, with a life expectancy much higher than the average of dogs of its size, to the point that some specimens reach the 15 years of age.
The thick, woolly coat of the Tornjak helps protect you from cold and bad weather, as well as the rays of the sun. It is clearly a dog made to live outdoors, who is not afraid of low temperatures as long as he has a place to take refuge. On the other hand, when the mercury rises and the heat wave sets in, it is better to limit your activities and make sure you have the opportunity to rest in a shady place.
Although they are generally healthy, the Bosnian and Herzegovinian - Croatian Shepherd Dog they are not exempt from certain problems, especially those that affect larger dog breeds. They are predisposed to ...:
Hip and elbow dysplasia, joint problems whose origins can be hereditary and cause more or less severe locomotor difficulties; gastric dilation-torsion, which often follows too rapid ingestion of large amounts of food, and it's fatal if a vet doesn't intervene quickly; protein intolerance, what can take, among other things, to a deterioration of the coat.
Other diseases have been reported occasionally in some subjects, but they are still exceptionally rare. These include anemia or von Willebrand disease, a hereditary condition.
To limit the risk of having a puppy with a hereditary and / or congenital problem, nothing better than adopting from a breeder Tornjak serious and responsible. In particular, the professional must present an updated health or vaccination record, that allows to verify the vaccines received by the animal, as well as a certificate of good health signed by a veterinarian. But, the professional should also be asked to provide the results of the genetic tests performed to both the parents and the child.
It also, the floppy ears of Tornjak can quickly become nests of infection if not cleaned weekly.
It also, how you spend most of your time outdoors, their fur is likely a breeding ground for parasites: even more than most tornjaks, it is imperative to be rigorous in the administration of regular pest control treatments to avoid this type of inconvenience.
Last, the fact that he is generally in good health does not exempt him from wearing it regularly (at least every year) to a routine check-up at the vet, just to keep it healthy. This not only ensures that you are up to date on your vaccinations, it also allows early detection of any health problems.
Grooming
The Tornjak rarely poses problems regarding your health, but its maintenance requires some effort.
First of all, its thick coat needs to be brushed once or twice a week to avoid knots and remove dirt, and its size means that this task takes some time.
During their annual molt periods in the spring and fall, a lot of undercoat is shed, and brushing should then become a daily routine to deal with the large amount of dead hair.
Brushing is also an opportunity to inspect your skin and make sure it is not injured., Court, sore or irritation. Spending most of the time outdoors, he is more exposed to this type of problem than his peers who live in an apartment and only go out for half an hour each day.
In any case, if grooming is done regularly, can remove a large part of the dirt from their fur, keeping it relatively clean and odorless. So, it is not necessary to bathe your dog often. Unless, of course, got particularly dirty, you can be content with doing it twice a year, at the time of the move. It is necessary to use a mild shampoo designed specifically for dogs every time.
On the other hand, as with any dog with floppy ears, special care is required to prevent dirt from building up and causing infection. So, at least once a week, brushing his coat should be followed by cleaning his ears with a clean cloth.
You should also take the opportunity to check your eyes and clean them, to limit the risk of eye infection, although, unlike ears, are not particularly susceptible to it.
To end the beauty maintenance session, a teeth cleaning is de rigueur. It´s, in effect, the best way to effectively protect them against dental plaque formation, cavities and other problems at this level. Ideally, it should be done daily.. No matter how often you do it, always use a toothpaste specially designed for dogs.
It may also be necessary to trim your dog's claws from time to time. Even if your dog lives outdoors, natural wear and tear is not always enough to file its strong claws. If you hear them hitting the ground when you walk, have grown too long and could injure or break: it's time to cut them with a special tool.
Although all these operations do not require any particular knowledge, it is better to learn to do them correctly, especially to avoid hurting or even injuring your partner. It can be useful the first time to have the help of a veterinarian or a professional groomer to learn the correct gestures to perform.
Buy a “Shepherd from Bosnia-Herzegovina and Croatia”
The price of a puppy Bosnian and Herzegovinian - Croatian Shepherd Dog is of some 1000 EUR, but it's a mean: the sale price varies according to the prestige of the breeding, the ancestry of the animal, but also and above all its characteristics. On the other hand, there is not a big difference according to sex: males and females are generally priced similarly.
Having said that, the Bosnian and Herzegovinian - Croatian Shepherd Dog still hard to find outside the countries of the former Yugoslavia. So, it may be wise to turn to a Croatian breeder, Slovenian, Bosnian or Serbian to find the right one. The sale price will not necessarily be much cheaper, but then import costs must be added to the budget, registration and transportation.
It is possible to find hatcheries in the United States, but it is also still very rare there.
Characteristics "Bosnian and Herzegovinian - Croatian Shepherd Dog"
Coexistence is important that you have with your new friend. Before considering the acquisition of a dog of the breed "Bosnian and Herzegovinian - Croatian Shepherd Dog" you know certain factors. Not all breeds of dogs are apt to live in an apartment, you must take into account his character, their need for exercise, their interaction with other pets, their care and if you have small children, their level of tolerance towards them.
Adaptation ⓘ2,0 of 5 stars (based on 1 review)
|
friendly dog ⓘ4,0 of 5 stars (based on 1 review)
|
hair loss ⓘ3,0 of 5 stars (based on 1 review)
|
|---|---|---|
Affection level ⓘ5,0 of 5 stars (based on 1 review)
|
Need for exercise ⓘ3,0 of 5 stars (based on 1 review)
|
Social need ⓘ3,0 of 5 stars (based on 1 review)
|
Home ⓘ3,0 of 5 stars (based on 1 review)
|
Toilet ⓘ3,0 of 5 stars (based on 1 review)
|
Friendly with strangers ⓘ4,0 of 5 stars (based on 1 review)
|
barking ⓘ3,0 of 5 stars (based on 1 review)
|
Health ⓘ2,0 of 5 stars (based on 1 review)
|
Territorial ⓘ3,0 of 5 stars (based on 1 review)
|
Cat friendly ⓘ3,0 of 5 stars (based on 1 review)
|
Intelligence ⓘ3,0 of 5 stars (based on 1 review)
|
Versatility ⓘ3,0 of 5 stars (based on 1 review)
|
Child friendly ⓘ4,0 of 5 stars (based on 1 review)
|
Surveillance ⓘ3,0 of 5 stars (based on 1 review)
|
joy ⓘ3,0 of 5 stars (based on 1 review)
|
Images of the «Pastor of Bosnia-Herzegovina and Croatia»
Photos:
1 – «Pastor of Bosnia-Herzegovina and Croatia» by https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Bosniantornjak.jpg
2 – And little Tornjak. Colour: white & black by Canarian, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
3 – And little Tornjak. Colour: white & brown by Canarian, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
4 – A Croatian Tornjak (aka Croatian Mountain Dog or Bosnian and Herzegovinian – Croatian Shepherd Dog) female by Canarian, CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
5 – And little Tornjak. Colour: white & black by Canarian, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
6 – Toro the Tornjak. Photo taken in a dog shelter in Zadar, Croatia by Mirta12, CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Videos of the «Pastor of Bosnia-Herzegovina and Croatia»
Type and recognitions:
- FCI CLASSIFICATION:
- Group :
- Section : . .
Federations:
- – FCI – Pinscher and Schnauzer-Molossoid type dogs – Swiss Mountain Dogs and Cattledogs. Section 2.2 Molossoid, mountain type. ⓘ
- – AKC – (FSS) ⓘ
FCI breed standard "Bosnian and Herzegovinian - Croatian Shepherd Dog"
Origin:
Bosnia y Herzegovina, CroatiaDate of publication of the valid original standard:
19.11.2007Use:
Herding and protection of livestock and farm pens and guard dog.
General appearance:
The Tornjak is a large and powerful dog, well proportioned and agile. The body is almost square in shape. The bone is not light, but it's not heavy or rough anyway. Standing and moving is strong, harmonious and well balanced. The coat is long and thick.
IMPORTANT PROPORTIONS:
The body is almost square. The length of the body must not exceed its height by more than one 8 %. The radius between the length of the skull and the muzzle is 1:1.
Behavior / temperament:
Of good disposition, friendly, brave, obedient, Intelligent, full of dignity and confidence. Fierce looking after the property entrusted to him, cannot be bribed and is suspicious of strangers. Devoted to his master and very calm in his presence. Very affectionate with the people who live in his environment. Learn quickly and keep this learning in your memory for a long time. Pleasantly performs the tasks assigned to you. It is easy to train.
