Content |
|---|
History
The Schwyz Hound has ancient origins, the details are a bit confusing though. Dogs of this type are represented in mosaics dating from the Roman Helvetian era and the first specimens of the breed were highly sought after in Italy during the 15th century and then by the French during the 18th century..
It is believed that the Schwyz Hound It was influenced by the French Hounds brought to Switzerland by traveling mercenaries and eventually became one of the five varieties of Hounds. “Swiss Hound”. More specifically, the Schwyz Hound it is one of the four breeds sometimes referred to – the other varieties are:
The first breed standard for the Schwyz Hound was established in 1882 and reviewed in 1909. The breed was accepted by the FCI under the name of Schweizer Laufhund in 2001.
Physical characteristics
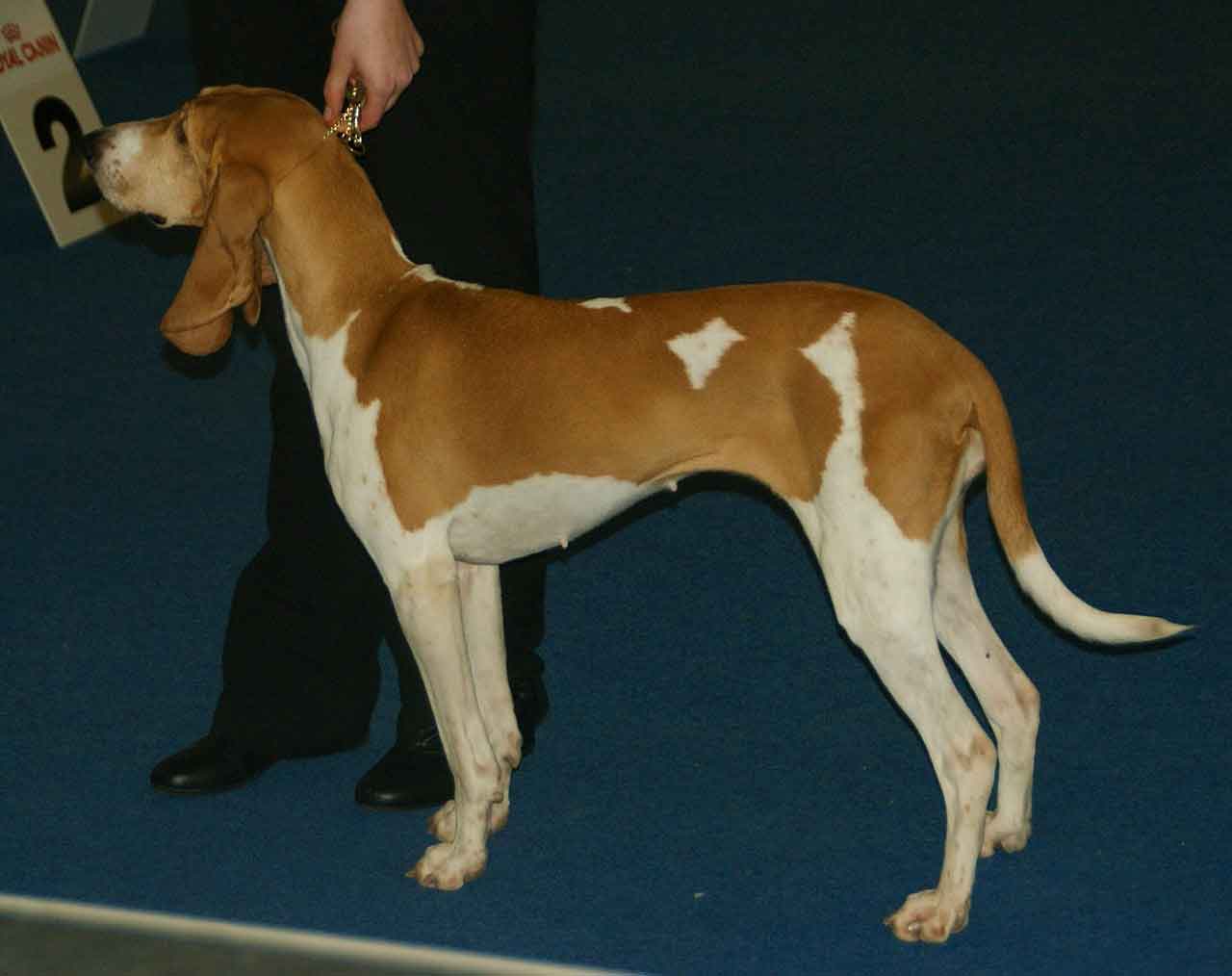
It is a dog with medium height at the withers. Your body structure indicates strength and tenacity. Its slim head with long snout and long ears give it an expression of nobility.