Head:
Elongated. The radius between the skull and the muzzle is 1:1.Cranial region:
The upper lines of the skull and snout are divergent.
Supra-orbital arches are slightly visible.
The back of the skull is elongated but moderately wide.
The area between the supra-orbital arches and the occiput is flat.
The occipital protrusion is very slight.
- Nasal frontal depression (stop): Slightly pronounced.
facial region:
Nose: Grand, with nostrils wide enough. Must have dark pigmentation. Pigmentation must be in harmony with the color of the coat. Depigmentation is not allowed.
Snout: Rectangular. The bridge of the nose is perfectly straight.
Lips: Tight, with dark pigmentation.
Jaws/teeth :The jaws are very long and strong. Perfect scissor bite, full dentition.
Eyes: Almond biscuits, attached eyelids, dark color. Dark pigmentation on the edge of the eyelids.
Ears: Medium-sized, triangular, bent and earrings, high insertion. Carried close to the cheeks. With shorter hair.
Neck:
Medium length, powerful, carried slightly low. Well attached skin. With abundant and long hair forming a mane.Body:
Cross: Moderately developed.
Back: Short, the court, moderately wide and straight.
Pork loin: The connection between the chest and the rump is short, moderately wide; in females it is a little longer.
Rump: Long Middle, wide and slightly inclined.
Breast
: Very spacious, deep, wide and oval. Lower chest reaches at least elbows. Never barrel shaped. The chest is strong with the tip of the sternum moderately pronounced.
bottom line: Well muscled abdomen. The lower line is not retracted but gradually rises from where the sternum ends towards the posterior.
Tail:
Long, inserted at a medium height, very mobile. When at rest it is always hanging and in motion it is always above the level of the upper line, this is a characteristic of the breed. With abundant hair and characteristic fringe.Tips
Strong and well angled.
PREVIOUS MEMBERS:well developed, with strong bone and tight muscles. Parallel and straight when stationary.
Blades:Long Middle, well leaning back. The scapulo-humeral angle is approximately 120º..
Humeri:Muscular and strong, almost the same length as the scapulae.
Elbows:Moderately close to the body.
forearms:Strong bones and developed, straight muscles.
Metacarpus:With slight inclination.
Previous feet:Fingers arched and together. Pigmented nails, desirable dark pigmentation. Elastic pads, hard and compact, dark pigmentation is desired. Front feet are more developed than rear feet.
LATER MEMBERS:Strong and parallel. Straight when standing with proper angulation. Well angled knees.
Thighs:Widths, strong, good muscular.
Warm:With good bodybuilding, strong wide and the same length as the femur.
Tarsos:Firms. Insertion a little high.
Metatarsals:Strong. They can have spurs.
Hind feet:Fingers arched and together. Pigmented nails, dark pigmentation is desirable. Elastic pads, hard and compact, dark pigmentation is desirable.
Movement:
The Tornjak is a trotter. The movement is well balanced, stretchy and powerful, harmonious and with great drive. In motion the top line is firm.Mantle
SKIN: The skin is thick, well adhered throughout the body.
Fur: In general, the Tornjak is a long-haired dog, thick, rustic and straight. It is especially long at the top of the rump; over shoulders and back can be slightly wavy. It is short on the muzzle and face, above the imaginary line that connects the ears, over the ears and on the front of the legs and feet.
It is especially abundant around the neck (mane), dense and long over the thighs. Forms fringes on the forearms. In well-coated dogs, it is also especially abundant on the back of the metatarsals.. The tail is very bushy with very long hair. The winter undercoat is long, very thick and with a pleasant woolly texture. The hair is thick and dense and should not split in two along the top line.
Color: As a rule, the Tornjak is of split color with characteristic markings in various solid colors.. Generally the dominant background color is white. There may be dogs with a black coat and white markings that usually appear around the neck, over the head and along the legs. There may also be almost entirely white dogs with only small markings.
Size and weight:
Height to the cross:
Males: 65 – 70 cm.
females: 60 – 65 cm.
Tolerance+/- 2cm.
Fouls:
Any deviation from the aforementioned criteria is considered as a fault and the severity of this is considered to the degree of the deviation to the standard and its consequences on the health and well-being of the dog..
- Too thin or too heavy bone.
- Very fine or very coarse head.
- Missing ears (inclusion, long, hair).
- Bite in clamp.
- Absence of 2 p2, 2 p3.
- Absence of more than 2 p1.
- Very long back.
- Curved or saddled top line.
- Obviously exaggerated dog.
- Angulations with faults.
- Elbows in or out.
- Tail resting on the back.
- Tail with little hair.
- Hair with insufficient length.
- dark mask.
- Weak feet.
FALTAS DESCALIFICANTES:
- Aggressiveness or extreme shyness.
- Any dog showing clear signs of physical or behavioral abnormalities must be disqualified..
- Lack of type (atypical dogs).
- Sexual type deviation.
- Anomalies in eye color and shape (wattled eyes, vicious expression, different colored eyes).
- Entropion, ectropion.
- Prognathism or enognatismo.
- Absence of any other tooth than those mentioned as missing.
- Too short hair.
- Lack of undercoat.
- Broken tail.
- Absence of tail.
- Solid color dogs.
- albinism.
- Atypical distribution of colors on the body.
- Differences in the limits of the indicated heights (including tolerance).
- Cosmetic treatment in the dog or evidence of cosmetic or surgical treatments.
N.B.:
- Males should have two normal-appearing testicles fully descended into the scrotum..
- Only functionally and clinically healthy dogs, with the typical conformation of the breed, should be used for parenting.
Alternative names:
1. Tornjak (English).
2. Tornjak (French).
3. Tornjak, Bosnien und Herzegowina und Kroatien (German).
4. Tornjak (Portuguese).
5. Tornjak (español).
▷ The world of Pets: Dogs, cats, birds, reptiles, amphibians
Central Asian Shepherd Dog  FCI 335 - Molossoid . Mountain
FCI 335 - Molossoid . Mountain
Content |
|---|
History
The dog Central Asian Shepherd Dog (среднеазиатская овчарка or Sredneaziatskaya Ovtcharka, also known as, Volkodav or The Crusher Wolf) is recognized by the FCI, as a breed of molosser dog Russia, where most of the copies.
Russian cynological clubs agree that this is one of the most popular breeds in the country, on many occasions, considering it the number 1 in the ranking of Russian dog breeds.
The Central Asian Shepherd Dog It probably originated in a geographical area between the Urals, the Caspian Sea, Asia minor, and the Northwest of the border of China. The Central Asian Shepherd Dog, as well as mixtures with other breeds, yet, can be found in their countries of origin, as Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, Kazakhstan, Afghanistan, Uzbekistan and neighboring countries.
Some serve as guardians of livestock, some protect their owners, and some are used for dog fighting, which is a national tradition in many countries of the region. Russian scientists and biologists have studied the local dog population since the 18th century., so far.
After the Communist revolution, the Soviet Government focused on the working dog breeds for the Red Army, and imported the best representatives of the race to Russia accordance with the requirements of the army and guard dogs. For decades, This practice has harmed the local population. In addition to a large number of casualties, the introduction of new breeds to the region led to crossbreeding. With the time, purebred dogs were only left with some pastors and race enthusiasts, but in other places there was an excess of crosses.
But, and despite all, today the population of purebred dogs Central Asian Shepherd Dog remains stable, in general, and the reproduction of some true quality dogs that do honor to his capacity for work has been, regardless of country of origin.
In Europe, the Central Asian Shepherd Dog is relatively unknown, but in the countries of Central Asia it is still used as a working dog and accompanies shepherds on their walks through the steppes.
Physical characteristics
This breed has many varieties that differ in the size, the color, head types, and the types of fur. For these reasons it is very difficult to establish an official standard of the breed.
The Central Asian Shepherd Dog it is a dog of large or medium size, of rough constitution and strong musculature. Its coat is composed of the hard and smooth top layer and the abundant and dense inner layer. The top layer can be short (3 – 5 cm.) or slightly longer (7 – 10 cm.). With a longer top layer forms a distinctive mane around the neck. Due to a well developed undercoat and different lengths of the top coat, dogs adapt well to different weather conditions.
The coat color of the Central Asian Shepherd Dog it's very diverse: it comes in the colors white, black, grey, red fox, Brown grey, straw yellow, mackerel, spotted and mottled.
The ears are triangular, low-set and pendulous. The tail is thick at the base and set quite high. The natural tail is long and is carried like a sickle tail. Tail and ear docking is still practiced in the countries of origin.
Although there are unique characteristics of the purebred breed of dog Central Asian Shepherd Dog, such as being extremely flexible, This is very notable in their joints, have false ribs, the very strong neck and a large Chin.
Some have a black mask. The head is very solid, the neck is of low insertion, short, with double chin. The body is quite broad and proportionate with very flat muscles.. The ribcage appears very long, because they have their famous false ribs. The legs are straight, typical movement is a gallop.
He has expressive eyes, almost human, revealing his inimitable intelligence.
According to the qualities of work required by the owners, the modern Pastor of Central Asia has been raised in different directions, trying to highlight specific skills. Within the traditional area of origin of these canes, the dog fights were always, but they were never so cruel and destructive as the fights of type Pit Bull Terrier.
Every year the shepherds of the area would gather to organize dog fights Central Asian Shepherd, but unlike the bloody and ruthless fights of which we are used to hearing news, in this case they were fighting for the guardianship of a herd, and the winner was the dog that eventually, it was done with the control of it. It was about 'domination' instead of destroying each other's own kind.
Dogs rarely hurt each other, minor scratches were caused in most cases. only true leaders, In fact, you measured through a real fight, but that was not the most common. The primary task of these dogs has always been the defence of the flock to the attacks of various predators and venomous snakes.
The Pastor of Central Asia, It is one of the most powerful group of livestock guardian dogs dogs, after the Caucasian Shepherd Dog, the Kangal, Akbash, for example.
The height at the cross 60 to 65 cm.. And weigh in 37 to 50 kg.
Character and skills
In the news, rural people continue to demand and use the Central Asian Shepherd Dog like cattle watchdog, Although not as well as old.
These dogs, to varying degrees, are protectors against human intruders, they are very territorial, excellent with children, shall ensure them as if were his flock were. Love and respect for older people are some of its characteristics, to protect all small animals from predators, they are very kind and attached with the members of the family.
They do not need any complicated training to learn the basic rules of the house but they are quite stubborn and very independent dogs., the Central Asian Shepherd Dog It must be able to work as a team to protect sheep against predators, therefore, If the animal has an overly aggressive character, both other dogs as with people outside the family, they cannot be members of a Pack, and it would not pass the simple test for the fulfillment of the object origin of the race.
The Central Asian Shepherd Dog can come from build lines which print a very different character: of work, combat, and livestock guardian, and act accordingly, regardless of the country of origin.
According to the different kennel clubs, the classification within the groups varies, The Russian Kennel Club classifies the Central Asian Shepherd Dog like a working dog, that is reflected in the exceptional results in obedience, protection and training relating to the army.
Modern reproduction of the main Canine Clubs of Russia requirements, require to register copies of Central Asian Shepherd Dog a mandatory temperament test and an accredited training certificate, Besides show rating. In these tests the ability of the dog stands for fit and adapt to dog guardians shepherds of other flocks, not be cause for conflict between dogs. The FCI classifies Central Asian Shepherd Dog in the group of dogs Molossoid.
While it is a good dog to live, We must not forget that the Pastor of Central Asia is a livestock protection dog, people and possessions, He was raised to solve single problems, is independent-minded, strong, brave and responsible.
It is a large but agile dog, sometimes described as a cat with dog skin, for that reason, and taking into account his strong instinct for protection and territoriality, It may not be a recommended breed for a novice owner.
Sensitive and Intelligent, the Central Asian Shepherd Dog You will respond better to someone who can inspire loyalty in you as well as strong leadership..
Heavy-handed training will be counterproductive with this breed, but respectful training, reflexive will result in a dedicated and inseparable companion.
The Central Asian Shepherd Dog he spent a considerable amount of time moving around in his homeland, and this kind of slow but steady exercise is what he likes more.
With a work to be done and a piece of property to protect, is the highest point of happiness and will always keep an eye on everything that happens.
Central Asian Shepherd Dog Health
the breed is still considered very healthy and extremely robust. Owners should not fear the typical diseases of the breed. But, from time to time, like in all big dogs, joint problems occur, especially on the knees.
Central Asian Shepherd Nutrition
Although many joint diseases are inherited, symptoms can often be prevented or at least relieved with the help of proper diet and posture. Particularly in the growth phase of dogs, care must be taken that animals do not shoot too fast. Too rapid growth due to excessive protein intake in the growing months is considered one of the most common causes of later joint diseases. In addition to a fairly low protein food, given in small amounts about three or four times a day, young dogs should also be physically preserved during this phase. Stairs or long walks should be avoided..
Meat as the main component of food
When the Central Asian Shepherd Dog is fully developed, the protein content of the feed can be increased again. The main component of dog food should be – like in all dogs – high quality meat. It can be cooked or raw or, if industrially produced food mixtures are used, can be dry or wet. Regardless of the feeding method preferred by the respective owner, it is important that the content and composition of the food is adapted to the needs of the dog. According to age, sex, size, activity level and living environment, the composition of the necessary nutrients can vary considerably. There is no correct food for Central Asian Shepherd Dog.
How much food does he need? Central Asian Shepherd Dog?
Nor can the question of the amount of food for all dogs of this breed be answered in general. If the composition of the food is correct, the Central Asian Shepherd Dog can cope with surprisingly small portions. So, two meals a day are usually enough for an adult dog, which should be given at fixed times if possible. Portions too large, too many "snacks" between meals and not resting after feeding can increase the risk of stomach torsion.
Central Asian Shepherd Dog care
Like nomadic dog, the Central Asian Shepherd Dog it's quite undemanding, this applies not only to the size of your food portions, but also in your care. Short to medium length coat proves to be very resistant and requires little grooming. But, should be brushed regularly to remove dirt and maintain healthy hair structure. The claws should also be trimmed to avoid injury and teeth, ears and eyes should be checked and cleaned regularly.
Central Asian Shepherd Dog Education
The purchase of a Central Asian Shepherd Dog must be well considered – although this applies to all breeds of dogs, it is especially true for this breed from Central Asia. It is not a family dog ​​in the classical sense nor is it suitable for a city life. This freedom-loving and independent dog finds it difficult to cope with living conditions in European industrial nations.
Who is this breed suitable for?
In the hands of livestock keepers and keepers who live in remote and isolated places, this protective dog of the pack is still in the best hands. Also people who live far from the city, own a large lot and wish to have a capable watchdog, can be considered as owners of this Central Asian Shepherd Dog. But, experience and some knowledge in dog training should be prerequisites to keep this breed. It also, an owner needs above all time and patience, because the socialization and education of this self-confident four-legged friend, who doesn't think much about blind obedience, It is hard work. How Central Asian dogs tend to dominate, they need a trainer who constantly sets limits for them and who shows them with the necessary empathy (not to be confused with willingness to compromise) that it is worth trusting and following your human.
Can a harmonious coexistence succeed?
The Central Asian Shepherd Dog certainly not a family dog ​​in the classical sense, so its maintenance as a pure house and companion dog is absolutely inadvisable. This does not mean that a Owtscharka can't live together with humans. In a family that appreciates its natural instinct for vigilance and protection and gives it its original task of guarding the house, the yard and the cattle, the Central Asian Shepherd Dog is quite adaptable and human-oriented. A basic socialization, that is to say, early contact with other people and animals, is as important to harmonious coexistence as sufficient opportunities for running and consistent parenting.
Central Asian Shepherd Dog Pictures
Central Asian Shepherd Dog Videos
Type and recognitions:
- FCI CLASSIFICATION:
- Group :
- Section : . .
Federations:
- – FCI – Pinscher and Schnauzer-Molossoid type dogs – Swiss Mountain Dogs and Cattledogs. Section 2.2 Molossoid, mountain type. ⓘ
- – AKC – FSS ⓘ
- – ANKC – Group 6 (utility dogs) ⓘ
- – NZKC – Utility dog ⓘ
- – UKC – Watchdog ⓘ
FCI breed standard "Central Asian Shepherd Dog"
Origin:
RussiaDate of publication of the valid original standard:
13.10.2010Use:
Guard and surveillance dog.
General appearance:
The Central Asian Shepherd Dog is of a harmonious build and great stature, moderately long (never with a long or short body). Robust and muscular body, bulky but not with visible muscles.
Clearly defined sexual dimorphism. Males are thicker and more courageous than females with a more pronounced cross and a larger head.. Full maturity is reached at the age of three.