Size: Males: 49-59 cm.. females: 47-57 cm..
Color: White with orange or orange "saddle" spots, sometimes with orange splashes; an orange coat is allowed.
Character and skills
The Schwyz Hound it is a friendly breed that can do well in a family environment as long as its exercise requirements are consistent. These dogs get along well with other dogs and can also be gentle with children. Just be careful around cats and other household pets because these dogs have strong hunting instincts – raising pets together and working on early socialization will help. You should also make sure your dog gets plenty of mental and physical exercise to avoid the kind of boredom that can lead to destructive behavior..
The Schwyz Hound they are a very lively and energetic breed that requires a significant amount of daily exercise. These dogs need at least an hour of moderate to vigorous exercise each day and will also appreciate having time to run around in a fenced yard.. This breed can also be a good candidate for dog sports, if you are looking for opportunities to get you some extra exercise.
Training
The Schwyz Hound has strong hunting instincts that can be developed and controlled through training. These dogs are trained to hunt in packs., so they are a bit independent by nature and can be stubborn at times. Keeping your training sessions short and offering plenty of food rewards will help ensure training success., in addition you must maintain a firm and consistent hand in leadership with this breed. Early socialization is also important for this breed.
Characteristics "Schwyz Hound"
Coexistence is important that you have with your new friend. Before considering the acquisition of a dog of the breed "Schwyz Hound" you know certain factors. Not all breeds of dogs are apt to live in an apartment, you must take into account his character, their need for exercise, their interaction with other pets, their care and if you have small children, their level of tolerance towards them.
Adaptation ⓘ3.0 out of 5 stars (based on 1 review)
|
friendly dog ⓘ4.0 out of 5 stars (based on 1 review)
|
hair loss ⓘ3.0 out of 5 stars (based on 1 review)
|
|---|---|---|
Affection level ⓘ5.0 out of 5 stars (based on 1 review)
|
Need for exercise ⓘ5.0 out of 5 stars (based on 1 review)
|
Social need ⓘ4.0 out of 5 stars (based on 1 review)
|
Home ⓘ4.0 out of 5 stars (based on 1 review)
|
Toilet ⓘ2.0 out of 5 stars (based on 1 review)
|
Friendly with strangers ⓘ4.0 out of 5 stars (based on 1 review)
|
barking ⓘ4.0 out of 5 stars (based on 1 review)
|
Health ⓘ4.0 out of 5 stars (based on 1 review)
|
Territorial ⓘ4.0 out of 5 stars (based on 1 review)
|
Cat friendly ⓘ2.0 out of 5 stars (based on 1 review)
|
Intelligence ⓘ4.0 out of 5 stars (based on 1 review)
|
Versatility ⓘ3.0 out of 5 stars (based on 1 review)
|
Child friendly ⓘ4.0 out of 5 stars (based on 1 review)
|
Surveillance ⓘ4.0 out of 5 stars (based on 1 review)
|
joy ⓘ5.0 out of 5 stars (based on 1 review)
|
Videos "Schwyz Hound"
|
Willie de Schwyzer Laufhund 2
|
Willie de Schwyzer Laufhund
|
|---|
Type and recognitions:
- FCI CLASSIFICATION: 59
- Group 6: Scent hounds, and related breeds.
- Section 1.2: Medium-sized hound-type dogs.. With proof of work..
Federations:
- – FCI – Group 6: Scent hounds, and related breeds. – Section 1.2: Medium-sized Hounds. ⓘ
- – UKC – Scenthounds ⓘ
FCI breed standard "Schwyz Hound"
Varieties of “Swiss hounds”
The four varieties of Swiss Hounds have their own specific hunting characteristics.:
– The Bernese Hound, with her beautiful throat (“the howler of the Jura”), demanding, mainly used for hares;
– The “Jura Hound“, an excellent recuperator
– The Lucerne Hound, reminiscent of Small Blue Gascony, he is an active and passionate dog that hunts deer very well;
– The “Schwyz Hound”, less widespread outside of Switzerland, is reserved for rabbits and hares.