IMPORTANT PROPORTIONS: The length of the body only slightly exceeds its height at the withers. Increased height is desired but proportional structure must remain. Length of forelimbs to elbows is 50 – 52% the height at the withers.
The length of the snout is less than ½ the length of the head but more than 1/3.
Behavior / temperament:
Self-confidence, silent, balanced, proud and independent. Dogs have great courage and high capacity for work, resistance and a natural instinct for territoriality. Courage in the face of large predators is one of its characteristics
Head:
Solid and well balanced with the overall appearance. The shape of the head is rectangular, top and side view.Cranial region:
- Skull: deep. The antecara is flat and the skull area is flat and long. Occiput well defined but hardly visible due to well-developed musculature. Supraorbital arch moderately defined.
- Depression links (Stop): Moderately defined.
facial region:
- Truffle: Grand, well developed but not exceeding the general outline of the muzzle. The color is black but in white and beige dogs the truffle may be somewhat lighter.
- Snout: The muzzle is blunt and of moderate length., it is rectangular seen from above and the sides tapering slightly towards the nose. The muzzle is bulky, deep and well filled under the eyes. Wide nasal bridge, straight and sometimes slightly sunken. Well developed chin.
- Lips: Thick. Upper lip tight, covering the bottom when the mouth is closed. Full black pigmentation preferred.
- Jaws / Teeth: The jaws are strong and wide. Teeth are big, white and next to each other, 42 in total. Incisors positioned aligned. Scissor bite accepted, reverse clip and scissors. Canines positioned well apart. An injury to a tooth that does not affect the use of the bite is of no consequence.
- Cheeks: Cheek bones are long and well developed, without interfering with the straight rectangular shape of the head.
- Eyes: Medium size, oval-shaped, placed well apart, looking well ahead. Moderately sunken placement. Eye color from dark brown to hazel. Darker color is preferred. The eyelids are thick and preferably with the lower eyelid not too loose. The third eyelid should not be visible. The edge of the eyelids is preferred fully pigmented. Whatever the hair color, the eyelids must be black. His expression is confident and dignified.
- Ears: Medium size, Triangular shape, thick, low insert and pendants. Your lower level or slightly below your eyes. Traditionally amputated ears as illustrated on the first page, which is practiced in the country of origin and in countries where it is not prohibited by law.
Neck:
Neck is medium length, very strong, oval transversely, well muscled and low set. The dewlap is a characteristic of the breed.Body:
- top line: Well proportioned and well sustained. In the posture you must maintain the typical upper line.
- Cross: Well defined, especially in males, muscle, long and tall with a well defined transition to the back.
- Back: Straight, width, good muscular; the length is ½ of the length of the withers to the insertion of the tail.
- Pork loin: Short, width, muscle, slightly arched.
- Rump: Moderately long, wide, well muscled, slightly inclined towards the tail insert. Height at withers exceeds height above hip in 1 – 2 cm..
- Breast : Deep, long, width, well developed, rib cage widening to the posterior. False long rib. Lower chest at elbow level or slightly below. The forechest extends slightly in front of the humerus/scapula joint.
- Bottom line and belly: Moderately retracted abdomen.
Tail:
Thick at the base and somewhat high insertion. The natural tail is carried curved in the shape of a sickle or curved in a loose ring that begins in its last third.. When alert, the tail rises to the level of the back or slightly higher. Traditionally the tail is docked in the illustrated manner which is practiced in the country of origin or in countries where it is not prohibited by law..
Natural glue is valued the same as amputated.Tips
PREVIOUS MEMBERS:
- General appearance: Right members of strong bones, viewed from the front parallel and not very close to each other. Seen on side, the forearm is straight.
- Shoulder: Long scapula, well inclined, forming an angle with the forearm of approximately 100°. Well muscled.
- Forearm: Oblique, long and strong.
- Elbows: Tight fitting without turning in or out. Arm: Straight, very strong bone, long, oval transversely.
- Metacarpus: Moderately long, width, strong, rights.
- Previous feet: Large, rounded, arched toes, bulky and thick pads; nails can be any color.
LATER MEMBERS:
- General appearance: Viewed from behind straight and parallel, placed somewhat more apart than the previous ones.
- Thigh: Width, moderately long and with strong musculature.
- Knee: Without turning neither inwards nor outwards. Its angulation is moderate.
- Leg: Always the same length as the thigh.
- The Hock joint: Moderately angled.
- Metatarsals: Very strong and of moderate length, perpendicular. Without spurs.
- Hind feet: Large, round, arched toes, bulky and thick pads; nails can be any color.
Movement:
Well balanced and elastic. Jog with free reach of the forelimbs and strong push from the rear. Top line remains firm during movement. All joints tilt effortlessly. The angulations of the posterior are more defined during the movement than during the stop..Mantle
SKIN: Thick, loose enough to prevent injury during combat against predators.
- Fur: Abundant, smooth, thick with well-developed inner hair. The hair on the head and on the front of the limbs is short and thick.. The hair on the cross is sometimes longer. Outer hair may be short or slightly longer. Depending on the length of the outer hair there may be shorter hair (3 – 5 cm.), covering the entire body or longer hair (7-10 cm.) forming a mane on the neck, feathers behind the ears and on the back of the limbs and on the tail.
- Color: All except genetic blue or genetic brown in any combination and black cloak on fire.
Size and weight:
Height to the cross:
- Males: Minimum 70 cm..
- females: Minimum 65 cm..
The largest size is desired but the proportional structure remains.
Weight:
- Males: Minimum 50 Kg.
- females: Minimum 40 Kg
Fouls:
Any deviation from the aforementioned criteria is considered as a fault and the severity of this is considered to the degree of the deviation to the standard and its consequences on the health and well-being of the dog..
- Slight deviation from the typicality of the breed.
- Females with male type tendencies.
- Rounded skull, narrow snout, narrow lower jaw, small nose.
- Oblique eye placement or eyes close together, loose eyelids.
- High insertion of the ears.
- Thin or hanging lips.
- Height above rump. Slightly short rump.
- Narrow forehead.
- Exaggerated angulations of the posterior.
- Open foot and long toes.
- Hackney movement, slightly unbalanced movement.
- Too short hair.
SERIOUS FAULTS:
- Too nervous.
- Significant deviations from the type and structure required.
- Long-limbed appearance, Lightweight bones, soft muscles.
- Very light eyes or protruding eyes.
- Top line descended.
- Croup much higher than the cross.
- Narrow rump, short and steep.
- Naturally short tail, broken tail.
- Very high metacarpus, low.
- Hindquarters placed too far apart under the body.
- Height to the cross 2 cm less than the minimum required in the standard.
FALTAS DESCALIFICANTES:
- Aggressiveness or extreme shyness.
- Any dog showing clear signs of physical or behavioral abnormalities must be disqualified..
- Shy or overexcited.
- Male female type.
- Prognathic or clearly enognathic bite.
- Different colored eyes, blue or green eyes, bizco.
- Loose joints.
- Hair of any combination of genetic brown or genetic blue.
- Fire color with a black cloak.
- Cloak the soft or smooth.
- Unbalanced movement.
N.B.:
Males should have two normal-appearing testicles fully descended into the scrotum..
Only functionally and clinically healthy dogs, with the typical conformation of the breed, should be used for parenting.
Source: F.C.I - International Cynological FederationAlternative names:
1. Alabai, Central Asian Ovtcharka, CAO Aziat (English).
2. Chien de berger d’Asie centrale (French).
3. Zentralasiatischer Owtscharka (German).
4. Türkmen Alabaý, mastim-da-ásia-central (Portuguese).
5. Perro Pastor de Asia Central (español).
▷ The world of Pets: Dogs, cats, birds, reptiles, amphibians
Leonberger  FCI 145 - Molossoid . Mountain
FCI 145 - Molossoid . Mountain
Content |
|---|
History
The Leonberger it is a very big and beautiful dog. In his head and in his charisma he remembers a St. Bernard and a lion at the same time. And this is not a coincidence, because the St. Bernard is one of the ancestors of Leonberger. The Leo, as his friends call it, It is a young and at the same time old breed of dog. This breed is ancient, because it has been specifically bred to the standard since 1846. The Leo It, therefore, one of the oldest dog breeds in modern breeding. At the same time it is a breed of young dog; because it was only created at that time. Most other pedigree dogs have a long history and originated from ancient working dog breeds..
The Leonberger, However, has a different and unique story. Among 1820 and 1850 San Bernardo became fashionable throughout Europe. The heroic exploits of the legendary St. Bernard Barry at the Great St. Bernard Pass in the Alps had a great effect. Barry has been shown to save more than 40 people of death by snow. Everywhere people wanted these big dogs and they were (and they are) really big dogs.
Breeders and traders were unable to meet the high demand. At the same time high prices were paid for a puppy of St. Bernard. So quite a few dog dealers from southwestern Germany helped out without further ado.. They mated St. Bernard with very big bitches from the region. The pups that looked like a St. Bernard they were sold as such, but for the others there were at most a few potatoes from a farmer. The dog trade was – as it still is today – a lucrative business and some sold hundreds of puppies a year and became rich.
Like Leonberg City Hall and dog vendor Heinrich Essig. An intelligent idea occurred to him and turned need into virtue. He created a brand out of the puppies that he could not market as St. Bernard. Instead of giving them away, sold the puppies for good money. Thus was born the Leonberger. Inspired by the lion from the coat of arms of his hometown, this new breed of dog has the appearance of a lion. His dogs were nicknamed Leonhardiner in the envious competition. Also in the official world of dogs these hybrids went unnoticed for a long time. Like this, el cinólogo Ludwig Beckmann, universally recognized at that time, He does not even mention the Leonhardiner in his work in two volumes "Die Rassen des sinks" (dog breeds) of 1895. From the point of view of health, such a genetically heterogeneous offspring is an advantage.
The Leonberger should be a success in all respects. Today it belongs to the primitive rocks of the world of purebred dogs., that no dog lover wants to miss. In 1895 The «International Dog Club was founded Leonberger«, which quickly achieved official recognition of the Leonberger like race. In 1948 He was followed by the «German Dog Club Leonberger»Based in Leonberg, who still represents the Leonberger at VDH and around the world. The Leonberger has a unique charisma, imposing and at the same time friendly, quiet and just sovereign. Its appearance is reminiscent of a lion and its character is also majestic, peaceful and totally suitable for families.
Physical characteristics
The Leonberger It is an impressive large dog with a height at the withers in males between 72 and 80 cm and in females between 65 and 75 cm.. No weight given. But, will be some 80 kg. The standard describes its appearance as:
«According to its original purpose, the Leonberger it's a very big dog, strong, muscular and elegant at the same time. It is characterized by a harmonious build and a self-assured calm with a lively temperament.. Especially the male dog is powerful and powerful. "
Its coat should be medium soft to thick, broadly long, well lying. The Leo has a strong inner layer. The shapes of your physique should be recognizable. On the neck and chest, the fur, especially in males, must form a mane. The coat will be lion yellow, red, reddish brown and all the combinations between them, but always with a black mask. In favor of this lion gaze, hereditary factors related to health and longevity have been neglected.
A study published by the University of Vienna evaluated 7582 layers of Leonberger between 1932 and 2009. «It was determined that the average death age of the Leonberger It was from 7,55 years". During the study period, life expectancy had even decreased in 1,5 years in the last three decades. With a healthy upbringing, 10 or 12 years would be normal. The breed has recognized these warning signs and is now focusing more on the health and extension of the life expectancy of these large dogs..
Character and skills
The mind of a Leonberger is pious as a lamb. Being with him is pure slowdown for man. The essence is described in the standard:
as family dog, the Leonberger is a pleasant companion in current living conditions, that can be carried everywhere without any difficulty and is characterized by a pronounced kindness towards children. He is neither shy nor aggressive. As a companion dog it is a pleasant companion., obedient and fearless in all life situations.
The strength of character required includes above all: self confidence, sovereign calm, average temperament (including game instinct), willingness to subordinate, good learning and memorizing ability and noise tolerance. The character of Leonberger impresses all dog lovers.
Once you get to know dogs better Leonberger, you will be enchanted by them forever. There is almost nothing that can disturb this giant. His very high stimulus threshold as well as his stoic composure are the necessary counterpart to his enormous strength.. These two poles thus characterize the nature of Leonberger. Here and there is something stubborn. Only good persuasion and pleading will help., then he will do everything for his master or lady. But as a family member he is very kind. Seeks proximity to its humans. It is a reliable protector for them. The Leonberger he is a great guy, a fascinating dog!
Fitness
The Leonberger not an easy dog ​​to keep due to its size. By its nature, has very few demands. A daily walk, brushed once a week, that was all. You don't need a big garden, but a garden is already useful. He likes to take possession of it. So, a small apartment on the nth floor would not be for him. Does not fit in all cars. One must consider: You're mine, the whole car will get wet. Leo can bear the heat, but it should not be challenged. prefers the cold. The Leonberger he is a great friend and not an object for acting addicts.
It should also be borne in mind that in our current society, large dogs are often rejected. Some people just fear a giant like Leo, even if he behaves – as is normal for him – exemplary. This is one of the reasons why it is not advisable to keep it in the big city..
One must have a sufficient budget to be able to pay a lot of good food and, in case of doubt, also the vet. It also, should have considered before buying what to do if the dog is sick and may need to bring 80 kg or more. Last, but not less important, there are many practical things that have a profound influence on everyday life. Here one must take real responsibility and honestly look in the mirror if all the conditions for a happy coexistence with dogs are met. Leonberger. Who can claim this, is in an enviable situation of dog owner. The Leonberger worth a sin.
Leonberger's Education
It must be remembered that in a Leo adult, the leash is just a symbol of control. The Leonberger has the power to control the other end of the strap. But he doesn't want. The Leonberger it's basically easy to train. Only his stubbornness has to be broken here and there with consistent smoothness.. He wants to follow his lord and master and he does it very reliably. It is an elementary duty of the owner of a Leonberger to pay attention to a consistent education already in the puppy. Because only this and not the leash makes wonderful walks in nature possible, that together with this great four-legged friend become a balm for the soul of agitated people. The great dog should never be "educated" by bumps or barracks methods. Because that would cause the exact opposite of education and end in disaster..
Leonberger care
Caring for a healthy Leo is not a problem. Brushing the coat once a week is enough.
Nutrition / Food
You need a lot of high quality food. A raised bowl is useful to counteract the risk of stomach twisting. Always pay attention to the weight.
Leonberger Health
As in most large dogs, we see hip or elbow dysplasia. Osteosarcoma, the most common bone tumor in dogs, It is also very common in Leonberger.
Leonberge life expectancy
Before the life expectancy of a Leonberger It was from 12 years, today is from 7 to 9 years. The breeding is working to recover the possible natural life of a healthy dog. He is accompanied here by a research project of the University of Veterinary Medicine Hannover.
Buy a Leonberger
The purchase of a Leo it should be long-term and well thought out. You should carefully check if you have all the requirements to be able to spend many wonderful years with this giant.. If you are looking for a puppy, you should make sure above all that the dogs are not bred too much. Ask about ancestors, their illnesses, his age reached. You should see an FCI affiliated breeder Leonberger. Really, a Leonberger it costs about 2.000 EUR.
Images "Leonberger"
Photos:
1 – Leonberger bitch by The animal photography at de.wikipedia / CC BY-SA
2 – Leonberger by https://pxhere.com/es/photo/1394923
3 – Leonberger, head photographed in 2004 at a dog show in Dresden by Karina Leo-Steffen, uploaded here from –Caronna 13:43, 15 Apr 2005 (UTC) / CC BY-SA
4 – Leonberger by https://www.pexels.com/es-es/foto/75295/
5 – Leonberger by https://pxhere.com/es/photo/1434187
6 – Leonberger by Pleple2000 / CC BY-SA
7 – Leonberger by https://www.needpix.com/photo/1100946/dog-leonberger-giant-pedigree-purebred-animal-canine
Videos "Leonberger"
Type and recognitions:
- FCI CLASSIFICATION:
- Group :
- Section : . .
Federations:
- – FCI – Pinscher and Schnauzer-Molossoid type dogs – Swiss Mountain Dogs and Cattledogs. Section 2.2 Molossoid, mountain type. ⓘ
- – AKC – Working dogs ⓘ
- – ANKC – Group 6 (utility dogs) ⓘ
- – CKC – Working dogs ⓘ
- – KC – Working dogs ⓘ
- – NZKC – Utility dog ⓘ
- – UKC – Watchdog ⓘ
FCI breed standard "Leonberger"
Origin:
GermanyDate of publication of the valid original standard:
04.01.1996Use:
Watchdog, Company and family.
General appearance:
Complying with the original use purposes, the Leonberger is a big dog, strong, muscular and elegant at the same time. It is characterized by its harmonious body structure and poised tranquility, aware of his own worth with a lively temperament. The male is especially powerful and robust.
PROPIMPORTANT ORTIONS: Relationship of the height of the cross with the length of the body = 9:10; the depth of the chest corresponds almost to 50% the height of the cross.
Behavior / temperament:
As a family dog, the Leonberger adapts to modern living and room conditions and turns out to be a pleasant companion that can be taken anywhere without causing problems. It also, It is very friendly with children and is not shy or aggressive. As a companion dog it is a pleasant companion., obedient and fearless in all situations that arise. To achieve his nature and strength, he mainly needs:
- Self -confidence and sovereign
- Medium balanced temperament (urge to judge).
- Willingness to submit.
- Good learning ability and attention.
- Be insensitive to noise.
Head:
In its entirety it is deeper than broad and seems longer than plump; the relationship between the muzzle and the cranial region is approximately 1:1. The skin is adherent on all parts and does not form frontal folds.Cranial region:
- Craging: Seen in profile and from the front it is slightly arched; is strong corresponding to the body and limbs, but it doesn't look heavy. The posterior region is not much wider than the region where the eyes are located.
- Ston: It is clearly noticeable and moderately marked.
facial region:
- Nariz: Black.
- Horcico: It is long, but it never ends on end. The nose is in broad correspondence, never sunk, but rather slightly arched (ram's nose).
- Labios: Adherents, black, with closed corners.Jaws / Teeth: Powerful jaws with a full scissor bite, regular and perfect with good adaptation of the upper incisors over the lower ones without leaving space. The teeth are implanted vertically in the maxilla, showing 42 healthy teeth according to dental formula (lack of M3 is tolerated). Caliper bite allowed; in the lower jaw there should be no narrowness next to the fangs.
- Cheeks: Poorly developed.
- Ojors: Light brown to as dark as possible, medium-sized, oval, or sunk or bulging, neither very together nor very separate from each other. Adherent eyelids, they don't show the conjunctiva. The whites of the eyes (visible part of the dermis) does not show redness.
- Obars: High insertion and placed not far behind, pendants, medium-sized, stuck and fleshy.
Neck:
Forms a light curve that continues without interruption to the cross. It is longer than it is wide; has no loose or double chin.Body:
- Cruz: Pronounced, especially in the male.Back: Robust, straight, wide.
- Itmors: Widths, powerful, well muscled.
- Glikeness: Wide, relatively long, gently rounded, in the form of progressive transition to the root of the tail, never higher than the back.
- Pecho: Large, deep, reaches at least to elbow height; not barrel-shaped but rather oval.
- Línand the bottom: Only slightly retracted.
Tail:
With lots of hair. When it is standing it carries it hung in a straight line; Also during the movement it folds only slightly without exceeding the back line.Tips
PREVIOUS MEMBERS: Straight, parallel, not closed.
- Shoulder / Arms: Long, obliquely placed; Among them form an angle not too obtuse. They have good muscles.
- Elbows: Glued to the body.
- Metacarpus: Strong, firm, viewed from the front they are straight and viewed from the side almost vertical.
- Pinis previous: Straight (no deviations outwards or inwards), rounded, compact; well arched fingers; black pads.
LATER MEMBERS: Viewed from behind they are not placed too tightly; they are parallel; lukewarm joints- tarsians and feet do not deviate inward or outward.
- Cadhere: In oblique position.
- Thigh: Rather long; placed obliquely, has strong muscles. The thigh and leg form a fairly sharp angle.
- Atibio-tarsal articulation: Powerful, with a marked angle between the leg and the metatarsal.
- Pinis later: Straight, just a little long; arched toes; black pads.
Movement:
Cover the ground, it is balanced in all walks; good momentum and breakthrough; both during walking and jogging, observed front and back, conducts limbs in a straight line.Mantle
- Fur: Hair should be a little soft to hard, quite long, stuck and never form a streak; Despite having a lot of internal fleece, you can recognize the shapes of your body structure. The hair is smooth, although it is allowed to be slightly wavy; on the neck and chest (especially in the male) a mane is formed; There are visible feathers in the anterior members and "pants" marked in the posterior members.
- Color: Yellow (lion color), red, reddish brown, also sand color (pale yellow, cream-coloured) and all its combinations, although with a black mask. Hair is allowed to have black tips; However, black should not be the basic hair color. The paleness of the basic color in the lower part of the tail, on the necklace, In the feathers of the previous members and in the "pants" of the posterior. A small white spot or a thin white streak is tolerated on the chest and white hairs on the fingers.
Size and weight:
Height to the cross:
- Males: 72 – 80 cm., ideal measure 76 cm.,
- females: 65 – 75 cm., ideal measure 70 cm..
Fouls:
Any deviation from the aforementioned criteria is considered as a fault and the severity of this is considered to the degree of the deviation to the standard and its consequences on the health and well-being of the dog..
FALTAS DESCALIFICANTES:
- Aggressiveness or extreme shyness.
- Any dog showing clear signs of physical or behavioral abnormalities must be disqualified..
- Severe anatomical failures (p. e.g.. notable cow members, carp back marked, badly beaten back, exaggerated outward deviation in the forefoot, absolutely insufficient angulation in the shoulder joints, elbow, knee and tibial-tarsian).
- brown truffle.
- Excessive depigmentation on the lips
- Lack of teeth (except the M3), superior and inferior prognathism; other faults in the bite.
- Eyes without brown color.
- Ectropión, ectropion.
- Tail too curled or carried too high and curled.
- Brown pads.
- Curly or frizzy hair.
- Lack of color (brown with brown truffle and brown pads; Black with fire; silver black; deer color).
- Total lack of mask
- Too much white color (that reaches from the fingers to the carpus, stain on the chest larger than a hand, white color elsewhere).
N.B.:
- Males should have two normal-appearing testicles fully descended into the scrotum..
- Only functionally and clinically healthy dogs, with the typical conformation of the breed, should be used for parenting.
TRANSLATION: Federation Canófila Mexicana a.c..
Alternative names:
1. Leo, Gentle Lion, Gentle Giant (English).
2. Chien Leonberg (French).
3. Leo (German).
4. Leo (Portuguese).
5. Leo (español).
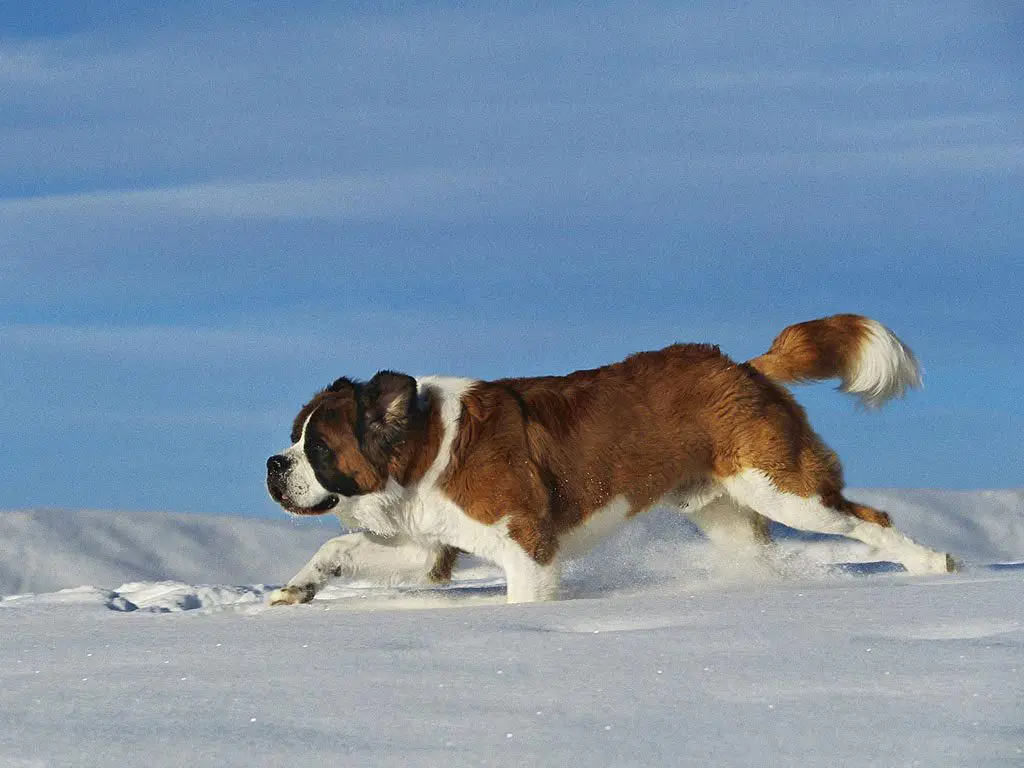














 St. Bernard #02 – puppy love
St. Bernard #02 – puppy love Brody and Bella. bella sharing her peice of ice
Brody and Bella. bella sharing her peice of ice evil kitten attacks saint bernard
evil kitten attacks saint bernard Saint-Bernard – 2 Chiens, 1 Kong
Saint-Bernard – 2 Chiens, 1 Kong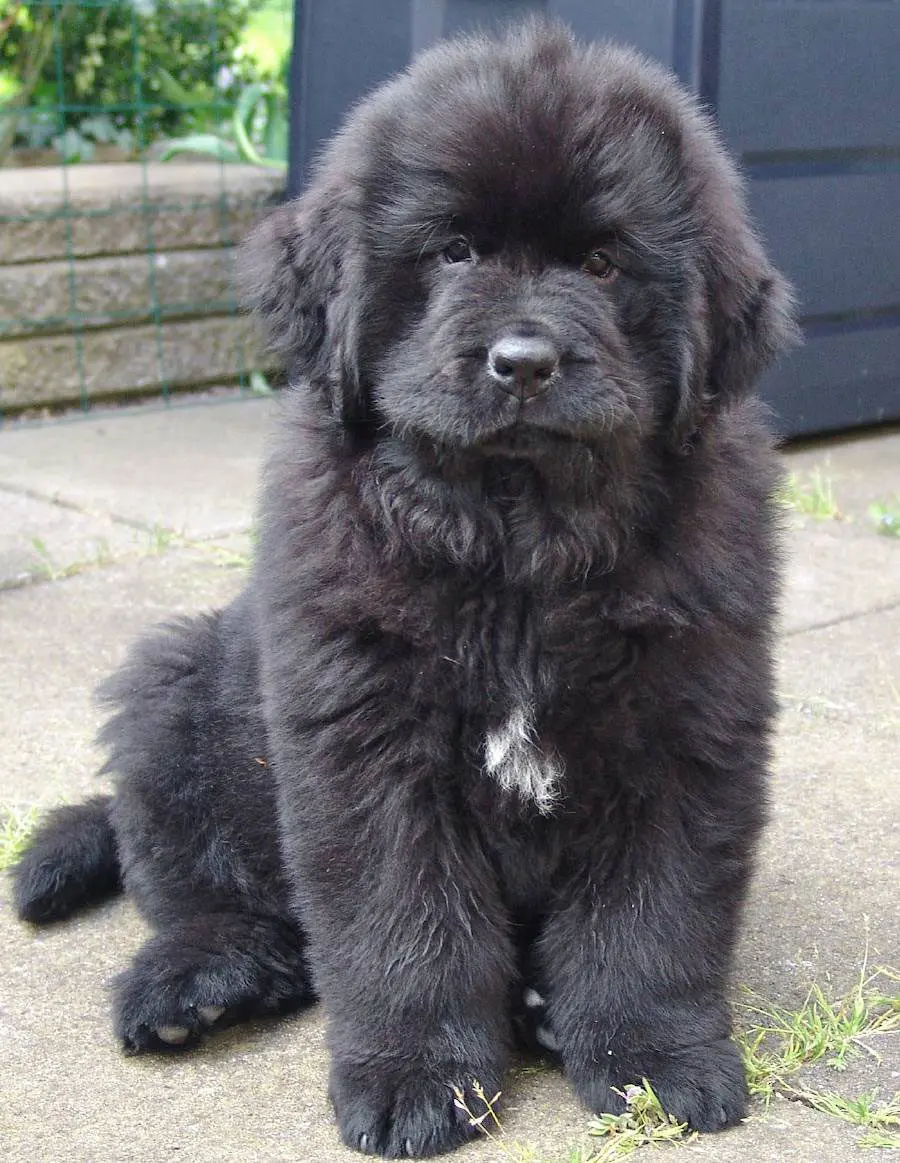






 Dogs 101: Newfoundland
Dogs 101: Newfoundland NEWFOUNDLAND DOG – Profile of a Hero Breed
NEWFOUNDLAND DOG – Profile of a Hero Breed Newfoundland 101! Everything You Need To Know About Owning A Newfoundland Puppy
Newfoundland 101! Everything You Need To Know About Owning A Newfoundland Puppy NEWFOUNDLAND FIVE THINGS YOU SHOULD KNOW
NEWFOUNDLAND FIVE THINGS YOU SHOULD KNOW The Newfoundland dog – GIANT dog breeds
The Newfoundland dog – GIANT dog breeds The Newfoundland characteristics of the breed, care etc.
The Newfoundland characteristics of the breed, care etc. Newfoundland: The noblest and sweetest dog in the world
Newfoundland: The noblest and sweetest dog in the world Newfoundland puppies
Newfoundland puppies
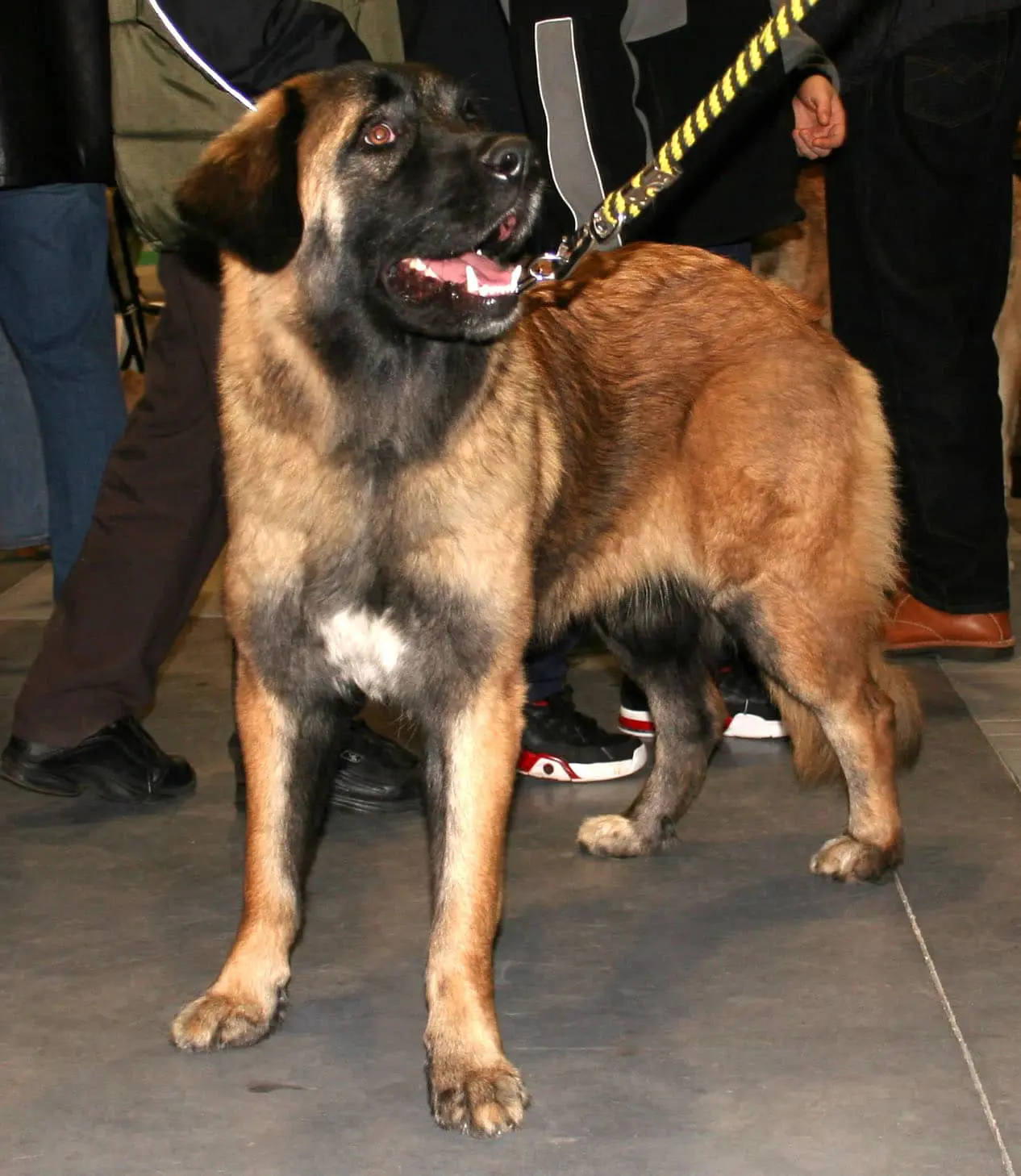













 Estrela Mountain Dog / Estrela Mountain Dog: Niara and Lyaoh’s puppies
Estrela Mountain Dog / Estrela Mountain Dog: Niara and Lyaoh’s puppies Discovering Serra da Estrela
Discovering Serra da Estrela Portuguese Estrela Mountain Dog
Portuguese Estrela Mountain Dog The Star River Mountain Dog
The Star River Mountain Dog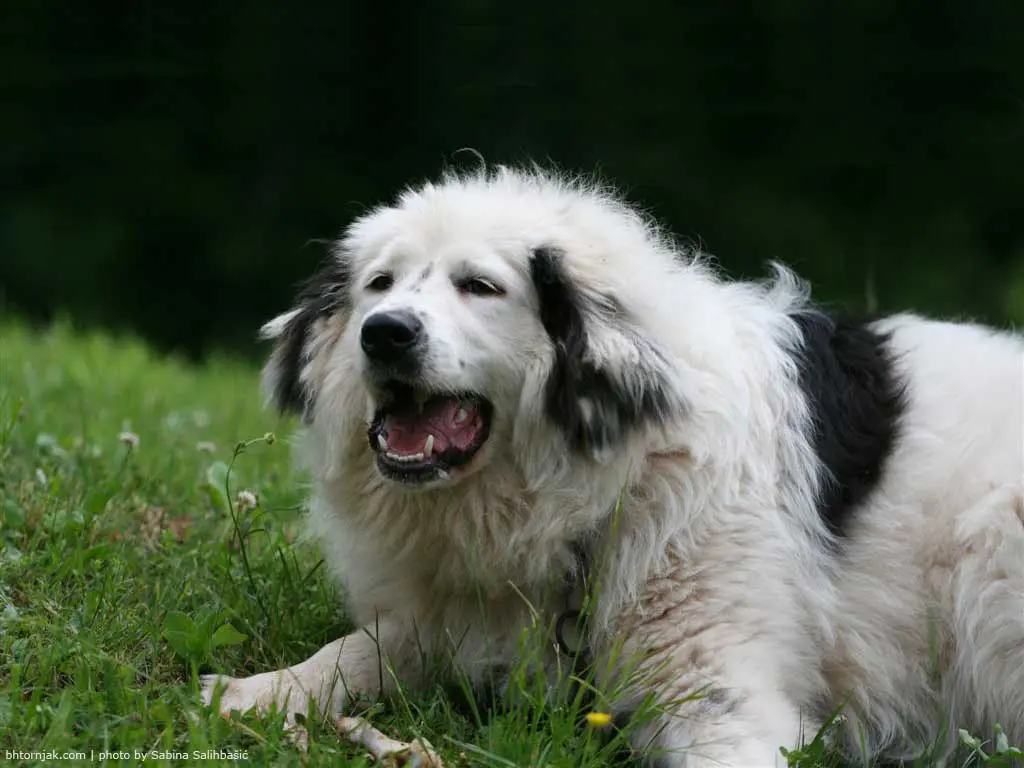



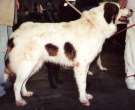


 Tornjak Dog Breed – Facts and Information
Tornjak Dog Breed – Facts and Information TORNJAK
TORNJAK Tornjak 14 months and 2 months
Tornjak 14 months and 2 months Tornjak – Andora Speed Agility
Tornjak – Andora Speed Agility












 cENTRAL aSIAN sHEPHERD Alabai Aman and Aziza
cENTRAL aSIAN sHEPHERD Alabai Aman and Aziza 8 Weeks Old cENTRAL aSIAN SHEPHERD Alabai Puppies
8 Weeks Old cENTRAL aSIAN SHEPHERD Alabai Puppies Central Asian Shepherd Dog
Central Asian Shepherd Dog Playing with a bear Central Asian Shepherd
Playing with a bear Central Asian Shepherd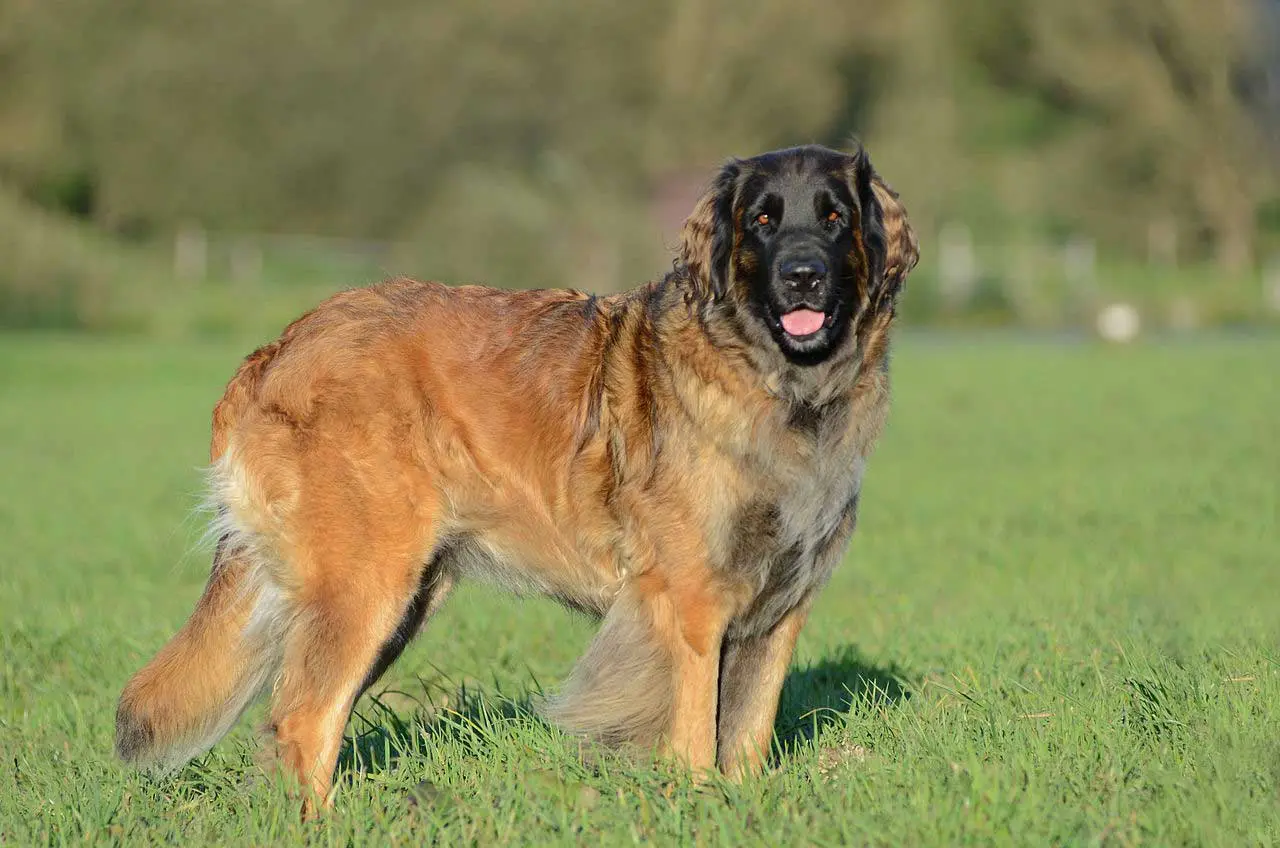






 Baby vs Leonberger | Leonberger playing with a baby
Baby vs Leonberger | Leonberger playing with a baby Leonberger XVI Spanish Monograph of the Leonberger CAC 2011
Leonberger XVI Spanish Monograph of the Leonberger CAC 2011 Leonberger – Breed of dog
Leonberger – Breed of dog Leonberger puppy 2016
Leonberger puppy 2016